How to register an Azure confidential ledger application with Microsoft Entra ID
In this article you'll learn how to integrate your Azure confidential ledger application with Microsoft Entra ID, by registering it with the Microsoft identity platform.
The Microsoft identity platform performs identity and access management (IAM) only for registered applications. Whether it's a client application like a web or mobile app, or it's a web API that backs a client app, registering it establishes a trust relationship between your application and the identity provider, the Microsoft identity platform. Learn more about the Microsoft identity platform.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription and permission to manage applications in Microsoft Entra ID. Create an account for free.
- A Microsoft Entra tenant. Learn how to set up a tenant.
- An application that calls Azure confidential ledger.
Register an application
Registering your Azure confidential ledger application establishes a trust relationship between your app and the Microsoft identity platform. The trust is unidirectional: your app trusts the Microsoft identity platform, and not the other way around.
Follow these steps to create the app registration:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
If you have access to multiple tenants, use the Directories + subscriptions filter in the top menu to switch to the tenant in which you want to register the application.
Search for and select Microsoft Entra ID.
Under Manage, select App registrations > New registration.
Enter a display Name for your application. Users of your application might see the display name when they use the app, for example during sign-in. You can change the display name at any time and multiple app registrations can share the same name. The app registration's automatically generated Application (client) ID, not its display name, uniquely identifies your app within the identity platform.
Specify who can use the application, sometimes called its sign-in audience.
Supported account types Description Accounts in this organizational directory only Select this option if you're building an application for use only by users (or guests) in your tenant.
Often called a line-of-business (LOB) application, this app is a single-tenant application in the Microsoft identity platform.Accounts in any organizational directory Select this option if you want users in any Microsoft Entra tenant to be able to use your application. This option is appropriate if, for example, you're building a software-as-a-service (SaaS) application that you intend to provide to multiple organizations.
This type of app is known as a multitenant application in the Microsoft identity platform.Accounts in any organizational directory and personal Microsoft accounts Select this option to target the widest set of customers.
By selecting this option, you're registering a multitenant application that can also support users who have personal Microsoft accounts.Personal Microsoft accounts Select this option if you're building an application only for users who have personal Microsoft accounts. Personal Microsoft accounts include Skype, Xbox, Live, and Hotmail accounts. Don't enter anything for Redirect URI (optional). You'll configure a redirect URI in the next section.
Select Register to complete the initial app registration.
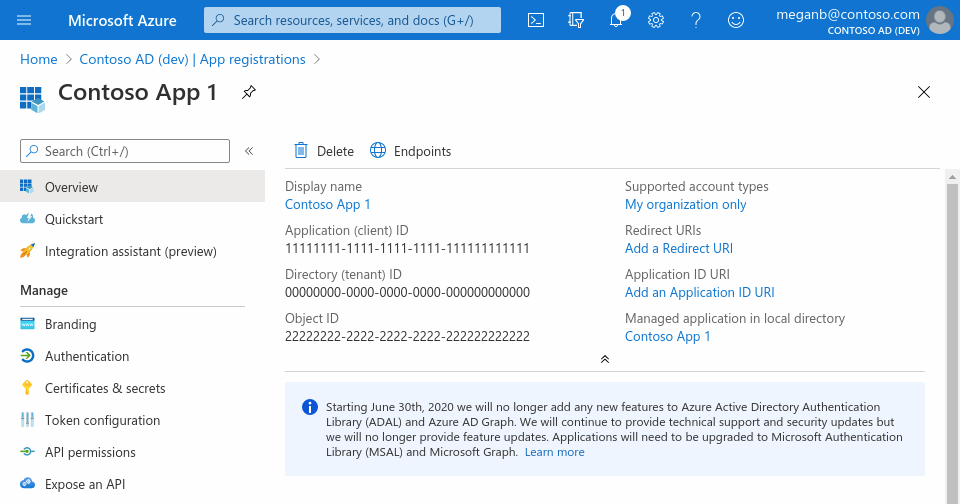
When registration finishes, the Azure portal displays the app registration's Overview pane. You see the Application (client) ID. Also called the client ID, this value uniquely identifies your application in the Microsoft identity platform.
