How to clean up SSISDB logs automatically
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
Once you provision an Azure-SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) integration runtime (IR) in Azure Data Factory (ADF) or Synapse Pipelines, you can use it to run SSIS packages deployed into:
- SSIS catalog (SSISDB) hosted by Azure SQL Database server/Managed Instance (Project Deployment Model)
- file system, Azure Files, or SQL Server database (MSDB) hosted by Azure SQL Managed Instance (Package Deployment Model)
In the Project Deployment Model, your Azure-SSIS IR will deploy SSIS projects into SSISDB, fetch SSIS packages to run from SSISDB, and write package execution logs back into SSISDB. SSISDB is also used to store SSIS job and IR operation logs. To manage the accumulated logs, we've provided relevant SSISDB properties and stored procedures that can be invoked automatically on schedule via ADF, Azure SQL Managed Instance Agent, or Elastic Database Jobs.
SSISDB log clean-up properties and stored procedures
To manage SSIS package execution logs, you can configure SSISDB log clean-up properties by connecting to SSISDB hosted by your Azure SQL Database server/Managed Instance using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), see Connecting to SSISDB. Once connected, on the Object Explorer window of SSMS, you can expand the Integration Services Catalogs node, right-click on the SSISDB subnode, and select the Properties menu item to open Catalog Properties dialog box. On the Catalog Properties dialog box, you can find the following SSISDB log clean-up properties:
- Clean Logs Periodically: Enables the clean-up of package execution logs, by default set to True.
- Retention Period (days): Specifies the maximum age of retained logs (in days), by default set to 365 and older logs are deleted when the relevant SSISDB stored procedure is invoked.
- Periodically Remove Old Versions: Enables the clean-up of stored project versions, by default set to True.
- Maximum Number of Versions per Project: Specifies the maximum number of stored project versions, by default set to 10 and older versions are deleted when the relevant SSISDB stored procedure is invoked.
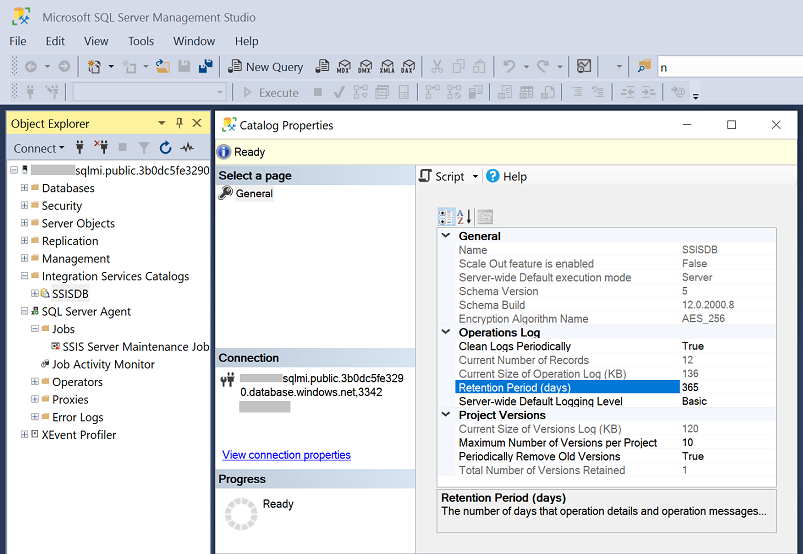
Once SSISDB log clean-up properties are configured, you can invoke the relevant SSISDB stored procedure, [internal].[cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive], to clean up SSIS package execution logs.
To clean up SSIS job logs, you can invoke the relevant SSISDB stored procedure, [internal].[cleanup_completed_jobs_exclusive]. The retention period is by default set to 60 minutes and older logs are deleted when the stored procedure is invoked.
To clean up SSIS IR operation logs, you can invoke the relevant SSISDB stored procedure, [internal].[cleanup_expired_worker]. The retention period is by default set to 168 hours and older logs are deleted when the stored procedure is invoked.
