Benchmark a disk
Applies to: ✔️ Linux VMs ✔️ Windows VMs ✔️ Flexible scale sets ✔️ Uniform scale sets
Benchmarking is the process of simulating different workloads on your application and measuring the application performance for each workload. Using the steps described in the designing for high performance article, you have gathered the application performance requirements. By running benchmarking tools on the VMs hosting the application, you can determine the performance levels that your application can achieve with premium SSDs. In this article, we provide you examples of benchmarking a Standard_D8ds_v4 VM provisioned with Azure premium SSDs.
We have used common benchmarking tools DiskSpd and FIO, for Windows and Linux respectively. These tools spawn multiple threads simulating a production like workload, and measure the system performance. Using the tools you can also configure parameters like block size and queue depth, which you normally cannot change for an application. This gives you more flexibility to drive the maximum performance on a high scale VM provisioned with premium SSDs for different types of application workloads. To learn more about each benchmarking tool visit DiskSpd and FIO.
To follow the examples below, create a Standard_D8ds_v4 and attach four premium SSDs to the VM. Of the four disks, configure three with host caching as "None" and stripe them into a volume called NoCacheWrites. Configure host caching as "ReadOnly" on the remaining disk and create a volume called CacheReads with this disk. Using this setup, you are able to see the maximum Read and Write performance from a Standard_D8ds_v4 VM. For detailed steps about creating a Standard_D8ds_v4 with premium SSDs, see Designing for high performance.
Warm up the Cache
The disk with ReadOnly host caching is able to give higher IOPS than the disk limit. To get this maximum read performance from the host cache, first you must warm up the cache of this disk. This ensures that the Read IOs that the benchmarking tool will drive on CacheReads volume, actually hits the cache, and not the disk directly. The cache hits result in more IOPS from the single cache enabled disk.
Important
You must warm up the cache before running benchmarks every time VM is rebooted.
DISKSPD
Download the DISKSP tool on the VM. DISKSPD is a tool that you can customize to create your own synthetic workloads. We will use the same setup described above to run benchmarking tests. You can change the specifications to test different workloads.
In this example, we use the following set of baseline parameters:
- -c200G: Creates (or recreates) the sample file used in the test. It can be set in bytes, KiB, MiB, GiB, or blocks. In this case, a large file of 200-GiB target file is used to minimize memory caching.
- -w100: Specifies the percentage of operations that are write requests (-w0 is equivalent to 100% read).
- -b4K: Indicates the block size in bytes, KiB, MiB, or GiB. In this case, 4K block size is used to simulate a random I/O test.
- -F4: Sets a total of four threads.
- -r: Indicates the random I/O test (overrides the -s parameter).
- -o128: Indicates the number of outstanding I/O requests per target per thread. This is also known as the queue depth. In this case, 128 is used to stress the CPU.
- -W7200: Specifies the duration of the warm-up time before measurements start.
- -d30: Specifies the duration of the test, not including warm-up.
- -Sh: Disable software and hardware write caching (equivalent to -Suw).
For a complete list of parameters, see the GitHub repository.
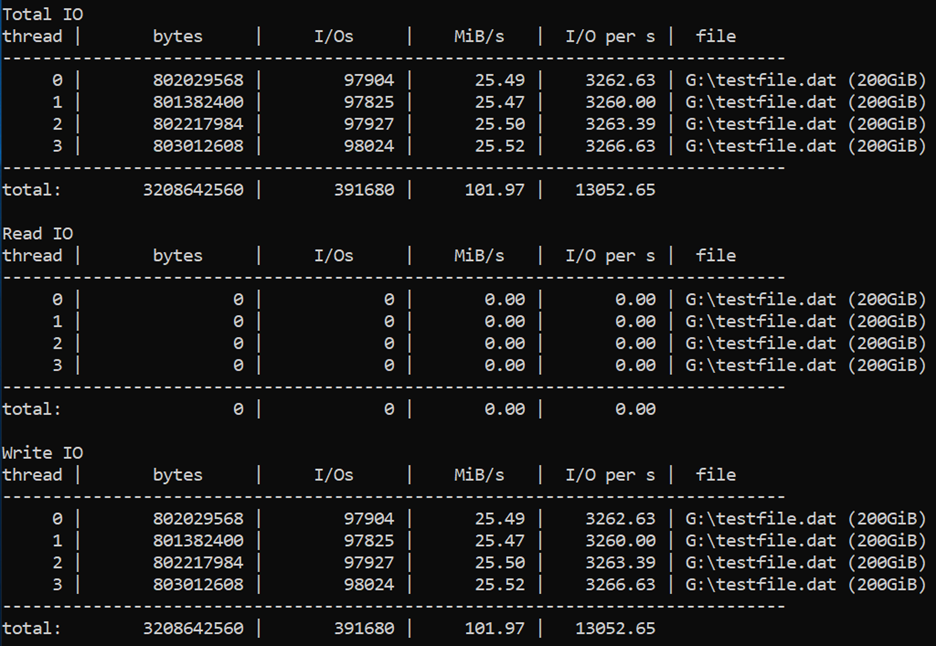
Maximum write IOPS
We use a high queue depth of 128, a small block size of 8 KB, and four worker threads for driving Write operations. The write workers are driving traffic on the “NoCacheWrites” volume, which has three disks with cache set to “None”.
