Use labels to provide per-environment configuration values.
Many applications need to use different configurations for different environments. Suppose that an application has a configuration value that defines the connection string to use for its back-end database. The application developers use a different database from the one used in production. The database connection string that the application uses must change as the application moves from development to production.
In Azure App Configuration, you can use labels to define different values for the same key. For example, you can define a single key with different values for development and production. You can specify which label to load when connecting to App Configuration.
To demonstrate this functionality, you'll modify the web app created in Quickstart: Create an ASP.NET Core app with Azure App Configuration to use different configuration settings for development versus production. Complete the quickstart before proceeding.
Specify a label when adding a configuration value
In the Azure portal, go to Configuration Explorer and find the TestApp:Settings:FontColor key that you created in the quickstart. Select its context menu and then select Add Value.
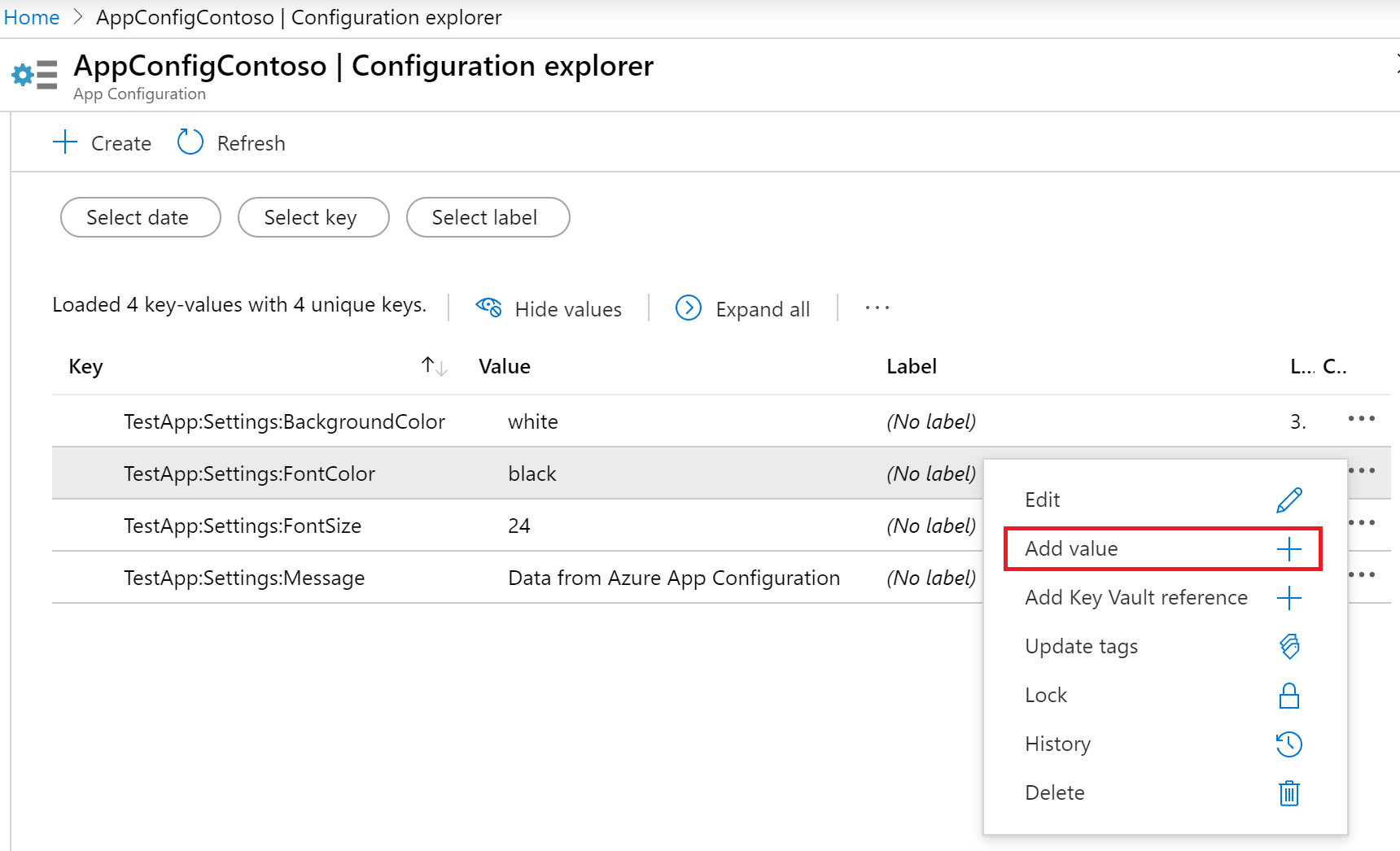
On the Add Value screen, enter a Value of red and a Label of Development. Leave Content type empty. Select Apply.
