New sessions setup for LDAP services take longer than expected if targeting host names
This article discusses a problem in which a new session setup for LDAP services takes longer than expected if it targets host names.
Applies to: Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10 – all editions
Original KB number: 4559609
Symptoms
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) queries that target host names randomly take longer than expected to respond.
Additionally, DNS client events such as the following may be logged In the event log:
Log Name: System
Source: Microsoft-Windows-DNS-Client
Event ID: 1014
Level: Warning
User: NETWORK SERVICE
Description:
Name resolution for the name _ldap._tcp.<site>._sites.<name> timed out after none of the configured DNS servers responded.
Note
In this log entry, the <name> parameter can be any of the following:
- Domain NETBIOS name
- Domain Controller host name
- Domain Controller DNS FQDN host name
This problem causes multiple issues that affect administrators, users, and applications. These issues include but aren't limited to the following:
- An LDAP connection against Windows Server 2008 R2 domain controllers (DCs) or later version DCs takes about six seconds. The same connections against Windows Server 2003 or Windows Server 2008 DCs usually takes less than one second. When this occurs, the subsequent LDAP operations, such as bind and LDAP searches, appear to have no additional delay after the initial LDAP connect.
- The LDIFDE.EXE command is slow regardless of whether the/Sparameter is used.
- The Microsoft System Center Active Directory Management Pack (SCOM ADMP) health check script (AD_General_Response.vbs) experiences slow run times.
- Microsoft Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) is slow to start or slow to open OU containers. Extensions in the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, DSA.MSC, uses the DC FQDN computer name as a domain name.
- Microsoft Active Directory Administrative Center (ADAC) Extensions in the Active Directory Administrative Center use the DC FQDN computer name as a domain name.
- Microsoft Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) doesn't consistently use name resolution flags.
- Visual Basic Script (VBS) scripts that make LDAP calls that reference the DC fully qualified DNS name are slow to run.
- .NET Framework applications that use System.DirectoryServices and System.DirectoryServices.Protocols may experience delays when they create server sessions.
Cause
Starting in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows introduced a change in name lookup behavior to fix two earlier problem scenarios:
- LDAP clients fall back to NTLM whenever the NetBIOS domain name is supplied as the host name in the LDAP connection.
- LDAP clients don't connect to a DC in the domain if a client has the same name as the targeted NetBIOS domain name.
The delay occurs because one of the following two conditions is true:
- You encounter a long wait time for a broadcast response. You don't see this delay if NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) name resolution through broadcasts is turned off.
- Delays in the DNS name resolution occur as the application queries for several DNS names that don't exist.
The delays can be observed in a network trace that shows LDAP clients running NetBIOS name lookups for a "[HOSTNAME]<0x1C>" record before they run a DNS lookup to locate the application host computer (see Figure A).
Figure A
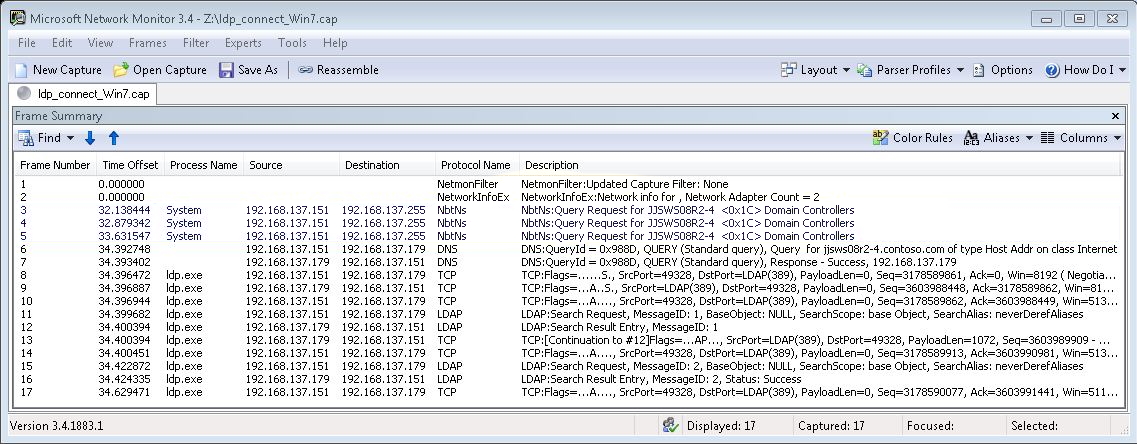
The network trace of a Windows Server 2003 or 2008 LDAP client showed that it directly ran the DNS lookup for the host computer without performing the NetBIOS lookup for the "<0x1C>" record.