These SSISDB stored procedures clean up different SSISDB tables:
| SSISDB stored procedures | SSISDB tables to clean up |
|---|---|
[internal].[cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive] |
[internal].[event_message_context_scaleout][internal].[event_messages_scaleout][internal].[executable_statistics][internal].[execution_component_phases][internal].[execution_data_statistics][internal].[execution_data_taps][internal].[execution_parameter_values][internal].[execution_parameter_values_noncatalog][internal].[execution_property_override_values][internal].[execution_property_override_values_noncatalog][internal].[executions][internal].[executions_noncatalog][internal].[extended_operation_info][internal].[operation_messages][internal].[operation_messages_scaleout][internal].[operation_permissions][internal].[operations][internal].[validations] |
[internal].[cleanup_completed_jobs_exclusive] |
[internal].[job_worker_agents][internal].[jobs][internal].[tasks] |
[internal].[cleanup_expired_worker] |
[internal].[worker_agents] |
These SSISDB stored procedures can also be invoked automatically on schedule via ADF, Azure SQL Managed Instance Agent, or Elastic Database Jobs.
Clean up SSISDB logs automatically via ADF or Synapse Pipelines
Regardless whether you use Azure SQL database server/Managed Instance to host SSISDB, you can always use ADF to clean up SSISDB logs automatically on schedule. To do so, you can prepare an Execute SSIS Package activity in ADF pipeline with an embedded package containing a single Execute SQL Task that invokes the relevant SSISDB stored procedures. See example 4) in our blog: Run Any SQL Anywhere in 3 Easy Steps with SSIS in Azure Data Factory.
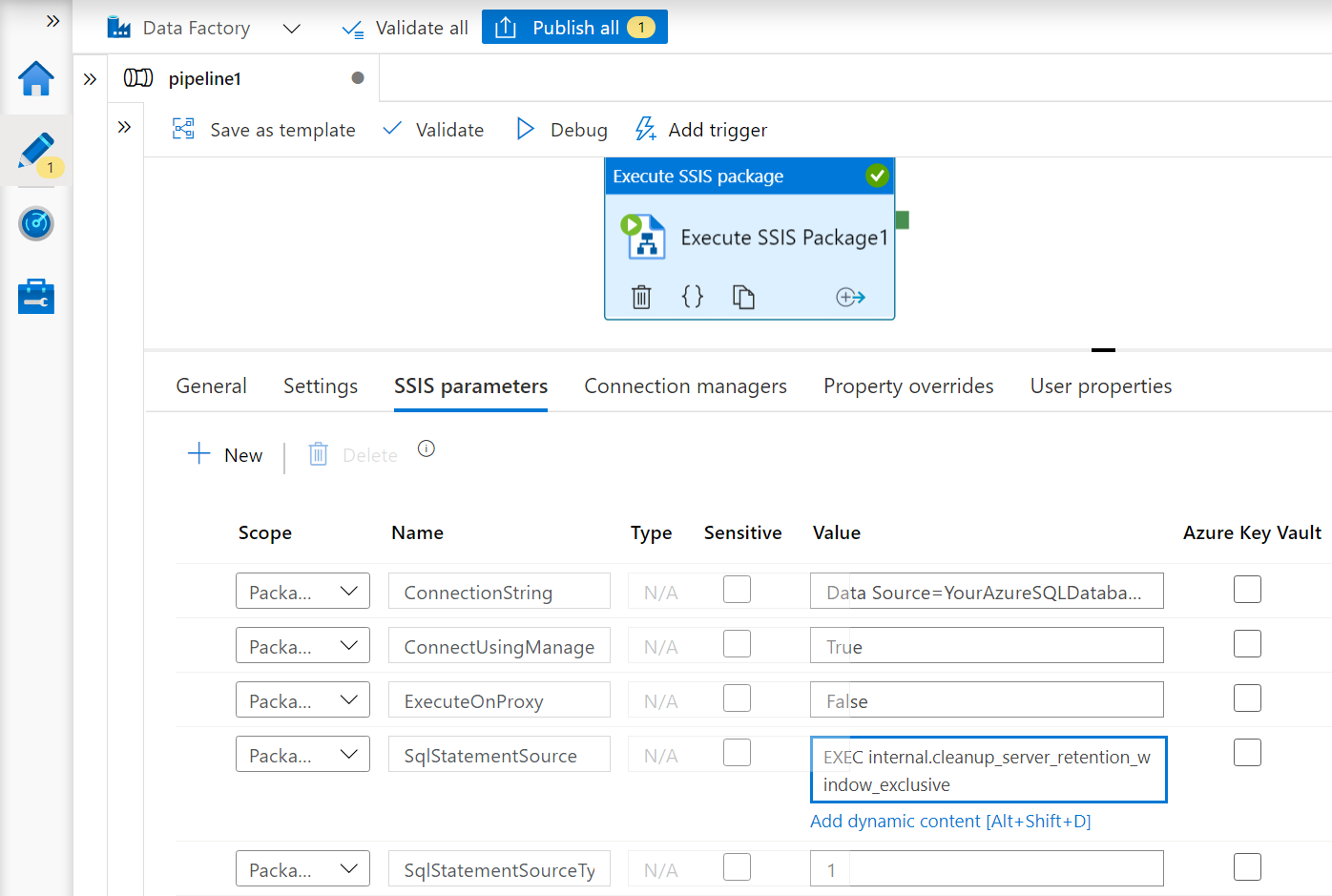
For the SQLStatementSource parameter, you can enter EXEC internal.cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive to clean up SSIS package execution logs.
