Configure meeting settings
Teams meeting settings apply to all Teams meetings. The Teams admin, who configures these settings in the Microsoft Teams admin center, uses these settings to:
- Control whether anonymous users can join Teams meetings.
- Control whether anonymous users can interact with apps in meetings.
- Customize meeting invitations.
- Customize settings to handle real-time media traffic.
- Set port ranges for real-time media traffic.
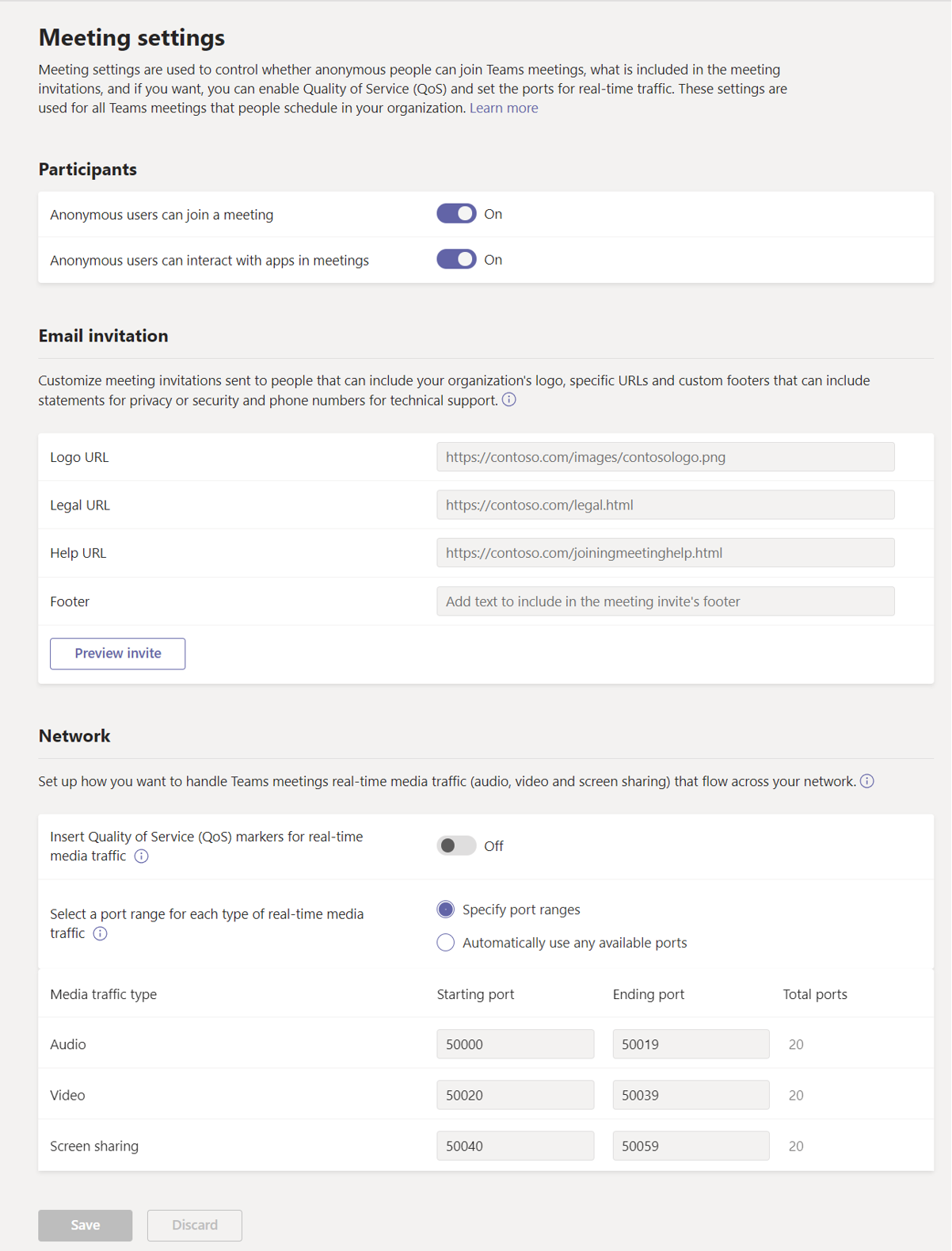
Meeting settings
Participants
Anonymous participants are users who can join a meeting without logging in, as long as they have the link for the meeting. The Teams admin can define whether anonymous participants can join and interact with apps in a meeting. Anonymous participant settings include:
Anonymous users can join a meeting - With anonymous join, anyone can join the meeting as an anonymous user by selecting the link in the meeting invitation.
You can use either policy, organization-wide (meeting setting) or per-organizer(meeting policy), to manage anonymous join. We recommend that you implement the per-organizer policy. The organization-wide policy setting will be deprecated in the future and the per-organizer policy will be the only way to control anonymous join.
Anonymous users can interact with apps in meetings - Anonymous users inherit the user-level global default permission policy. This control enables anonymous users to interact with apps in Teams meetings as long as the user-level permission policy has enabled the app.
Note
Anonymous users can only interact with apps that are already available in a meeting. They can't acquire and/or manage these apps.
Email invitation
Organizations can customize the following information in their Teams meeting invitations:
Logo URL - An organization can customize meeting requests by displaying its company logo in the email invitation. The logo can be no more than 188 pixels wide by 30 pixels tall in a JPG or PNG format.
Legal URL - If an organization has a legal disclaimer it wants meeting attendees to read, it can enter the URL of its legal website here.
Help URL - If an organization has a support website that it wants people to go to if they have a question about a meeting, it can enter the support URL here.
Footer - An organization can optionally enter text that it wants to include as a footer in the email invitation.
To see a preview of your meeting invitation, select Preview invite.
Network
If an organization uses Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize network traffic, it can enable QoS markers and set port ranges for each type of media traffic.
To allow DSCP markings to be used for QoS, turn on Insert Quality of Service (QoS) markers for real-time media traffic. You can only turn the use of markers On or Off with this setting. You can't set custom markers for each traffic type.
To specify port ranges, next to Select a port range for each type of real-time media traffic, select Specify port ranges, and then enter the starting and ending ports for audio, video, and screen sharing. Selecting this option is required to implement QoS.
If you select Automatically use any available ports, available ports between 1024 and 65535 are used. This option can only be used if you're not implementing QoS.
Important
If QoS is enabled or global settings are changed in the Microsoft Teams admin center, matching settings must be applied to all user devices and all internal network devices to fully implement the changes to QoS.
Configure Meeting settings in the Teams admin center
You must be a Teams admin to configure meeting settings in the Teams admin center. Complete the following steps to configure meeting settings:
Sign into the Microsoft Teams admin center, select Meetings, and then select Meeting settings.
Configure the settings based on your organization's business needs.
Select Save.
Tip
It may take approximately an hour for the setting changes to propagate through the system and take effect. At that point, you should schedule a Teams meeting to see if the information in the meeting invitation is correct.