Load configuration values with a specified label
By default, Azure App Configuration only loads configuration values with no label. If you've defined labels for your configuration values, you'll want to specify the labels to use when connecting to App Configuration.
In the previous section, you created a different configuration value for the development environment. You use the HostingEnvironment.EnvironmentName variable to dynamically determine which environment the app currently runs in. To learn more, see Use multiple environments in ASP.NET Core.
Add a reference to the Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.AzureAppConfiguration namespace in order to access the KeyFilter and LabelFilter classes.
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.AzureAppConfiguration;
Load configuration values with the label corresponding to the current environment by passing the environment name into the Select method:
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Configuration.AddAzureAppConfiguration(options =>
{
options.Connect(builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("AppConfig"))
// Load configuration values with no label
.Select(KeyFilter.Any, LabelFilter.Null)
// Override with any configuration values specific to current hosting env
.Select(KeyFilter.Any, builder.Environment.EnvironmentName);
});
Important
The preceding code snippet uses the Secret Manager tool to load App Configuration connection string. For information storing the connection string using the Secret Manager, see Quickstart for Azure App Configuration with ASP.NET Core.
The Select method is called twice. The first time, it loads configuration values with no label. Then, it loads configuration values with the label corresponding to the current environment. These environment-specific values override any corresponding values with no label. You don't need to define environment-specific values for every key. If a key doesn't have a value with a label corresponding to the current environment, it uses the value with no label.
Test in different environments
Open the launchSettings.json file under the Properties directory. Find the config entry under profiles. In the environmentVariables section, set the ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT variable to Production.
With the new values set, build and run your application.
dotnet build
dotnet run
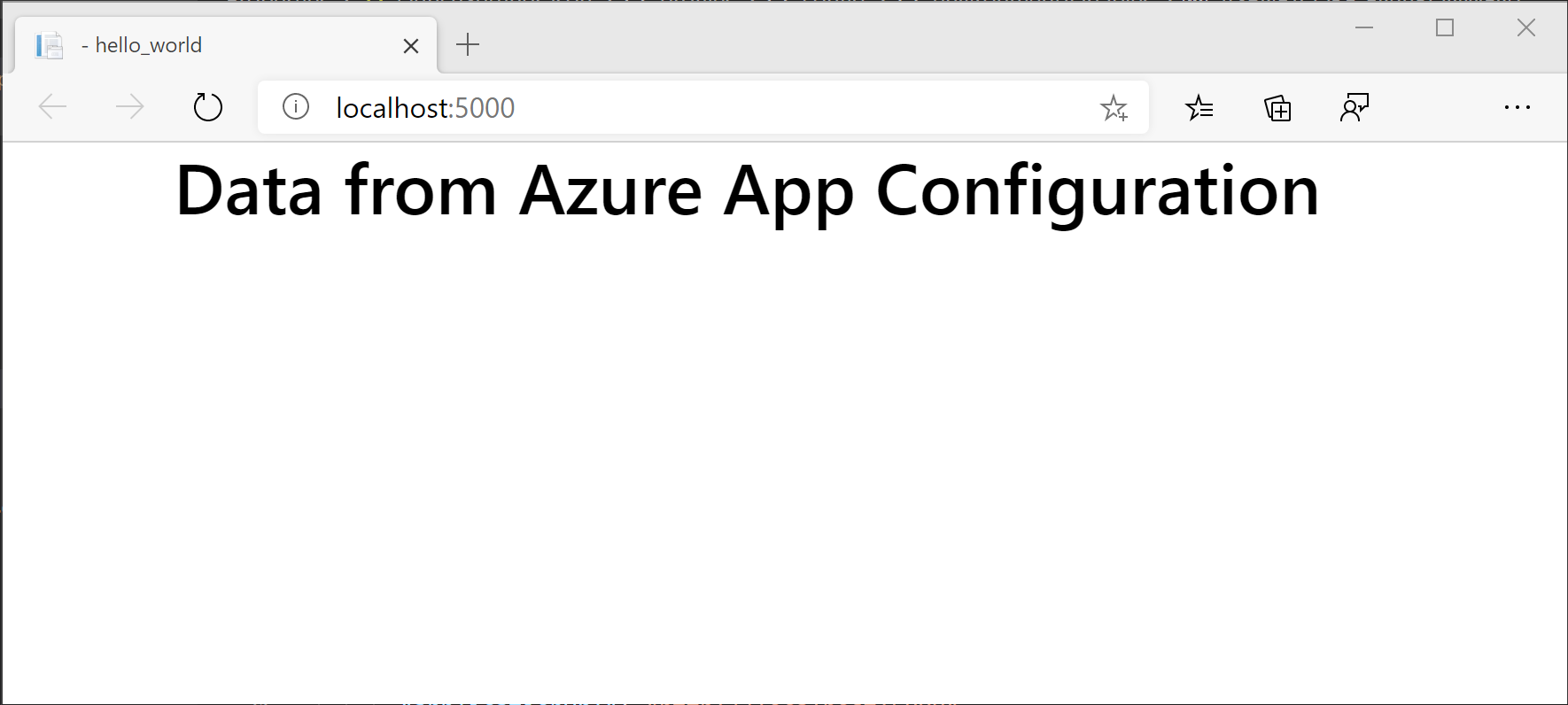
Use a web browser to go to http://localhost:5000. You'll notice that the font color is black.