To clean up SSIS job logs, you can add EXEC internal.cleanup_completed_jobs_exclusive [@minutesToKeep=’Number of minutes to set as retention period’].
To clean up SSIS IR operation logs, you can add EXEC internal.cleanup_expired_worker [@hoursToKeep=’Number of hours to set as retention period’] .
Once your ADF pipeline is prepared, you can attach a schedule trigger to run it periodically, see How to trigger ADF pipeline on a schedule.
Clean up SSISDB logs automatically via Azure SQL Managed Instance Agent
If you use Azure SQL Managed Instance to host SSISDB, you can also use its built-in job orchestrator/scheduler, Azure SQL Managed Instance Agent, to clean up SSISDB logs automatically on schedule. If SSISDB is recently created in your Azure SQL Managed Instance, we've also created a T-SQL job called SSIS Server Maintenance Job under Azure SQL Managed Instance Agent to specifically clean up SSIS package execution logs. It's by default disabled and configured with a schedule to run daily. If you want to enable it and or reconfigure its schedule, you can do so by connecting to your Azure SQL Managed Instance using SSMS. Once connected, on the Object Explorer window of SSMS, you can expand the SQL Server Agent node, expand the Jobs subnode, and double click on the SSIS Server Maintenance Job to enable/reconfigure it.
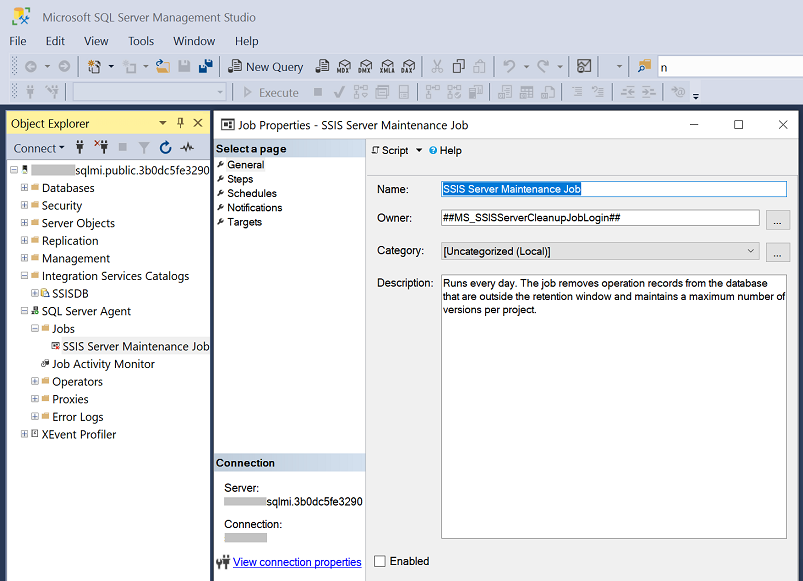
If your Azure SQL Managed Instance Agent doesn't yet have the SSIS Server Maintenance Job created under it, you can add it manually by running the following T-SQL script on your Azure SQL Managed Instance.
