Advanced Configuration Options in Azure Synapse Link
Azure Synapse Link offers multiple ways to write and read your data to fit various analytical scenarios.
Note
Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse was formerly known as Export to data lake. The service was renamed effective May 2021 and will continue to export data to Azure Data Lake as well as Azure Synapse Analytics.
This article covers:
- In-place updates vs. append-only writes.
- User-specified data partitioning.
In-place updates vs. append-only writes
While writing Dataverse table data to the Azure data lake, based on the createdOn value, which is the date and time when the record was created, there are two different settings to choose from. They are, In place update and Append only.
The default setting (for tables where createdOn is available) is to do an in-place update or upsert (update or insert) of the incremental data in the destination. If the change is new and a corresponding row doesn't exist in the lake, in the case of a create, the destination files are scanned, and the changes are inserted into the corresponding file partition in the lake. If the change is an update and a row exists in the lake, the corresponding file in the lake is updated, rather than inserted, with the incremental data. In other words, the default setting for all CUD (create, update, delete) changes in Dataverse tables, where createdOn is available, is to do an in place update in the destination, in Azure data lake.
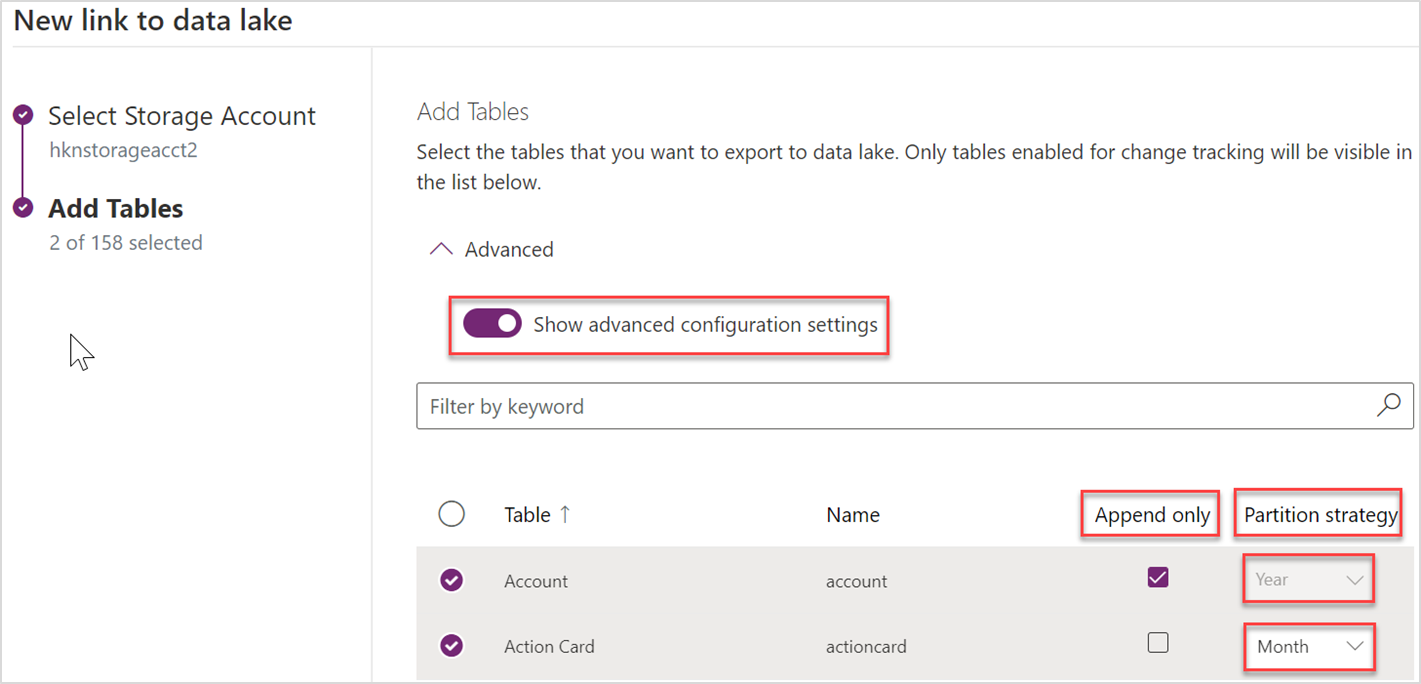
You can switch the default behavior of an in place update by using an optional setting called Append only. Rather than an In place update, in Append only mode, incremental data from Dataverse tables are appended to the corresponding file partition in the lake. This is a per table setting and available as a checkbox under Advanced > Show advanced configuration settings. For Dataverse tables with Append only turned on, all the CUD changes are incrementally appended to the corresponding destination files in the lake. When you choose this option, the partition strategy defaults to Year and when data is written to the data lake, it's partitioned by yearly basis. Append only is also the default setting for Dataverse tables that don't have createdOn value.