Important
New app registrations are hidden to users by default. When you are ready for users to see the app on their My Apps page you can enable it. To enable the app, in the Azure portal navigate to Microsoft Entra ID > Enterprise applications and select the app. Then on the Properties page toggle Visible to users? to Yes.
Your application's code, or more typically an authentication library used in your application, also uses the client ID. The ID is used as part of validating the security tokens it receives from the identity platform.
Add a redirect URI
A redirect URI is the location where the Microsoft identity platform redirects a user's client and sends security tokens after authentication.
In a production web application, for example, the redirect URI is often a public endpoint where your app is running, like https://contoso.com/auth-response. During development, it's common to also add the endpoint where you run your app locally, like https://127.0.0.1/auth-response or http://localhost/auth-response.
You add and modify redirect URIs for your registered applications by configuring their platform settings.
Configure platform settings
Settings for each application type, including redirect URIs, are configured in Platform configurations in the Azure portal. Some platforms, like Web and Single-page applications, require you to manually specify a redirect URI. For other platforms, like mobile and desktop, you can select from redirect URIs generated for you when you configure their other settings.
To configure application settings based on the platform or device you're targeting, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, in App registrations, select your application.
Under Manage, select Authentication.
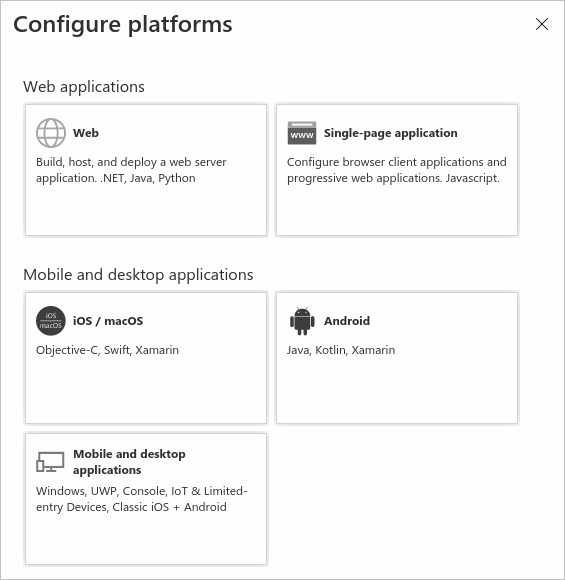
Under Platform configurations, select Add a platform.
Under Configure platforms, select the tile for your application type (platform) to configure its settings.
Platform Configuration settings Web Enter a Redirect URI for your app. This URI is the location where the Microsoft identity platform redirects a user's client and sends security tokens after authentication.
Select this platform for standard web applications that run on a server.Single-page application Enter a Redirect URI for your app. This URI is the location where the Microsoft identity platform redirects a user's client and sends security tokens after authentication.
Select this platform if you're building a client-side web app by using JavaScript or a framework like Angular, Vue.js, React.js, or Blazor WebAssembly.iOS / macOS Enter the app Bundle ID. Find it in Build Settings or in Xcode in Info.plist.
A redirect URI is generated for you when you specify a Bundle ID.Android Enter the app Package name. Find it in the AndroidManifest.xml file. Also generate and enter the Signature hash.
A redirect URI is generated for you when you specify these settings.Mobile and desktop applications Select one of the Suggested redirect URIs. Or specify a Custom redirect URI.
For desktop applications using embedded browser, we recommendhttps://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient
For desktop applications using system browser, we recommendhttp://localhost
Select this platform for mobile applications that aren't using the latest Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) or aren't using a broker. Also select this platform for desktop applications.Select Configure to complete the platform configuration.
Redirect URI restrictions
There are some restrictions on the format of the redirect URIs you add to an app registration. For details about these restrictions, see Redirect URI (reply URL) restrictions and limitations.
Add credentials
Credentials are used by confidential client applications that access a web API. Examples of confidential clients are web apps, other web APIs, or service-type and daemon-type applications. Credentials allow your application to authenticate as itself, requiring no interaction from a user at runtime.
You can add both certificates and client secrets (a string) as credentials to your confidential client app registration.
Add a certificate
Sometimes called a public key, a certificate is the recommended credential type because they're considered more secure than client secrets. For more information about using a certificate as an authentication method in your application, see Microsoft identity platform application authentication certificate credentials.