USE msdb
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM sys.server_principals where name = '##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##')
DROP LOGIN ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##
DECLARE @loginPassword nvarchar(256)
SELECT @loginPassword = REPLACE (CONVERT( nvarchar(256), CRYPT_GEN_RANDOM( 64 )), N'''', N'''''')
EXEC ('CREATE LOGIN ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin## WITH PASSWORD =''' +@loginPassword + ''', CHECK_POLICY = OFF')
ALTER LOGIN ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin## DISABLE
USE master
GRANT VIEW SERVER STATE TO ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##
USE SSISDB
IF EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sys.database_principals WHERE name = '##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser##')
DROP USER ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser##
CREATE USER ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser## FOR LOGIN ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##
GRANT EXECUTE ON [internal].[cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive] TO ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser##
GRANT EXECUTE ON [internal].[cleanup_server_project_version] TO ##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobUser##
USE msdb
EXEC dbo.sp_add_job
@job_name = N'SSIS Server Maintenance Job',
@enabled = 0,
@owner_login_name = '##MS_SSISServerCleanupJobLogin##',
@description = N'Runs every day. The job removes operation records from the database that are outside the retention period and maintains a maximum number of versions per project.'
DECLARE @IS_server_name NVARCHAR(30)
SELECT @IS_server_name = CONVERT(NVARCHAR, SERVERPROPERTY('ServerName'))
EXEC sp_add_jobserver @job_name = N'SSIS Server Maintenance Job',
@server_name = @IS_server_name
EXEC sp_add_jobstep
@job_name = N'SSIS Server Maintenance Job',
@step_name = N'SSIS Server Operation Records Maintenance',
@subsystem = N'TSQL',
@command = N'
DECLARE @role int
SET @role = (SELECT [role] FROM [sys].[dm_hadr_availability_replica_states] hars INNER JOIN [sys].[availability_databases_cluster] adc ON hars.[group_id] = adc.[group_id] WHERE hars.[is_local] = 1 AND adc.[database_name] =''SSISDB'')
IF DB_ID(''SSISDB'') IS NOT NULL AND (@role IS NULL OR @role = 1)
EXEC [SSISDB].[internal].[cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive]',
@database_name = N'msdb',
@on_success_action = 3,
@retry_attempts = 3,
@retry_interval = 3;
EXEC sp_add_jobstep
@job_name = N'SSIS Server Maintenance Job',
@step_name = N'SSIS Server Max Version Per Project Maintenance',
@subsystem = N'TSQL',
@command = N'
DECLARE @role int
SET @role = (SELECT [role] FROM [sys].[dm_hadr_availability_replica_states] hars INNER JOIN [sys].[availability_databases_cluster] adc ON hars.[group_id] = adc.[group_id] WHERE hars.[is_local] = 1 AND adc.[database_name] =''SSISDB'')
IF DB_ID(''SSISDB'') IS NOT NULL AND (@role IS NULL OR @role = 1)
EXEC [SSISDB].[internal].[cleanup_server_project_version]',
@database_name = N'msdb',
@retry_attempts = 3,
@retry_interval = 3;
EXEC sp_add_jobschedule
@job_name = N'SSIS Server Maintenance Job',
@name = 'SSISDB Scheduler',
@enabled = 1,
@freq_type = 4, /*daily*/
@freq_interval = 1,/*every day*/
@freq_subday_type = 0x1,
@active_start_date = 20001231,
@active_end_date = 99991231,
@active_start_time = 0,
@active_end_time = 120000
You can also configure the existing SSIS Server Maintenance Job or modify the above T-SQL script to additionally clean up SSIS job/IR operation logs by invoking the relevant SSISDB stored procedures.
Clean up SSISDB logs automatically via Elastic Database Jobs
If you use Azure SQL Database server to host SSISDB, it doesn't have a built-in job orchestrator/scheduler, so you must use an external component, e.g. ADF (see above) or Elastic Database Jobs (see the rest of this section), to clean up SSISDB logs automatically on schedule.
Elastic Database Jobs is an Azure service that can automate and run jobs against a database or group of databases. You can schedule, run, and monitor these jobs by using Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, T-SQL, or REST APIs. Use Elastic Database Jobs to invoke the relevant SSISDB stored procedures for log clean-up one time or on a schedule. You can choose the schedule interval based on SSISDB resource usage to avoid heavy database load.
For more info, see Manage groups of databases with Elastic Database Jobs.
The following sections describe how to invoke the relevant SSISDB stored procedures, [internal].[cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive]/[internal].[cleanup_completed_jobs_exclusive]/[internal].[cleanup_expired_worker], which remove SSISDB logs that are outside their specific retention periods.