Run the following command for 30 seconds of warm-up and 30 seconds of measurement:
diskspd -c200G -w100 -b8K -F4 -r -o128 -W30 -d30 -Sh testfile.dat
Results show that the Standard_D8ds_v4 VM is delivering its maximum write IOPS limit of 12,800.
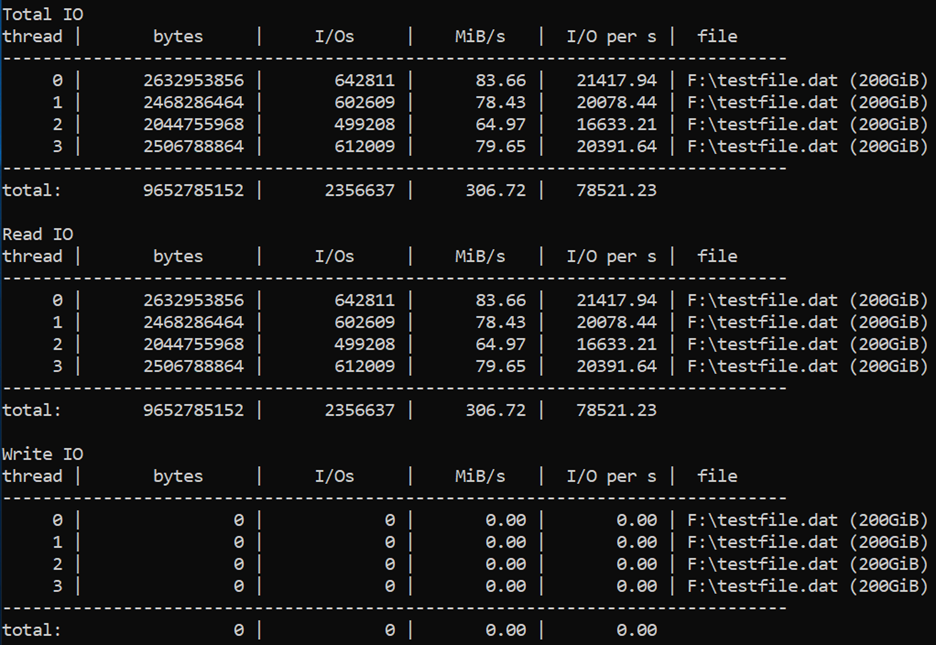
Maximum read IOPS
We use a high queue depth of 128, a small block size of four KB, and four worker threads for driving Read operations. The read workers are driving traffic on the “CacheReads” volume, which has one disk with cache set to “ReadOnly”.
Run the following command for two hours of warm-up and 30 seconds of measurement:
diskspd -c200G -b4K -F4 -r -o128 -W7200 -d30 -Sh testfile.dat
Results show that the Standard_D8ds_v4 VM is delivering its maximum read IOPS limit of 77,000.
Maximum throughput
To get the maximum read and write throughput, you can change to a larger block size of 64 KB.
FIO
FIO is a popular tool to benchmark storage on the Linux VMs. It has the flexibility to select different IO sizes, sequential or random reads and writes. It spawns worker threads or processes to perform the specified I/O operations. You can specify the type of I/O operations each worker thread must perform using job files. We created one job file per scenario illustrated in the examples below. You can change the specifications in these job files to benchmark different workloads running on Premium Storage. In the examples, we are using a Standard_D8ds_v4 running Ubuntu. Use the same setup described in the beginning of the benchmark section and warm up the cache before running the benchmark tests.
Before you begin, download FIO and install it on your virtual machine.
Run the following command for Ubuntu,
apt-get install fio
We use four worker threads for driving Write operations and four worker threads for driving Read operations on the disks. The write workers are driving traffic on the "nocache" volume, which has three disks with cache set to "None". The read workers are driving traffic on the "readcache" volume, which has one disk with cache set to "ReadOnly".
Maximum write IOPS
Create the job file with following specifications to get maximum Write IOPS. Name it "fiowrite.ini".
[global]
size=30g
direct=1
iodepth=256
ioengine=libaio
bs=4k
numjobs=4
[writer1]
rw=randwrite
directory=/mnt/nocache
Note the follow key things that are in line with the design guidelines discussed in previous sections. These specifications are essential to drive maximum IOPS,
- A high queue depth of 256.
