Azure Pipelines - Sprint 209 Update
Features
- Disable showing the last commit message for a pipeline run
- Consumed resources and template parameters in Pipelines Runs Rest API
- Add support for string split function in YAML template expressions
- Do not sync tags when fetching a Git repository
- Updated brownout schedule for Ubuntu 18.04 images
Disable showing the last commit message for a pipeline run
Previously, the Pipelines UI used to show the last commit message when displaying a pipeline's run.
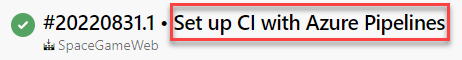
This message can be confusing, for example, when your YAML pipeline's code lives in a repository different from the one that holds the code it's building. We heard your feedback from the Developer Community asking us for a way to enable/disable appending the latest commit message to the title of every pipeline run.
With this update, we've added a new YAML property, named appendCommitMessageToRunName, that lets you do exactly that. By default, the property is set to true. When you set it to false, the pipeline run will only display the BuildNumber.
Consumed resources and template parameters in Pipelines Runs Rest API
The extended Pipelines Runs REST API now returns more types of artifacts used by a pipeline run and the parameters used to trigger that run. We enhanced the API to return the container and pipeline resources and the template parameters used in a pipeline run. You can now, for example, write compliance checks that evaluate the repositories, containers, and other pipeline runs used by a pipeline.
Here is an example of the new response body.
"resources":
{
"repositories":
{
"self":
{
"repository":
{
"id": "e5c55144-277b-49e3-9905-2dc162e3f663",
"type": "azureReposGit"
},
"refName": "refs/heads/main",
"version": "44153346ecdbbf66c68c20fadf27f53ea1394db7"
},
"MyFirstProject":
{
"repository":
{
"id": "e5c55144-277b-49e3-9905-2dc162e3f663",
"type": "azureReposGit"
},
"refName": "refs/heads/main",
"version": "44153346ecdbbf66c68c20fadf27f53ea1394db7"
}
},
"pipelines":
{
"SourcePipelineResource":
{
"pipeline":
{
"url": "https://dev.azure.com/fabrikam/20317ad0-ae49-4588-ae92-6263028b4d83/_apis/pipelines/51?revision=3",
"id": 51,
"revision": 3,
"name": "SourcePipeline",
"folder": "\\source"
},
"version": "20220801.1"
}
},
"containers":
{
"windowscontainer":
{
"container":
{
"environment":
{
"Test": "test"
},
"mapDockerSocket": false,
"image": "mcr.microsoft.com/windows/servercore:ltsc2019",
"options": "-e 'another_test=tst'",
"volumes":
[
"C:\\Users\\fabrikamuser\\mount-fabrikam:c:\\mount-fabrikam"
],
"ports":
[
"8080:80",
"6379"
]
}
}
}
},
"templateParameters":
{
"includeTemplateSteps": "True"
}
Add support for string split function in YAML template expressions
YAML pipelines provide you convenient ways to reduce code duplication, such as looping through each value of a list or property of an object.
Sometimes, the set of items to iterate through is represented as a string. For example, when the list of environments to deploy to is defined by the string integration1, integration2.
As we listened to your feedback from the Developer Community, we heard you wanted a string split function in YAML template expressions.
Now, you can split a string and iterate over each of its substrings.
variables:
environments: integration1, integration2
jobs:
- job: Deploy
steps:
- ${{ each env in split(variables.environments, ', ') }}:
- script: ./deploy.sh -e ${{ env }}
- script: ./runTest.sh -e ${{ env }}
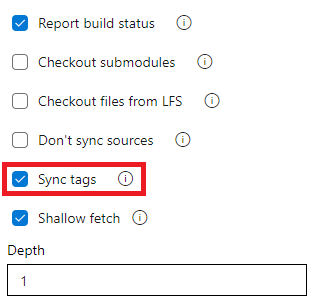
Do not sync tags when fetching a Git repository
The checkout task uses --tags option in fetching the contents of a Git repository. This causes the server to fetch all tags as well as all objects that are pointed to by those tags. This increases the time to run the task in a pipeline - particularly if you have a large repository with a number of tags. Furthermore, the checkout task syncs tags even when you enable the shallow fetch option, thereby possibly defeating its purpose. To reduce the amount of data fetched or pulled from a Git repository, we have now added a new option to the task to control the behavior of syncing tags. This option is available both in classic and YAML pipelines.