Configure Elastic Database Jobs using Azure PowerShell
Important
Using this Azure feature from PowerShell requires the AzureRM module installed. This
is an older module only available for Windows PowerShell 5.1 that no longer receives new features.
The Az and AzureRM modules are not compatible when installed for the same versions of PowerShell.
If you need both versions:
- Uninstall the Az module from a PowerShell 5.1 session.
- Install the AzureRM module from a PowerShell 5.1 session.
- Download and install PowerShell Core 6.x or later.
- Install the Az module in a PowerShell Core session.
The following Azure PowerShell scripts create a new Elastic Job that invokes your selected SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure. For more info, see Create an Elastic Job agent using PowerShell.
Create parameters
# Parameters needed to create your job database
param(
$ResourceGroupName = $(Read-Host "Please enter an existing resource group name"),
$AgentServerName = $(Read-Host "Please enter the name of an existing Azure SQL Database server, for example myjobserver, to hold your job database"),
$SSISDBLogCleanupJobDB = $(Read-Host "Please enter a name for your job database to be created in the given Azure SQL Database server"),
$StoredProcName = $(Read-Host "Please enter the name of SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure to be invoked by your job (internal.cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive/internal.cleanup_completed_jobs_exclusive/internal.cleanup_expired_worker)"),
# Your job database should be a clean, empty S0 or higher service tier. We set S0 as default.
$PricingTier = "S0",
# Parameters needed to create your Elastic Job agent
$SSISDBLogCleanupAgentName = $(Read-Host "Please enter a name for your Elastic Job agent"),
# Parameters needed to create credentials in your job database for connecting to SSISDB
$PasswordForSSISDBCleanupUser = $(Read-Host "Please provide a new password for the log clean-up job user to connect to SSISDB"),
# Parameters needed to create the login and user for SSISDB
$SSISDBServerEndpoint = $(Read-Host "Please enter the name of target Azure SQL Database server that contains SSISDB, for example myssisdbserver") + '.database.windows.net',
$SSISDBServerAdminUserName = $(Read-Host "Please enter the target server admin username for SQL authentication"),
$SSISDBServerAdminPassword = $(Read-Host "Please enter the target server admin password for SQL authentication"),
$SSISDBName = "SSISDB",
# Parameters needed to set the job schedule for invoking SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure
$RunJobOrNot = $(Read-Host "Please indicate whether you want to run your job that cleans up SSISDB logs outside their retention period immediately (Y/N). Make sure the specific retention period is set properly before running the following scripts as deleted logs cannot be recovered."),
$IntervalType = $(Read-Host "Please enter the interval type for SSISDB log clean-up schedule: Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second are supported."),
$IntervalCount = $(Read-Host "Please enter the count of interval type for SSISDB log clean-up schedule."),
# The start time for SSISDB log clean-up schedule is set to current time by default.
$StartTime = (Get-Date)
Invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure
# Install the latest PowerShell PackageManagement module that PowerShellGet v1.6.5 depends on
Find-Package PackageManagement -RequiredVersion 1.1.7.2 | Install-Package -Force
# You may need to restart your PowerShell session
# Install the latest PowerShellGet module that adds the -AllowPrerelease flag to Install-Module
Find-Package PowerShellGet -RequiredVersion 1.6.5 | Install-Package -Force
# Install AzureRM.Sql preview cmdlets side by side with the existing AzureRM.Sql version
Install-Module -Name AzureRM.Sql -AllowPrerelease -Force
# Sign in to your Azure account
Connect-AzureRmAccount
# Create your job database for defining SSISDB log clean-up job and tracking the job history
Write-Output "Creating a blank SQL database to be used as your job database ..."
$JobDatabase = New-AzureRmSqlDatabase -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -ServerName $AgentServerName -DatabaseName $SSISDBLogCleanupJobDB -RequestedServiceObjectiveName $PricingTier
$JobDatabase
# Enable Elastic Database Jobs preview in your Azure subscription
Register-AzureRmProviderFeature -FeatureName sqldb-JobAccounts -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.Sql
# Create your Elastic Job agent
Write-Output "Creating your Elastic Job agent..."
$JobAgent = $JobDatabase | New-AzureRmSqlElasticJobAgent -Name $SSISDBLogCleanupAgentName
$JobAgent
# Create job credentials in your job database for connecting to SSISDB in target server
Write-Output "Creating job credentials for connecting to SSISDB..."
