Configure a Spring Cloud Config Server
In this module, you'll configure a Spring Cloud Config Server that's entirely managed and supported by Azure Spring Apps, to be used by Spring Boot microservices.
This Spring Cloud Config Server gets its configuration data from a Git repository, where Spring Boot configuration files are stored. Storing configuration files using this mechanism has the following advantages:
- Your application's sensitive parameters (like your database password) won't be checked into your application code.
- The Git repository storing your configuration can be secured, so that only an operations team has access to it.
- As the configuration files are stored in Git, you can tag them or roll back them, making it easy to manage your production environment.
- It provides a centralized place to store all your configuration data, for all your microservices.
Create a Git repository for storing the application configuration
On your GitHub account, create a new private repository where the Spring Boot configurations will be stored.
In the new private GitHub repository, add a new application.yml file, which stores configuration data for all our microservices.
Typically, each Spring Boot application includes such a file within the application binaries to contain application settings. A Spring Cloud Configuration Server allows such settings to be stored outside your application, which provides the following benefits:
- It allows storing sensitive parameters (like your database password) outside of your application.
- Your configuration is stored in a Git repository, so its data can be tagged or rolled back.
- It uses a specific Git repository, which can be secured separately.
- It provides a centralized place to store all your configuration data, for all your microservices.
For the moment, our application.yml will just store a message to check if the configuration is successful:
application:
message: Configured by Azure Spring Apps
Commit and push the new file:
git add application.yml
git commit -m 'Add new Spring Boot configuration file'
git push
Create a GitHub personal token
Azure Spring Apps can access Git repositories that are public, secured by SSH, or secured using HTTP basic authentication. We'll use that last option, as it's easier to create and manage with GitHub.
Follow the GitHub guide to create a personal token and save your token. When asked to select scopes, check off the entire "repo" section and nothing else.
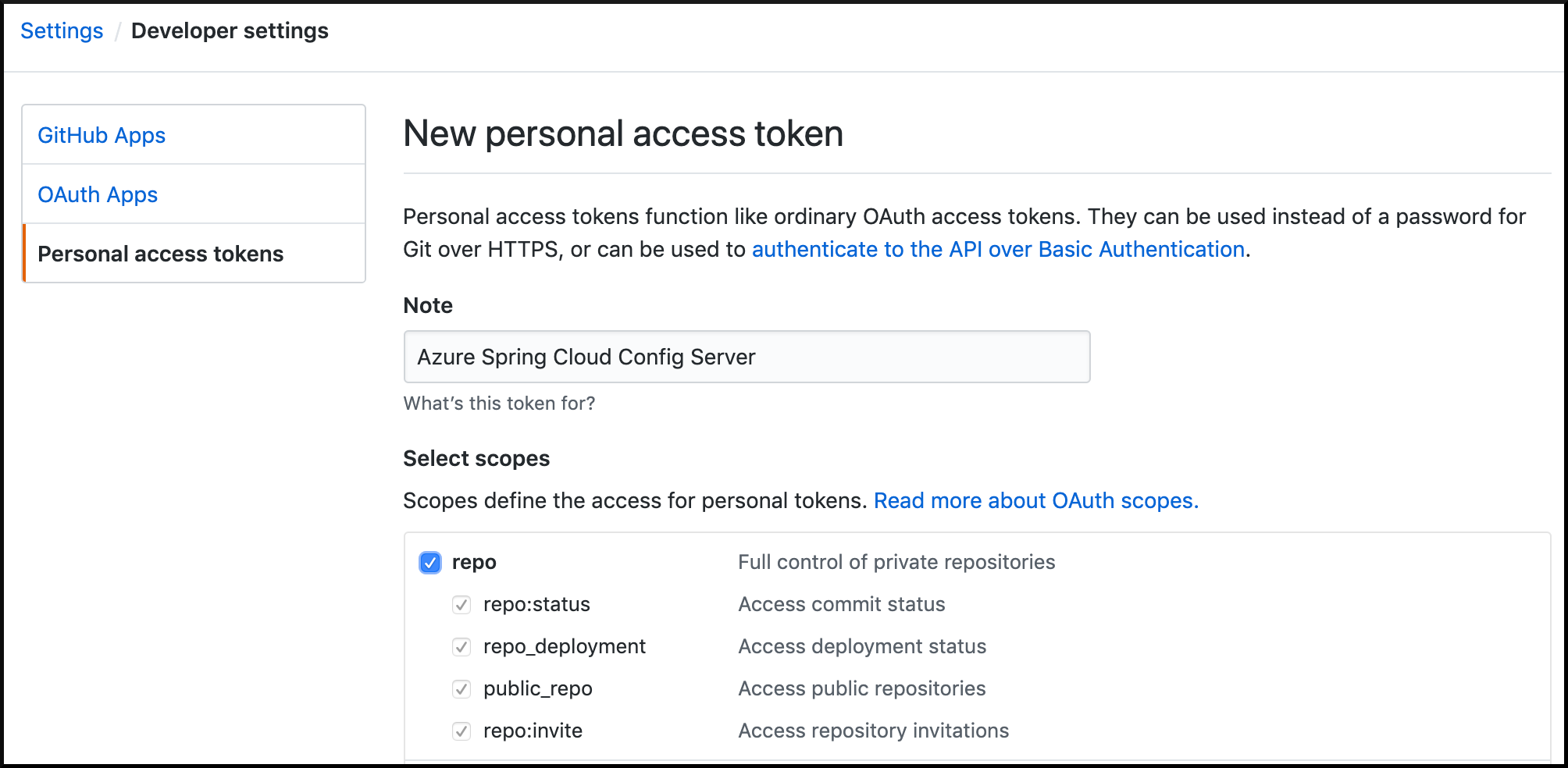
Once the token is generated, leave that tab open until the end of this section.