This behavior can either be controlled from the YAML file or from the UI.
To opt-out from syncing the tags through YAML file, add the fetchTags: false to the checkout step. When the fetchTags option is not specified, it's the same as if fetchTags: true is used.
steps:
- checkout: self # self represents the repo where the initial Pipelines YAML file was found
clean: boolean # whether to fetch clean each time
fetchTags: boolean # whether to sync the tags
fetchDepth: number # the depth of commits to ask Git to fetch
lfs: boolean # whether to download Git-LFS files
submodules: boolean | recursive # set to 'true' for a single level of submodules or 'recursive' to get submodules of submodules
path: string # path to check out source code, relative to the agent's build directory (e.g. \_work\1)
persistCredentials: boolean # set to 'true' to leave the OAuth token in the Git config after the initial fetch
If you want to change the behavior of existing YAML pipelines, it may be more convenient to set this option in the UI instead of updating the YAML file. To navigate to the UI, open the YAML editor for the pipeline, select Triggers, then Process, and then the Checkout step.
If you specify this setting both in the YAML file and in the UI, then the value specified in the YAML file takes precedence.
For all new pipelines you create (YAML or Classic), tags are still synced by default. This option does not change the behavior of existing pipelines. Tags will still be synced in those pipelines unless you explicitly change the option as described above.
Updated brownout schedule for Ubuntu 18.04 images
Azure Pipelines is deprecating the Ubuntu 18.04 image (ubuntu-18.04) on our hosted pools. This image will be retired December 1st. You may start to see longer queue times.
To help you better identify which pipelines are using the ubuntu-18.04 image, we are planning brownouts. Jobs will fail during a brownout period.
- Warning messages are displayed on pipeline runs using the ubuntu-18.04 image
- A script is available to help you find pipelines using deprecated images, including ubuntu-18.04
- We are scheduling short "brownouts". Any ubuntu-18.04 runs will fail during the brownout period. Therefore, it is recommended to migrate your pipelines prior to the brownouts.
Brownout schedule (updated)
- October 3, 12:00 UTC - October 3, 14:00 UTC
- October 18, 14:00 UTC - October 18, 16:00 UTC
- November 15, 18:00 UTC - November 15, 20:00 UTC
- November 30, 20:00 UTC - November 30, 22:00 UTC
- December 15, 20:00 UTC - December 16 00:00 UTC
- January 5, 10.00 UTC - January 5, 14.00 UTC
- January 13, 12.00 UTC - January 13, 16.00 UTC
- January 18, 14.00 UTC - January 18, 18.00 UTC
- January 24, 16.00 UTC - January 24, 20.00 UTC
- February 1, 18.00 UTC - February 1, 22.00 UTC
- February 7, 16.00 UTC - February 7, 22.00 UTC
- February 13, 14.00 UTC - February 13, 22.00 UTC
- February 21, 10.00 UTC - February 21, 22.00 UTC
- February 28, 10.00 UTC - February 28, 22.00 UTC
- March 6, 00.00 UTC - March 7, 00.00 UTC
- March 13, 00.00 UTC - March 14, 00.00 UTC
- March 21, 00.00 UTC - March 22, 00.00 UTC
Next steps
Note
These features will roll out over the next two to three weeks.
Head over to Azure DevOps and take a look.
How to provide feedback
We would love to hear what you think about these features. Use the help menu to report a problem or provide a suggestion.
You can also get advice and your questions answered by the community on Stack Overflow.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for