What is Azure Private 5G Core?
Azure Private 5G Core is an Azure cloud service for deploying and managing 5G core network functions on an Azure Stack Edge device, as part of an on-premises private mobile network for enterprises. The 5G core network functions connect with standard 4G and 5G standalone radio access networks (RANs) to provide high performance, low latency, and secure connectivity for 5G Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Azure Private 5G Core gives enterprises full control and visibility of their private mobile networks.
Azure Private 5G Core provides:
Complete 5G core network functions
Azure Private 5G Core instantiates a single enterprise private mobile network distributed across one or more sites around the world. Each site contains a packet core instance, which is a complete set of 5G network functions. These network functions include the subscriber database, policy control, control plane, and user plane. These are all deployed on a multi-access edge compute platform.
You can also configure packet core instances to operate in 4G mode to support Private Long-Term Evolution (LTE) use cases.
Azure service management
Azure Private 5G Core provides a centralized software lifecycle and service management for the private mobile network across multiple sites. You can use the Azure portal and Azure Resource Manager (ARM) APIs to carry out all management and monitoring tasks.
Azure visibility
Azure Private 5G Core integrates with Azure Monitor to collect data from across the sites and provide real-time monitoring of the entire private mobile network. You can extend this capability to capture radio analytics to provide a complete network view from Azure.
You'll also need the following to deploy a private mobile network using Azure Private 5G Core. These aren't included as part of the service.
Azure Stack Edge and Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes
Packet core instances run on a Kubernetes cluster, which is connected to Azure Arc and deployed on an Azure Stack Edge Pro with GPU device. These platforms provide security and manageability for the entire core network stack from Azure. Additionally, Azure Arc allows Microsoft to provide support at the edge.
For more information, see Azure Arc overview and Azure Kubernetes Service on Azure Stack HCI.
RANs and SIMs
The Azure private multi-access edge compute (MEC) solution offers an ecosystem of technology solution partners, including the following:
- Radio vendors who can connect Azure Private 5G Core to a gNodeB (for 5G deployments) or eNodeB (for 4G deployments), allowing you to choose from a broad range of shared or licensed spectrum options available in different countries/regions.
- SIM vendors offering physical SIM and eSIM services. These vendors can integrate directly with Azure Private 5G Core through the SIM manager to securely provision physical SIMs and eSIMs.
For more information, see What is Azure private multi-access edge compute?.
The following diagram shows the key components of Azure Private 5G Core.
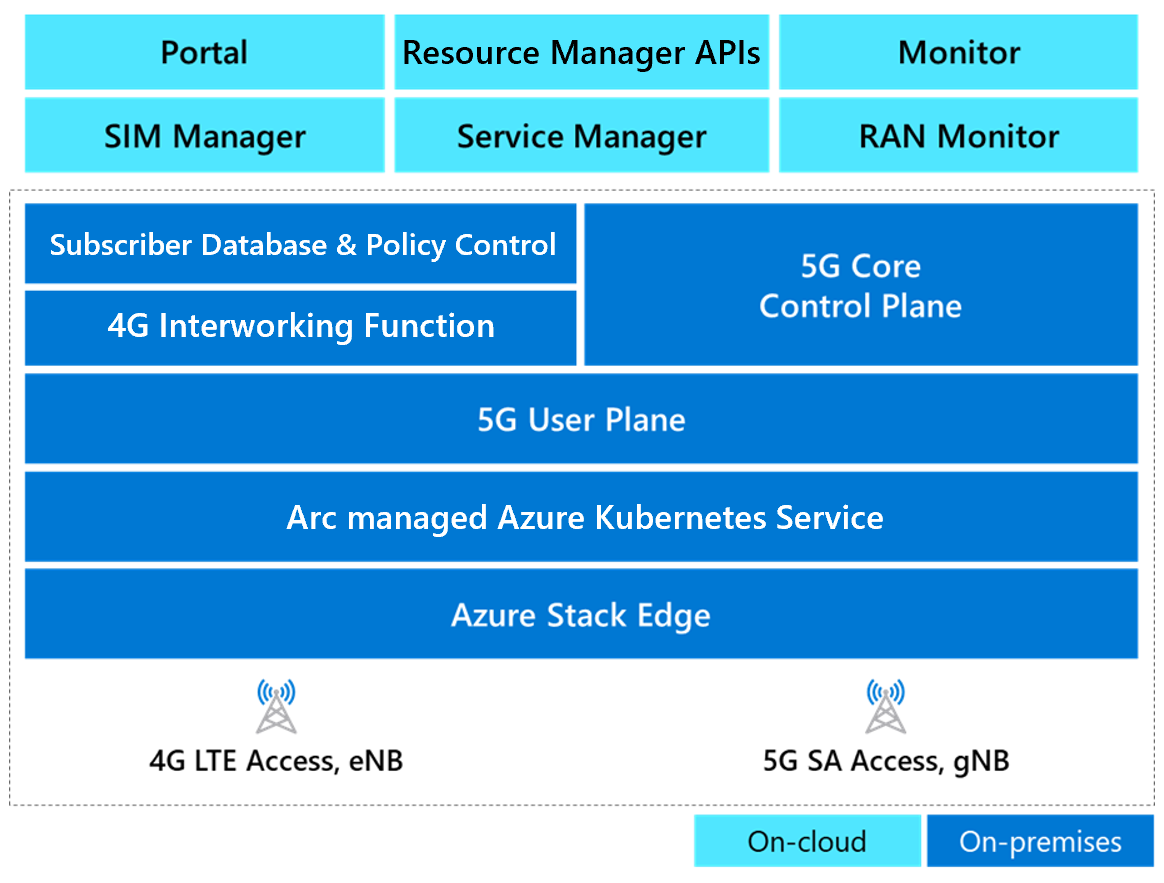
Diagram showing the components of Azure Private 5G Core. They're split between cloud components and components provided on premises. The cloud components include Azure portal, ARM APIs, Azure Monitor, SIM Manager, Service Manager, and RAN Monitor. The on-premises components include Subscriber Database and Policy Control, 4G Interworking Function, 5G Core Control Plane, 5G User Plane, Arc-enabled Kubernetes, and Azure Stack Edge.