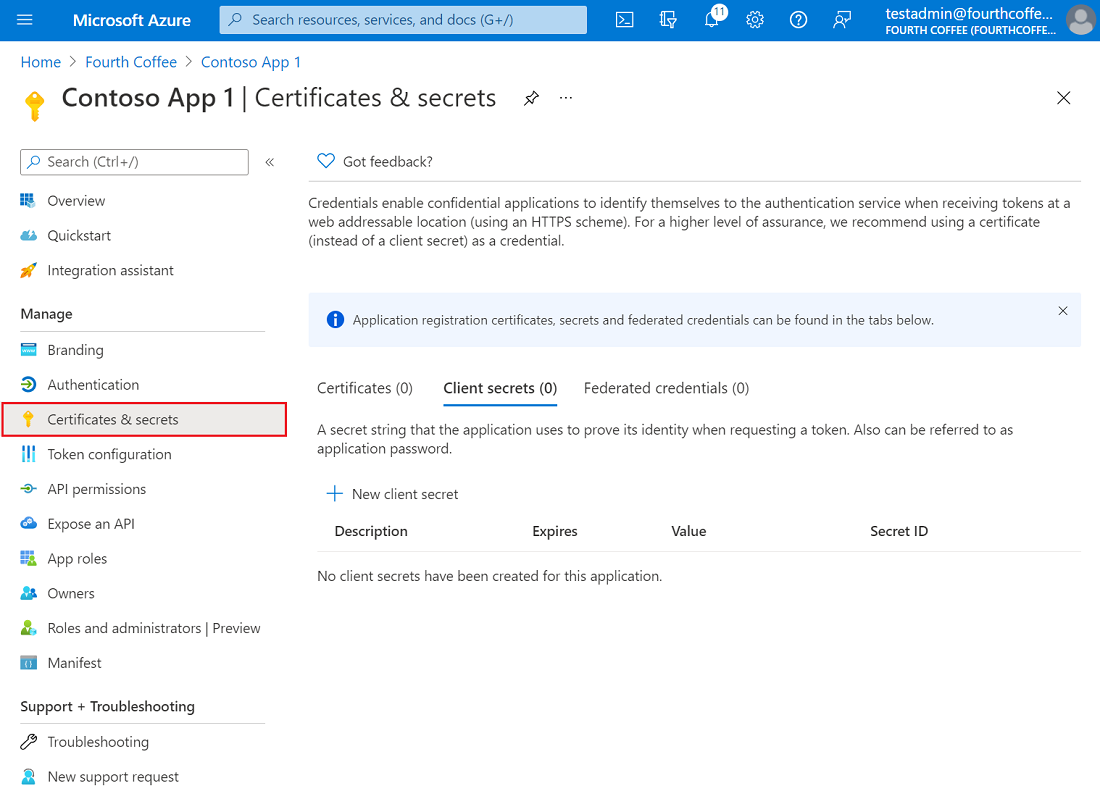
- In the Azure portal, in App registrations, select your application.
- Select Certificates & secrets > Certificates > Upload certificate.
- Select the file you want to upload. It must be one of the following file types: .cer, .pem, .crt.
- Select Add.
Add a client secret
Sometimes called an application password, a client secret is a string value your app can use in place of a certificate to identity itself.
Client secrets are considered less secure than certificate credentials. Application developers sometimes use client secrets during local app development because of their ease of use. However, you should use certificate credentials for any of your applications that are running in production.
- In the Azure portal, in App registrations, select your application.
- Select Certificates & secrets > Client secrets > New client secret.
- Add a description for your client secret.
- Select an expiration for the secret or specify a custom lifetime.
- Client secret lifetime is limited to two years (24 months) or less. You can't specify a custom lifetime longer than 24 months.
- Microsoft recommends that you set an expiration value of less than 12 months.
- Select Add.
- Record the secret's value for use in your client application code. This secret value is never displayed again after you leave this page.
For application security recommendations, see Microsoft identity platform best practices and recommendations.
Next steps
- Azure confidential ledger authentication with Microsoft Entra ID
- Overview of Microsoft Azure confidential ledger
- Integrating applications with Microsoft Entra ID
- Use portal to create a Microsoft Entra application and service principal that can access resources
- Create an Azure service principal with the Azure CLI.
- Authenticating Azure confidential ledger nodes
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for