$JobCredSecure = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $PasswordForSSISDBCleanupUser -AsPlainText -Force
$JobCred = New-Object -TypeName "System.Management.Automation.PSCredential" -ArgumentList "SSISDBLogCleanupUser", $JobCredSecure
$JobCred = $JobAgent | New-AzureRmSqlElasticJobCredential -Name "SSISDBLogCleanupUser" -Credential $JobCred
# Create the job user login in master database of target server
Write-Output "Grant permissions on the master database of target server..."
$Params = @{
'Database' = 'master'
'ServerInstance' = $SSISDBServerEndpoint
'Username' = $SSISDBServerAdminUserName
'Password' = $SSISDBServerAdminPassword
'OutputSqlErrors' = $true
'Query' = "CREATE LOGIN SSISDBLogCleanupUser WITH PASSWORD = '" + $PasswordForSSISDBCleanupUser + "'"
}
Invoke-SqlCmd @Params
# Create SSISDB log clean-up user from login in SSISDB and grant it permissions to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure
Write-Output "Grant appropriate permissions on SSISDB..."
$TargetDatabase = $SSISDBName
$CreateJobUser = "CREATE USER SSISDBLogCleanupUser FROM LOGIN SSISDBLogCleanupUser"
$GrantStoredProcedureExecution = "GRANT EXECUTE ON " + $StoredProcName + " TO SSISDBLogCleanupUser"
$TargetDatabase | ForEach-Object -Process {
$Params.Database = $_
$Params.Query = $CreateJobUser
Invoke-SqlCmd @Params
$Params.Query = $GrantStoredProcedureExecution
Invoke-SqlCmd @Params
}
# Create your target group that includes only SSISDB to clean up
Write-Output "Creating your target group that includes only SSISDB to clean up..."
$SSISDBTargetGroup = $JobAgent | New-AzureRmSqlElasticJobTargetGroup -Name "SSISDBTargetGroup"
$SSISDBTargetGroup | Add-AzureRmSqlElasticJobTarget -ServerName $SSISDBServerEndpoint -Database $SSISDBName
# Create your job to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure
Write-Output "Creating your job to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure..."
$JobName = "CleanupSSISDBLog"
$Job = $JobAgent | New-AzureRmSqlElasticJob -Name $JobName -RunOnce
$Job
# Add your job step to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure
Write-Output "Adding your job step to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure..."
$SqlText = "EXEC " + $StoredProcName
$Job | Add-AzureRmSqlElasticJobStep -Name "Step to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure" -TargetGroupName $SSISDBTargetGroup.TargetGroupName -CredentialName $JobCred.CredentialName -CommandText $SqlText
# Run your job to immediately invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure once
if ($RunJobOrNot -eq 'Y')
{
Write-Output "Invoking SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure immediately..."
$JobExecution = $Job | Start-AzureRmSqlElasticJob
$JobExecution
}
# Schedule your job to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure periodically, deleting SSISDB logs outside their retention period
Write-Output "Starting your schedule to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure periodically..."
$Job | Set-AzureRmSqlElasticJob -IntervalType $IntervalType -IntervalCount $IntervalCount -StartTime $StartTime -Enable
Configure Elastic Database Jobs using T-SQL
The following T-SQL scripts create a new Elastic Job that invokes your selected SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure. For more info, see Use T-SQL to create and manage Elastic Database Jobs.
Identify an empty S0/higher service tier of Azure SQL Database or create a new one for your job database. Then create an Elastic Job Agent in Azure portal.
In your job database, create credentials for connecting to SSISDB in your target server.
-- Connect to the job database specified when creating your job agent. -- Create a database master key if one doesn't already exist, using your own password. CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD= '<EnterStrongPasswordHere>'; -- Create credentials for SSISDB log clean-up. CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL SSISDBLogCleanupCred WITH IDENTITY = 'SSISDBLogCleanupUser', SECRET = '<EnterStrongPasswordHere>';Define your target group that includes only SSISDB to clean up.
