Service to service calls using client credentials (shared secret or certificate)
Warning
This content is for the older Azure AD v1.0 endpoint. Use the Microsoft identity platform for new projects.
The OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials Grant Flow permits a web service (confidential client) to use its own credentials instead of impersonating a user, to authenticate when calling another web service. In this scenario, the client is typically a middle-tier web service, a daemon service, or web site. For a higher level of assurance, Azure AD also allows the calling service to use a certificate (instead of a shared secret) as a credential.
Client credentials grant flow diagram
The following diagram explains how the client credentials grant flow works in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
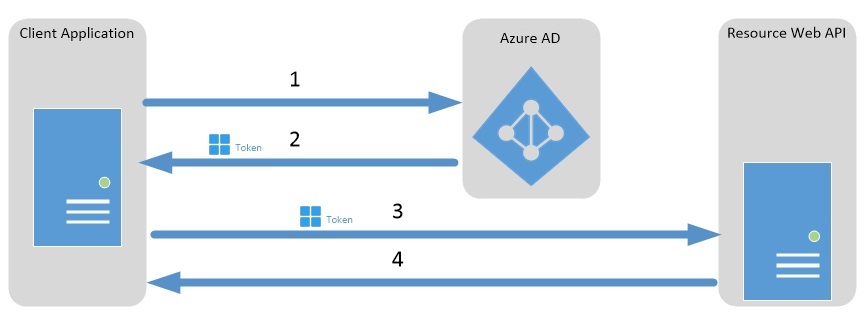
- The client application authenticates to the Azure AD token issuance endpoint and requests an access token.
- The Azure AD token issuance endpoint issues the access token.
- The access token is used to authenticate to the secured resource.
- Data from the secured resource is returned to the client application.
Register the Services in Azure AD
Register both the calling service and the receiving service in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). For detailed instructions, see Integrating applications with Azure Active Directory.
Request an Access Token
To request an access token, use an HTTP POST to the tenant-specific Azure AD endpoint.
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant id>/oauth2/token
Service-to-service access token request
There are two cases depending on whether the client application chooses to be secured by a shared secret, or a certificate.
First case: Access token request with a shared secret
When using a shared secret, a service-to-service access token request contains the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| grant_type | required | Specifies the requested grant type. In a Client Credentials Grant flow, the value must be client_credentials. |
| client_id | required | Specifies the Azure AD client id of the calling web service. To find the calling application's client ID, in the Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory, click App registrations, click the application. The client_id is the Application ID |
| client_secret | required | Enter a key registered for the calling web service or daemon application in Azure AD. To create a key, in the Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory, click App registrations, click the application, click Settings, click Keys, and add a Key. URL-encode this secret when providing it. |
| resource | required | Enter the App ID URI of the receiving web service. To find the App ID URI, in the Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory, click App registrations, click the service application, and then click Settings and Properties. |
Example
The following HTTP POST requests an access token for the https://service.contoso.com/ web service. The client_id identifies the web service that requests the access token.
POST /contoso.com/oauth2/token HTTP/1.1
Host: login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=client_credentials&client_id=625bc9f6-3bf6-4b6d-94ba-e97cf07a22de&client_secret=qkDwDJlDfig2IpeuUZYKH1Wb8q1V0ju6sILxQQqhJ+s=&resource=https%3A%2F%2Fservice.contoso.com%2F
Second case: Access token request with a certificate
A service-to-service access token request with a certificate contains the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| grant_type | required | Specifies the requested response type. In a Client Credentials Grant flow, the value must be client_credentials. |
| client_id | required | Specifies the Azure AD client id of the calling web service. To find the calling application's client ID, in the Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory, click App registrations, click the application. The client_id is the Application ID |
| client_assertion_type | required | The value must be urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer |
| client_assertion | required | An assertion (a JSON Web Token) that you need to create and sign with the certificate you registered as credentials for your application. Read about certificate credentials to learn how to register your certificate and the format of the assertion. |
| resource | required | Enter the App ID URI of the receiving web service. To find the App ID URI, in the Azure portal, click Azure Active Directory, click App registrations, click the service application, and then click Settings and Properties. |
Notice that the parameters are almost the same as in the case of the request by shared secret except that the client_secret parameter is replaced by two parameters: a client_assertion_type and client_assertion.
Example
The following HTTP POST requests an access token for the https://service.contoso.com/ web service with a certificate. The client_id identifies the web service that requests the access token.
POST /<tenant_id>/oauth2/token HTTP/1.1
Host: login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
resource=https%3A%2F%contoso.onmicrosoft.com%2Ffc7664b4-cdd6-43e1-9365-c2e1c4e1b3bf&client_id=97e0a5b7-d745-40b6-94fe-5f77d35c6e05&client_assertion_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Aclient-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer&client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Imd4OHRHeXN5amNScUtqRlBuZDdSRnd2d1pJMCJ9.eyJ{a lot of characters here}M8U3bSUKKJDEg&grant_type=client_credentials
Service-to-Service Access Token Response
A success response contains a JSON OAuth 2.0 response with the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| access_token | The requested access token. The calling web service can use this token to authenticate to the receiving web service. |
| token_type | Indicates the token type value. The only type that Azure AD supports is Bearer. For more information about bearer tokens, see The OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework: Bearer Token Usage (RFC 6750). |
| expires_in | How long the access token is valid (in seconds). |
| expires_on | The time when the access token expires. The date is represented as the number of seconds from 1970-01-01T0:0:0Z UTC until the expiration time. This value is used to determine the lifetime of cached tokens. |
| not_before | The time from which the access token becomes usable. The date is represented as the number of seconds from 1970-01-01T0:0:0Z UTC until time of validity for the token. |
| resource | The App ID URI of the receiving web service. |
Example of response
The following example shows a success response to a request for an access token to a web service.
{
"access_token":"eyJ0eXAiO ... 0X2tnSQLEANnSPHY0gKcgw",
"token_type":"Bearer",
"expires_in":"3599",
"expires_on":"1388452167",
"resource":"https://service.contoso.com/"
}
Use the access token to access the secured resource
The service can use the acquired access token to make authenticated requests to the downstream web API by setting the token in the Authorization header.
Example
GET /me?api-version=2013-11-08 HTTP/1.1
Host: graph.microsoft.com
Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiO ... 0X2tnSQLEANnSPHY0gKcgw