- A small block size of 4 KB.
- Multiple threads performing random writes.
Run the following command to kick off the FIO test for 30 seconds,
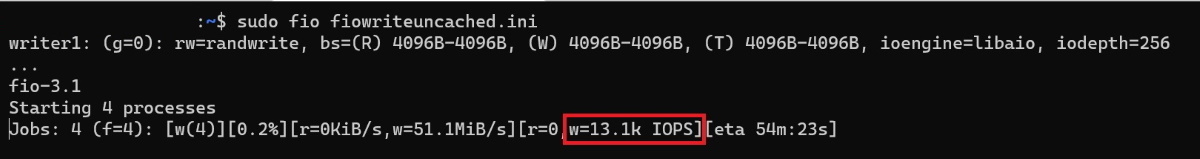
sudo fio --runtime 30 fiowrite.ini
While the test runs, you are able to see the number of write IOPS the VM and Premium disks are delivering. As shown in the sample below, the Standard_D8ds_v4 VM is delivering its maximum write IOPS limit of 12,800 IOPS.
Maximum read IOPS
Create the job file with following specifications to get maximum Read IOPS. Name it "fioread.ini".
[global]
size=30g
direct=1
iodepth=256
ioengine=libaio
bs=4k
numjobs=4
[reader1]
rw=randread
directory=/mnt/readcache
Note the follow key things that are in line with the design guidelines discussed in previous sections. These specifications are essential to drive maximum IOPS,
- A high queue depth of 256.
- A small block size of 4 KB.
- Multiple threads performing random writes.
Run the following command to kick off the FIO test for 30 seconds,
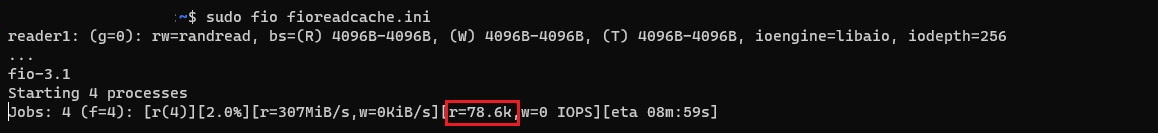
sudo fio --runtime 30 fioread.ini
While the test runs, you are able to see the number of read IOPS the VM and Premium disks are delivering. As shown in the sample below, the Standard_D8ds_v4 VM is delivering more than 77,000 Read IOPS. This is a combination of the disk and the cache performance.
Maximum read and write IOPS
Create the job file with following specifications to get maximum combined Read and Write IOPS. Name it "fioreadwrite.ini".
[global]
size=30g
direct=1
iodepth=128
ioengine=libaio
bs=4k
numjobs=4
[reader1]
rw=randread
directory=/mnt/readcache
[writer1]
rw=randwrite
directory=/mnt/nocache
rate_iops=3200
Note the follow key things that are in line with the design guidelines discussed in previous sections. These specifications are essential to drive maximum IOPS,
- A high queue depth of 128.
- A small block size of 4 KB.
- Multiple threads performing random reads and writes.
Run the following command to kick off the FIO test for 30 seconds,
sudo fio --runtime 30 fioreadwrite.ini
While the test runs, you are able to see the number of combined read and write IOPS the VM and Premium disks are delivering. As shown in the sample below, the Standard_D8ds_v4 VM is delivering more than 90,000 combined Read and Write IOPS. This is a combination of the disk and the cache performance.
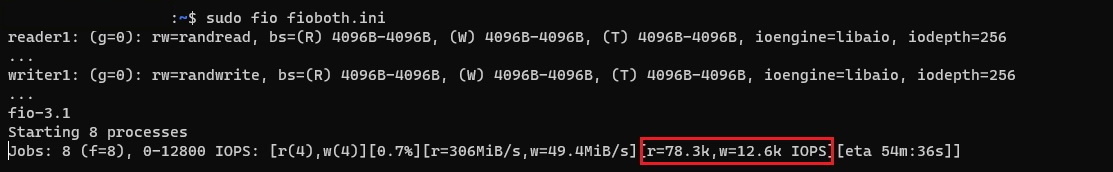
Maximum combined throughput
To get the maximum combined Read and Write Throughput, use a larger block size and large queue depth with multiple threads performing reads and writes. You can use a block size of 64 KB and queue depth of 128.
Next steps
Proceed to our article on designing for high performance.
In that article, you create a checklist similar to your existing application for the prototype. Using Benchmarking tools you can simulate the workloads and measure performance on the prototype application. By doing so, you can determine which disk offering can match or surpass your application performance requirements. Then you can implement the same guidelines for your production application.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for