The table below describes how rows are handled in the lake against CUD events for each of the data write options.
| Event | In place update | Append only |
|---|---|---|
| Create | The row is inserted in the partition file and is based on the createdOn value on the row. |
The row is added to the end of the partition file and is based on the createdOn value of the record. |
| Update | If the row exists in the partition file, then it's replaced or updated with updated data. If it doesn't exist, it's inserted in the file. | The row, along with the updated version, is added to the end of the partition file. |
| Delete | If the row exists in the partition file, it's removed from the file. | The row is added to the end of the partition file with IsDelete column = True. |
Note
For Dataverse tables where Append only is enabled, deleting a row in the source will not delete or remove the row in the lake. Instead, the deleted row is appended as a new row in the lake and the isDeleted column is set to True.
Dirty read (ALLOW_INCONSISTENT_READS) for serverless is enabled for append only mode. ALLOW_INCONSISTENT_READS means that user is able to read the files that can be constantly modified while the SELECT query is running. Results will be consistent and equivalent to reading a snapshot of the file. (It isn't equivalent to database snapshot isolation because of the different snapshot generation time.)
Not all CUD changes will be captured in append only: The Synapse Link processes changes in data in groups or "batches" before publishing them to the data lake. As a result, if the user makes changes within a short time interval, not all CUD changes will be captured in the data lake.
Here are some more details on when to use either of the options.
- In place update: This option is the default setting and recommended only if you want to connect directly to the data in lake and need the current state (not history or incremental changes). The file contains the full data set and can be utilized via Power BI or by copying the entire dataset for ETL (Extract, Transfer, Load) pipelines.
- Append only: Select this option if you aren't directly connecting to data in the lake and want to incrementally copy data to another target using ETL pipelines. This option provides a history of changes to enable AI and ML scenarios.
You can toggle the Show advanced configuration settings under Advanced in Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse to customize your data partition strategy and select options to write to the Azure data lake.
Data partitioning
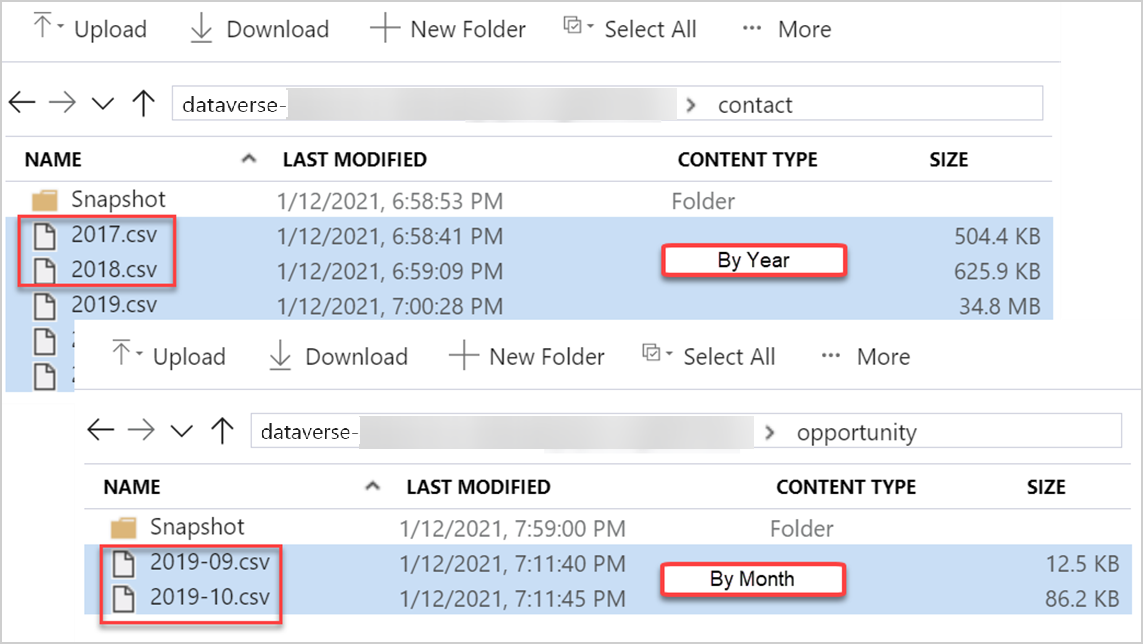
When you write Dataverse table data to Azure data lake storage using Azure Synapse Link, the tables are partitioned (instead of a single file) in the lake based on the createdOn value on each row in the source. The default partition strategy is by month and data is partitioned in Azure data lake on a monthly basis.
Based on the Dataverse table volume and data distribution, you can choose to partition your data by year. With this option, when Dataverse table data is written to the Azure data lake, it will be partitioned on a yearly basis based on the createdOn value on each row in the source. For tables without the createdOn column, the rows of data are partitioned into a new file every 5,000,000 records. This is a per table setting and is available as a checkbox under Advanced > Show advanced configuration settings.
More details with examples of how data is handled in the lake with yearly or monthly partition strategy:
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for