Describe governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) concepts
Organizations face increasing complexity and change in regulatory environments, calling for a more structured approach for managing governance, risk, and compliance (GRC).
As organizations establish GRC competency they can establish a framework that includes implementing specific policies, operational processes, and technologies. A structured approach for managing GRC helps organizations reduce risk and improve compliance effectiveness.
An important prerequisite to establishing GRC competency is understanding the key terms.
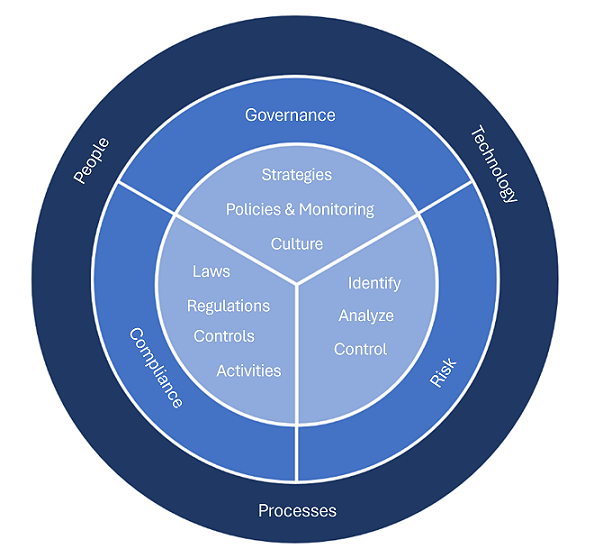
Governance
Governance is the system of rules, practices, and processes an organization uses to direct and control its activities. Many governance activities arise from external standards, obligations and expectations. For example, organizations establish rules and process that define the who, what, where, and when users and applications can access corporate resources and who has administrative privileges and for how long.
Risk
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and responding to threats or events that can impact company or customer objectives. Organizations face risk from both external and internal sources. External risks can come from political and economic forces weather related events, pandemics, and security breaches to name just a few sources. Internal risks are risks that come from within the organization itself. Examples include leaks of sensitive data, intellectual property theft, fraud, and insider trading.
Compliance
Compliance refers to the country/region, state or federal laws or even multi-national regulations that an organization must follow. These regulations define what types of data must be protected, what processes are required under the legislation, and what penalties are issued to organizations that fail to comply.
It's important to note that compliance is not the same as security. But, security should be considered when building a compliance plan as effective security is frequently a compliance requirement. Compliance requires only that the legally mandated minimum standards are met whereas data security covers all the processes, procedures and technologies that define how you look after sensitive data and guard against breaches.
Some compliance-related concepts include:
- Data residency - When it comes to compliance, data residency regulations govern the physical locations where data can be stored and how and when it can be transferred, processed, or accessed internationally. These regulations can differ significantly depending on jurisdiction.
- Data sovereignty - Another important consideration is data sovereignty, the concept that data, particularly personal data, is subject to the laws and regulations of the country/region in which it's physically collected, held, or processed. This can add a layer of complexity when it comes to compliance because the same piece of data can be collected in one location, stored in another, and processed in still another; making it subject to laws from different countries/regions.
- Data privacy - Providing notice and being transparent about the collection, processing, use, and sharing of personal data are fundamental principles of privacy laws and regulations. Personal data means any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person. Privacy laws encompass any data that is directly linked or indirectly linkable back to a person. Organizations are subject to, and must operate consistent with, a multitude of laws, regulations, codes of conduct, industry-specific standards, and compliance standards governing data privacy.
All organizations manage data so understanding terminology and concepts related to compliance is important as they work to meet the minimum, mandated laws and/or regulations.