Key benefits and use cases
Deploying a private mobile network using Azure Private 5G Core at the enterprise edge ensures complete ownership of all data by the enterprise. It also positions the packet core instance as close as possible to the devices it serves, removing any reliance on cloud connectivity. This allows it to deliver low latency levels through local data processing when combined with application logic in the same location. This provides many valuable benefits:
- Machine to machine automation - Ultra reliable low latency connectivity (URLLC) for command and control messages from automated systems (like robots or automated guide vehicles). These messages can be processed in real time to prevent stalling, enabling high productivity.
- Massive IoT telemetry - Secure cloud connectivity for data collection from a large density and volume of IoT sensors and devices. Data for health assessment and automated systems can be processed in real time to prevent accidents and ensure on-site safety.
- Real-time analytics - Local processing of real-time operational and diagnostics data. For example, live video feeds can be processed at the edge at minimal expense using AI, ensuring vital actions aren't delayed.
Azure Private 5G Core is able to leverage this low latency with the security and high bandwidth offered by private 5G networks. This puts it in the optimal position to support Industry 4.0 use cases, such as the following:
- Manufacturing - Production-line analytics and warehouse automation with robots.
- Public safety - Mobility and connectivity for emergency workers and disaster recovery operatives.
- Energy and utilities - Backhaul networks for smart meters and network slicing/control.
- Defense - Connected command posts and battlefield with real-time analytics.
- Smart farms - Connected equipment for farm operation.
Packet core architecture
Azure Private 5G Core instantiates a single private mobile network distributed across one or more enterprise sites across the world. Each site contains a packet core instance, which is a cloud-native implementation of the 3GPP standards-defined 5G Next Generation Core (5G NGC or 5GC). A packet core instance authenticates end devices and aggregates their data traffic over 5G Standalone wireless and access technologies. Each packet core instance includes the following components:
- A high performance (25 Gbps rated load) and highly programmable 5G User Plane Function (UPF).
- Core control plane functions including policy and subscriber management.
- A portfolio of service-based architecture elements.
- Management components for network monitoring.
You can also deploy packet core instances in 4G mode to support Private Long-Term Evolution (LTE) use cases. For example, you can use the 4G Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) spectrum. 4G mode uses the same cloud-native components as 5G mode (such as the UPF). This is in contrast to other solutions that need to revert to a legacy 4G stack.
The following diagram shows the network functions supported by a packet core instance. It also shows the interfaces these network functions use to interoperate with third-party components.