Figure B
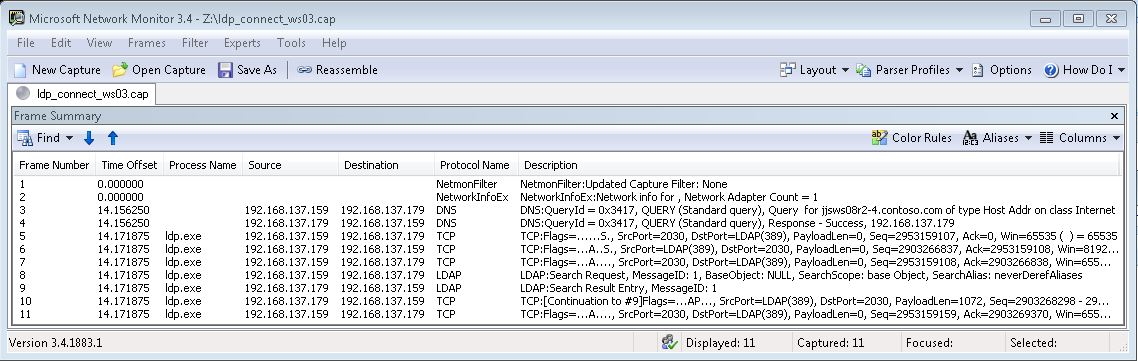
In the case of DNS, you see name queries for names that end in a DC computer name, such as the following:
_ldap._tcp.Default-First-Site-Name._sites.ADDC01.contoso.com
_ldap._tcp.ADDC01.contoso.com
_ldap._tcp.Default-First-Site-Name._sites.ADDC01
_ldap._tcp.ADDC01
Resolution
When you target an LDAP server by host name instead of domain name, you should use the LDAP_OPT_AREC_EXCLUSIVE session option to indicate that the target is a host name instead of a domain name.
This option is set differently depending on the programming interface that is used. Use the following information as reference.
Wldap32
If an Active Directory DNS server name is passed for theHostNameparameter, ldap_set_option should be called to set the LDAP_OPT_AREC_EXCLUSIVE flag before calling any LDAP function that creates the actual connection.
Doing this forces an A-record lookup and bypasses any SRV record lookup when the computer resolves the host name. In some scenarios, it improves network performance. For example, in a branch office that uses a dial-up connection, using A-Record lookup can avoid forcing the dialup to query a remote DNS server for SRV records when it resolves names.
ADSI
If you must specify a server, use the ADS_SERVER_BIND flag to avoid unnecessary or incorrect queries to the DNS server. For more information, see this documentation of ADsOpenObject() and related functions.
System.DirectoryServices
If your ADsPath includes a server name, specify the AuthenticationTypes.ServerBind flag when you use the LDAP provider. Don't use this flag for paths that include a domain name or for serverless paths. Specifying a server name without also specifying this flag causes unnecessary network traffic.
For example:
DirectoryEntry ent = new DirectoryEntry("LDAP://server01",null,null,AuthenticationTypes.ServerBind);
System.DirectoryServices.Protocols
When you prepare a new LDAP connection, include an LdapDirectoryIdentifier object that is constructed by using a host name and optional port that you want to contact, and also includes a <fullyQualifiedDnsHostName> parameter that is set to True.
The new default behavior in Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, and later versions can be reverted to pre-Windows 7 behavior. This may reintroduce problems that affect NetBIOS names as described in the "Cause" section. However, there are also scenarios in which the Pre-Windows 7 behavior provides better results. Therefore, which setting produces the better results depends on the main LDAP client use scenario.
The long-term solution should always be to get the application to use server and domain names that have the appropriate flags when calling into LDAP, ADSI, or .NET interfaces. You should use the correct flags to make the application independent from scenario dependencies when the directory services client code has to decide the resolution method in ambiguous situations.
You can revert to pre-Windows 7 behavior by setting the following registry value:
Subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\LDAP
Entry: UseOldHostResolutionOrder
Type: REG_DWORD
Value data: 1
As an additional approach, you can turn off name resolution by using broadcasting for NetBt. See 819108 Settings for minimizing periodic WAN traffic to configure NodeType as "p-mode."
Configuration for nodes
- Use 0x00000008 for hybrid node or h-node
- Use 0x00000004 for mixed node or m-node
- Use 0x00000002 for point-to-point WINS or p-node
- Use 0x00000001 for broadcast node or b-node
Name resolution node types
- B-Node (broadcasting): Uses broadcasts to resolve names. (Not recommended for larger networks.)
- P-Node (peer to peer): Uses WINS only, no broadcasts. No WINS server, no resolution.
- M-Node (mixed): Broadcast first, then WINS. (Not recommended because you want to minimize broadcasts.)
- H-Node (hybrid) - uses WINS first, then broadcasts. (Recommended because it reduces the number of broadcasts by trying WINS first and resorting to broadcasting only as last resort.)
References
For more information, see the following articles:
LDAP session options (see LDAP_OPT_AREC_EXCLUSIVE, 0x98)
ADSI function AdsopenObject
ADSI AuthenticationEnum with the ADS_SERVER_BIND value
S.DS AuthenticationTypes Enum with the ServerBind value
S.DS.P LdapDirectoryIdentifier constructor with the fullyQualifiedDnsHostName flag
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for