Windows smart card sign-in using Microsoft Entra certificate-based authentication
Microsoft Entra users can authenticate using X.509 certificates on their smart cards directly against Microsoft Entra ID at Windows sign-in. There's no special configuration needed on the Windows client to accept the smart card authentication.
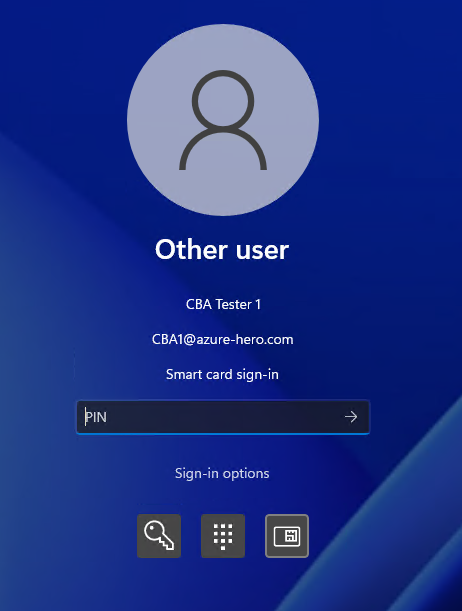
User experience
Follow these steps to set up Windows smart card sign-in:
Join the machine to either Microsoft Entra ID or a hybrid environment (hybrid join).
Configure Microsoft Entra CBA in your tenant as described in Configure Microsoft Entra CBA.
Make sure the user is either on managed authentication or using Staged Rollout.
Present the physical or virtual smart card to the test machine.
Select the smart card icon, enter the PIN, and authenticate the user.
Users will get a primary refresh token (PRT) from Microsoft Entra ID after the successful sign-in. Depending on the CBA configuration, the PRT will contain the multifactor claim.
Expected behavior of Windows sending user UPN to Microsoft Entra CBA
| Sign-in | Microsoft Entra join | Hybrid join |
|---|---|---|
| First sign-in | Pull from certificate | AD UPN or x509Hint |
| Subsequent sign-in | Pull from certificate | Cached Microsoft Entra UPN |
Windows rules for sending UPN for Microsoft Entra joined devices
Windows will first use a principal name and if not present then RFC822Name from the SubjectAlternativeName (SAN) of the certificate being used to sign into Windows. If neither are present, the user must additionally supply a User Name Hint. For more information, see User Name Hint
Windows rules for sending UPN for Microsoft Entra hybrid joined devices
Hybrid Join sign-in must first successfully sign-in against the Active Directory(AD) domain. The users AD UPN is sent to Microsoft Entra ID. In most cases, the Active Directory UPN value is the same as the Microsoft Entra UPN value and is synchronized with Microsoft Entra Connect.
Some customers may maintain different and sometimes may have non-routable UPN values in Active Directory (such as user@woodgrove.local) In these cases the value sent by Windows may not match the users Microsoft Entra UPN. To support these scenarios where Microsoft Entra ID can't match the value sent by Windows, a subsequent lookup is performed for a user with a matching value in their onPremisesUserPrincipalName attribute. If the sign-in is successful, Windows will cache the users Microsoft Entra UPN and is sent in subsequent sign-ins.
Note
In all cases, a user supplied username login hint (X509UserNameHint) will be sent if provided. For more information, see User Name Hint
Important
If a user supplies a username login hint (X509UserNameHint), the value provided MUST be in UPN Format.
For more information about the Windows flow, see Certificate Requirements and Enumeration (Windows).
Supported Windows platforms
The Windows smart card sign-in works with the latest preview build of Windows 11. The functionality is also available for these earlier Windows versions after you apply one of the following updates KB5017383:
- Windows 11 - kb5017383
- Windows 10 - kb5017379
- Windows Server 20H2- kb5017380
- Windows Server 2022 - kb5017381
- Windows Server 2019 - kb5017379
Supported browsers
| Edge | Chrome | Safari | Firefox |
|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Note
Microsoft Entra CBA supports both certificates on-device as well as external storage like security keys on Windows.
Windows Out of the box experience (OOBE)
Windows OOBE should allow the user to login using an external smart card reader and authenticate against Microsoft Entra CBA. Windows OOBE by default should have the necessary smart card drivers or the smart card drivers previously added to the Windows image before OOBE setup.
Restrictions and caveats
- Microsoft Entra CBA is supported on Windows devices that are hybrid or Microsoft Entra joined.
- Users must be in a managed domain or using Staged Rollout and can't use a federated authentication model.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for