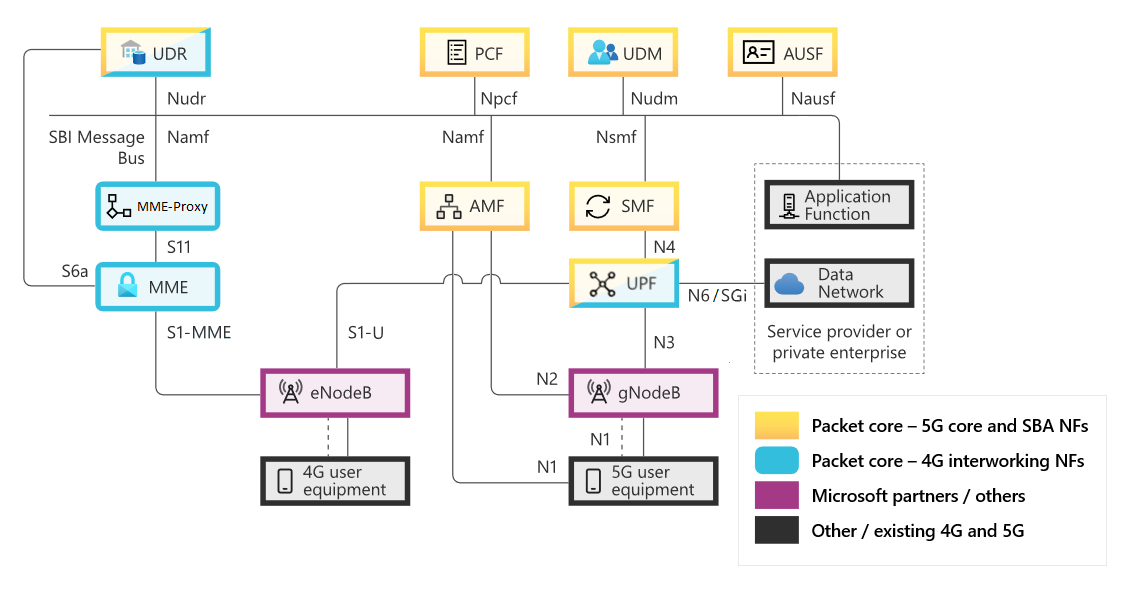
Diagram displaying the packet core architecture. The packet core includes the following 5G network functions: the AMF, the SMF, the UPF, the UDR, the PCF, the UDM, and the AUSF. The AMF communicates with 5G user equipment over the N1 interface. A g NodeB provided by a Microsoft partner communicates with the AMF over the N2 interface and the UPF over the N3 interface. The UPF communicates with the data network over the N6 interface. When operating in 4G mode, the packet core includes MME Proxy and MME network functions. The MME Proxy communicates with the MME over the S11 interface. An e NodeB provided by a Microsoft partner communicates with the MME over the S1-MME interface.
Each packet core instance is connected to the local RAN network to provide coverage for cellular wireless devices. You can choose to limit these devices to local connectivity. Alternatively, you can provide multiple routes to the cloud, internet, or other enterprise data centers running IoT and automation applications.
Feature support
Supported 5G network functions
- Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF)
- Session Management Function (SMF)
- User Plane Function (UPF)
- Policy Control Function (PCF)
- Authentication Server Function (AUSF)
- Unified Data Management (UDM)
- Unified Data Repository (UDR)
Supported 4G network functions
Azure Private 5G Core uses the following network functions when supporting 4G UEs, in addition to the 5G network functions listed above.
- Mobile Management Entity (MME)
- MME-Proxy - The MME-Proxy works to allow 4G UEs to be served by 5G network functions.
The following 5G network functions perform specific roles when supporting 4G UEs.
- The UDR operates as a Home Subscriber Store (HSS).
- The UPF operates as a System Architecture Evolution Gateway (SAEGW-U).
Supported 5G and 4G procedures
For information on Azure Private 5G Core's support for standards-based 5G and 4G procedures, see Statement of compliance - Azure Private 5G Core.
User equipment (UE) authentication and security context management
Azure Private 5G Core supports the following authentication methods:
- Authentication using Subscription Permanent Identifiers (SUPI) and 5G Globally Unique Temporary Identities (5G-GUTI) for 5G user equipment (UEs).
- SUPI concealment using encrypted Subscription Concealed Identifiers (SUCI).
