Exercise - Add connection string to Azure Functions app settings
It's time to put some gasoline in this API engine and fire it up. That's an analogy for connecting the function endpoints to the database. You're probably better at coding than we are with analogies.
Get the database connection string
When you open the sandbox, part of that process creates the database and populates it with sample data. The database connection string is created during that process.
After you open the sandbox, paste the following code into Azure Cloud Shell and press Enter to get the connection string.
cd mslearn-build-api-azure-functions/DB_SETUP && ./GET_CONNECTION_STRING.shCopy the database connection string that is returned in Azure Cloud Shell.
Add connection string to local settings
In Visual Studio Code, open the
local.settings.jsonfile.In the "Values" section, add a setting for "CONNECTION_STRING", and paste in the value you copied in the previous section.
{ "IsEncrypted": false, "Values": { "AzureWebJobsStorage": "", "FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "node", "AzureWebJobsFeatureFlags": "EnableWorkerIndexing", "CONNECTION_STRING": "<YOUR-CONNECTION-STRING>" } }
Examine the productsService for the connection string
Open the api/src/services/product.services.ts file.
Look at line 4. Notice that the connection string is read from the process.env variable.
const CONNECTION_STRING = process.env.CONNECTION_STRING;
Test out the GetProducts endpoint from Visual Studio Code
To start the project, press F5.
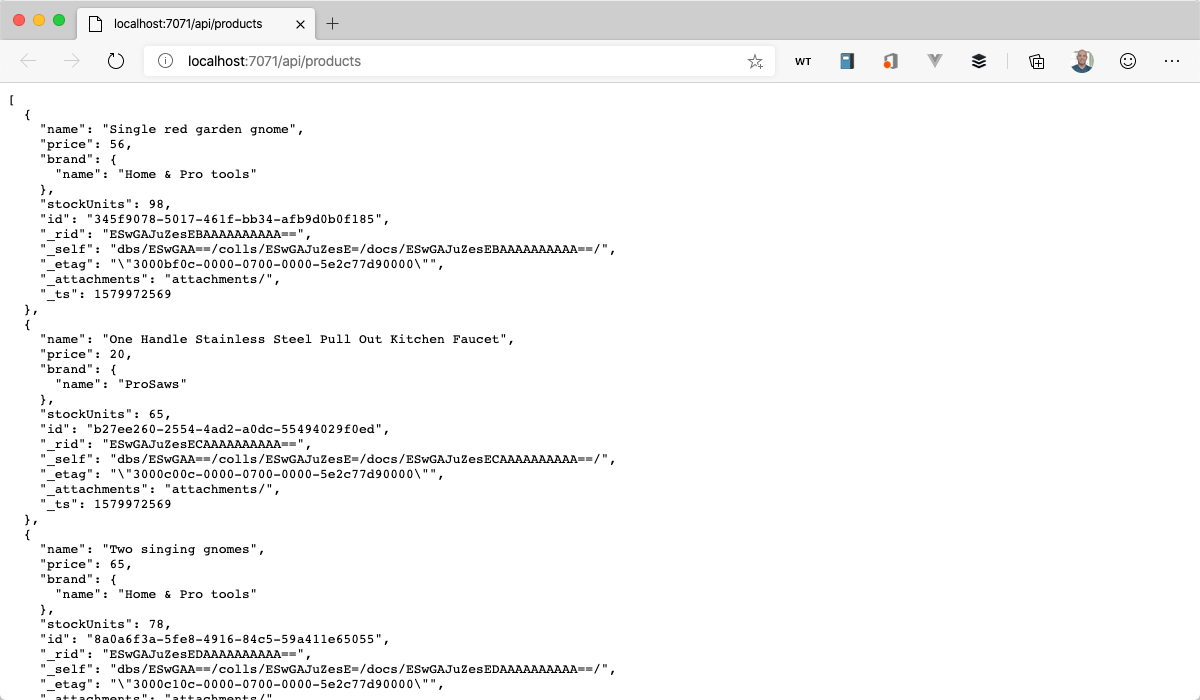
Go to the /api/GetProducts URL.
http://localhost:7071/api/GetProductsBehold the products.