Update launchSettings.json to set the ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT variable to Development. Run dotnet run again.
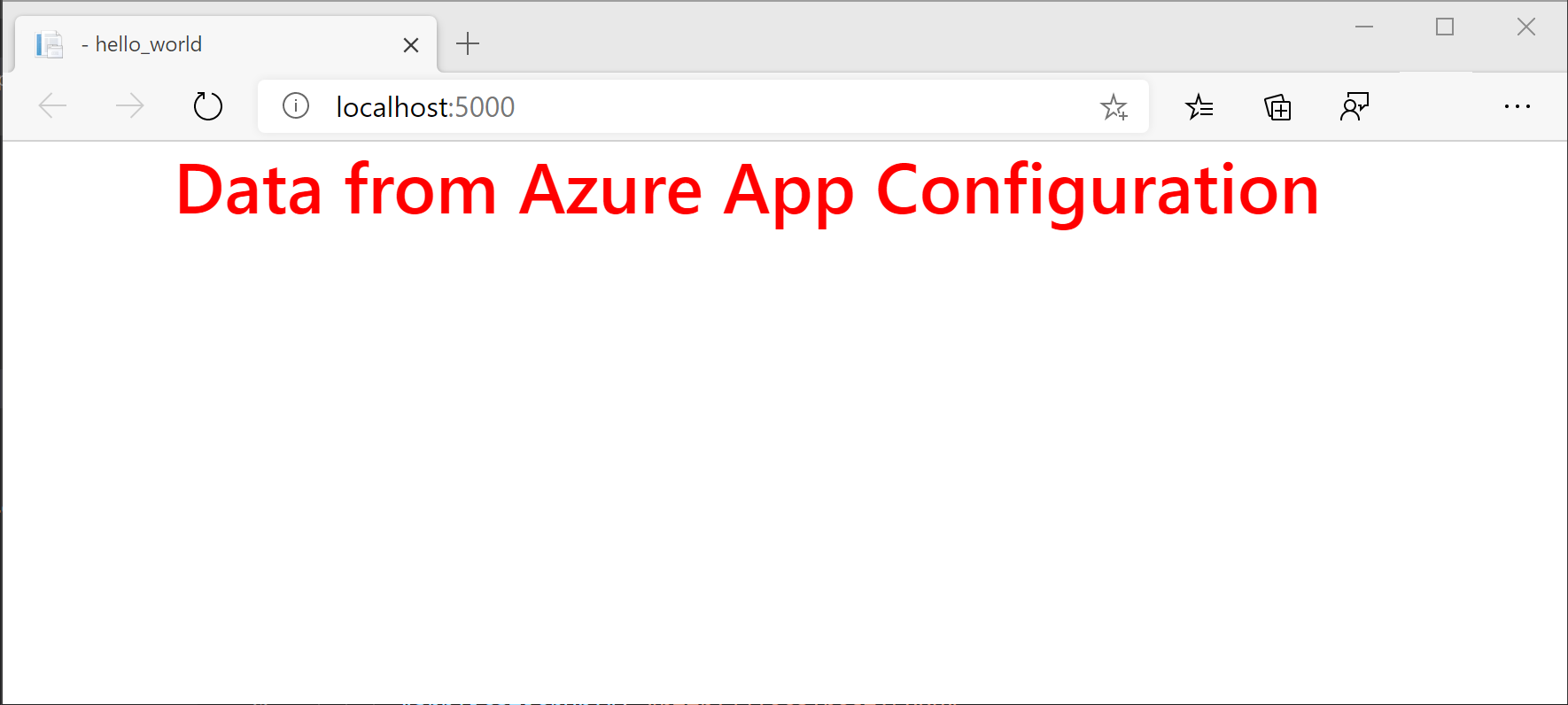
You'll notice that the font color is now red. This is because the application now uses the value of TestApp:Settings:FontColor that has the Development label. All other configuration values remain the same as their production values.
Next steps
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for