Configure Azure Spring Apps to access the Git repository
Go to the Azure portal and search for Azure Spring Apps.
Go to the overview page of your Azure Spring Apps server and select Config Server in the menu.
Configure the repository you previously created:
Add the repository URL, for example
https://github.com/<YOUR_USERNAME>/azure-spring-cloud-configorgit@github.com:<YOUR_USERNAME>/azure-spring-cloud-config.git.Tip
Make sure you include the
.gitending in the URL, or use the qualified URI.Add your branch in
Label. It defaults tomainon GitHub, but older repositories or alternate Git providers might still usemaster.Select Authentication and select HTTP Basic.
The username is your GitHub login name.
The password is the personal token we created in the previous section.
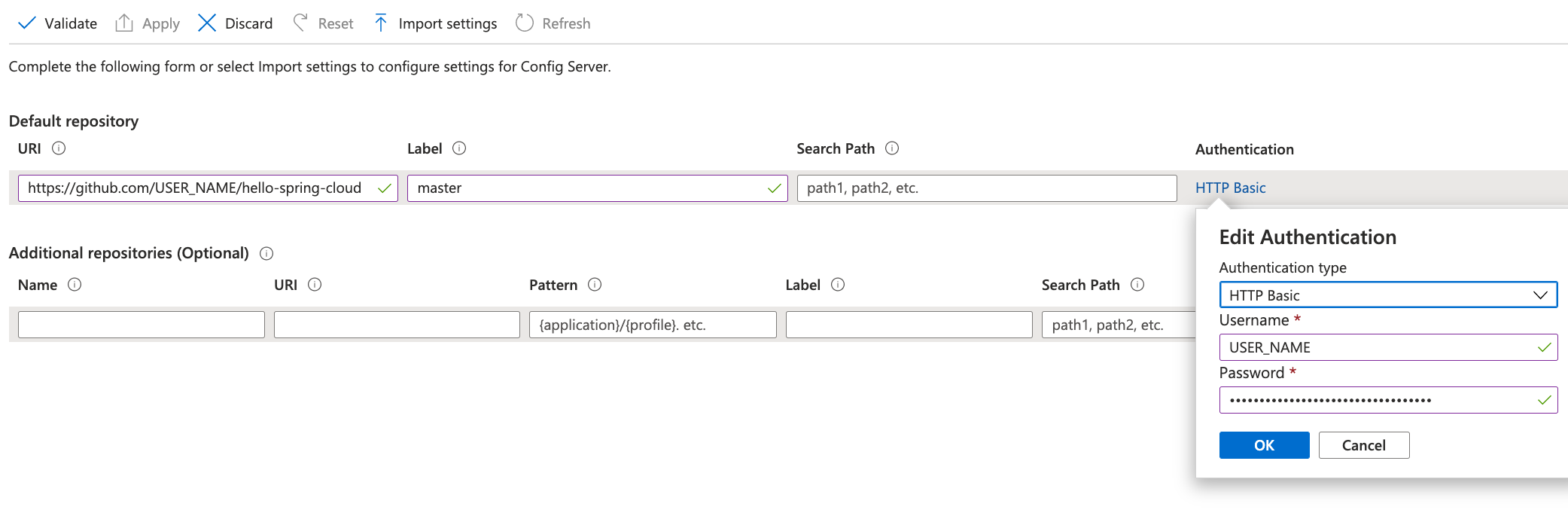
Select Validate and wait for the operation to succeed.
Select Apply and wait for the operation to succeed.
Review
We created a private configuration repository. We also enabled Azure Spring Apps to create a configuration server with the configuration files from this repository.