-- Connect to your job database. -- Add your target group. EXEC jobs.sp_add_target_group 'SSISDBTargetGroup' -- Add SSISDB to your target group EXEC jobs.sp_add_target_group_member 'SSISDBTargetGroup', @target_type = 'SqlDatabase', @server_name = '<EnterSSISDBTargetServerName>', @database_name = 'SSISDB' -- View your recently created target group and its members. SELECT * FROM jobs.target_groups WHERE target_group_name = 'SSISDBTargetGroup'; SELECT * FROM jobs.target_group_members WHERE target_group_name = 'SSISDBTargetGroup';Create SSISDB log clean-up user from login in SSISDB and grant it permissions to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure. For detailed guidance, see Manage logins.
-- Connect to the master database of target server that hosts SSISDB CREATE LOGIN SSISDBLogCleanupUser WITH PASSWORD = '<strong_password>'; -- Connect to SSISDB CREATE USER SSISDBLogCleanupUser FROM LOGIN SSISDBLogCleanupUser; GRANT EXECUTE ON '<internal.cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive/internal.cleanup_completed_jobs_exclusive/internal.cleanup_expired_worker>' TO SSISDBLogCleanupUserCreate your job and add your job step to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure.
-- Connect to your job database. -- Add your job to invoke the relevant SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure. EXEC jobs.sp_add_job @job_name='CleanupSSISDBLog', @description='Remove SSISDB logs outside their specific retention period' -- Add your job step to invoke the relevant SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure EXEC jobs.sp_add_jobstep @job_name='CleanupSSISDBLog', @command=N'<EXEC internal.cleanup_server_retention_window_exclusive/EXEC internal.cleanup_completed_jobs_exclusive/EXEC internal.cleanup_expired_worker>', @credential_name='SSISDBLogCleanupCred', @target_group_name='SSISDBTargetGroup'Before continuing, make sure you set the specific retention period properly. SSISDB logs outside this period will be deleted and can't be recovered. You can then run your job immediately to start SSISDB log clean-up.
-- Connect to your job database. -- Run your job immediately to invoke SSISDB log clean-up stored procedure. declare @je uniqueidentifier exec jobs.sp_start_job 'CleanupSSISDBLog', @job_execution_id = @je output -- Watch SSISDB log clean-up results select @je select * from jobs.job_executions where job_execution_id = @jeOptionally, you can delete SSISDB logs outside their retention period on a schedule. Configure your job parameters as follows.
-- Connect to your job database. EXEC jobs.sp_update_job @job_name='CleanupSSISDBLog', @enabled=1, @schedule_interval_type='<EnterIntervalType(Month,Day,Hour,Minute,Second)>', @schedule_interval_count='<EnterDetailedIntervalValue>', @schedule_start_time='<EnterProperStartTimeForSchedule>', @schedule_end_time='<EnterProperEndTimeForSchedule>'
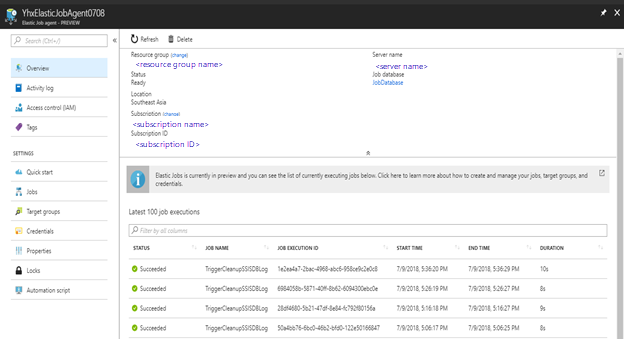
Monitor SSISDB log clean-up job using Azure portal
You can monitor SSISDB log clean-up job in Azure portal. For each execution, you can see its status, start time, and end time.
Monitor SSISDB log clean-up job using T-SQL
You can also use T-SQL to view the execution history of SSISDB log clean-up job.
-- Connect to your job database.
-- View all SSISDB log clean-up job executions.
SELECT * FROM jobs.job_executions WHERE job_name = 'CleanupSSISDBLog'
ORDER BY start_time DESC
-- View all active executions.
SELECT * FROM jobs.job_executions WHERE is_active = 1
ORDER BY start_time DESC
Related content
To manage and monitor your Azure-SSIS IR, see the following articles.
Povratne informacije
Uskoro: tokom 2024. postepeno ćemo ukidati probleme s uslugom GitHub kao mehanizam povratnih informacija za sadržaj i zamijeniti ga novim sistemom povratnih informacija. Za više informacija, pogledajte https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Pošalјite i prikažite povratne informacije za