- Authentication using International Mobile Subscriber Identities (IMSI) and Globally Unique Temporary Identities (GUTI) for 4G UEs.
- 5G Authentication and Key Agreement (5G-AKA) for mutual authentication between 5G UEs and the network.
- Evolved Packet System based Authentication and Key Agreement (EPS-AKA) for mutual authentication between 4G UEs and the network.
The packet core instance performs ciphering and integrity protection of 5G non-access stratum (NAS). During UE registration, the UE includes its security capabilities for 5G NAS with 128-bit keys.
Azure Private 5G Core supports the following algorithms for ciphering and integrity protection:
- 5GS null encryption algorithm
- 128-bit Snow3G
- 128-bit Advanced Encryption System (AES) encryption
UE-to-UE traffic
Azure Private 5G Core supports traffic flow from UE to UE through the user plane, allowing machine-to-machine (M2M) communication between 5G devices for a range of applications including robot control.
An external router is responsible for hairpinning traffic from UE to UE over the N6 interface. This means that traffic leaving the UPF destined to a UE IP address will be routed back to the UPF’s N6 IP address.
Index to RAT/Frequency Selection Priority (RFSP)
The packet core instance can provide a RAN with an RFSP Index. The RAN can match the RFSP Index to its local configuration to apply specific radio resource management (RRM) policies, such as cell reselection or frequency layer redirection.
Multi-Operator Core Network (MOCN)
Multi-operator Core Network (MOCN) aims to maximize resource usage by sharing a RAN between multiple core networks. Azure Private 5G Core supports MOCN, allowing multiple public land mobile networks (PLMNs) to be shared by a gNodeB (for 5G deployments) or eNodeB (for 4G deployments).
In the context of private mobile networks, a single RAN can connect to both a private and a standard macro network, with traffic automatically routed to the appropriate core network based on the PLMN ID.
Flexible integration with Azure private multi-access edge compute (MEC) partners
Each packet core instance is standards-compliant and compatible with several RAN partners in the Azure private MEC ecosystem.
Azure Private 5G Core exposes an N2 and N3 interface for the 5G control plane and user plane respectively. It complies with the following 3GPP Technical Specifications, allowing you to integrate with a wide range of RAN models:
For 4G, it exposes S1-MME and S1-U interfaces to interoperate with 4G RAN models.
It also employs a simple, scalable provisioning model to allow you to bring the SIM partner of your choice to Azure.
Azure centralized service management
Azure Private 5G Core is available as a native Azure service, offering the same levels of reliability, security, and availability for deployment and management that are key tenets of all Azure services. This allows you to use Azure as a central access point to manage individual instances of private mobile networks across multiple enterprise sites. You can use the Azure portal (accessible from a choice of any Azure region in the world) or Azure Resource Manager (ARM) APIs to do any of the following tasks:
- Deploy and configure a packet core instance on your Azure Stack Edge device in minutes.
- Create a virtual representation of your physical mobile network through Azure using mobile network and site resources.
- Provision SIM resources to authenticate devices in the network, while also supporting redundancy.
- Employ Azure Monitor and other observability services to view the health of your network and take corrective action through Azure.
- Use Azure role-based access control (RBAC) to allow granular access to the private mobile network to different personnel or teams within your organization, or even a managed service provider.
- Use an Azure Stack Edge device's compute capabilities to run applications that can benefit from low-latency networks.
- Seamlessly connect your existing Azure deployments to your new private mobile network using Azure hybrid compute, networking, and IoT services.
- Access the large ecosystem of Microsoft independent software vendor (ISV) partners for applications and network functions.
- Utilize Azure Lighthouse and the Azure Expert Managed Services Provider (MSP) program to simplify the end-to-end deployment of a private mobile network through Azure.
Azure centralized monitoring
Azure Private 5G Core is integrated with Azure Monitor Metrics Explorer, allowing you to monitor and analyze activity in your private mobile network directly from the Azure portal. You can write queries to retrieve records or visualize data in dashboards.
For more information on using Azure Monitor to analyze metrics in your deployment, see Monitor Azure Private 5G Core with Azure Monitor platform metrics.
Azure Private 5G Core can be configured to integrate with Azure Monitor Event Hubs, allowing you to monitor UE usage.
For more information on using Event Hubs to monitor UE usage in your deployment, see Monitor UE usage via Azure Event Hubs.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for