Data encryption in Azure Cosmos DB
APPLIES TO:
NoSQL
MongoDB
Cassandra
Gremlin
Table
"Encryption at rest" is a phrase that commonly refers to the encryption of data on nonvolatile storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSDs) and hard-disk drives (HDDs). Azure Cosmos DB stores its primary databases on SSDs. Its media attachments and backups are stored in Azure Blob Storage, which are generally backed up by HDDs. With the release of encryption at rest for Azure Cosmos DB, all your databases, media attachments, and backups are encrypted. Your data is now encrypted in transit (over the network) and at rest (nonvolatile storage), giving you end-to-end encryption.
As a platform as a service (PaaS), Azure Cosmos DB is easy to use. Because all user data stored in Azure Cosmos DB is encrypted at rest and in transport, you don't have to take any action. In other words, encryption at rest is "on" by default. There are no controls to turn it off or on. Azure Cosmos DB uses AES-256 encryption on all regions where the account is running.
We provide this feature while we continue to meet our availability and performance service-level agreements (SLAs). Data stored in your Azure Cosmos DB account is automatically and seamlessly encrypted with keys managed by Microsoft (service-managed keys). Optionally, you can choose to add a second layer of encryption with your own keys as described in the customer-managed keys article.
Implementation of encryption at rest for Azure Cosmos DB
Encryption at rest is implemented by using several security technologies, including secure key storage systems, encrypted networks, and cryptographic APIs. Systems that decrypt and process data have to communicate with systems that manage keys. The diagram shows how storage of encrypted data and the management of keys is separated.
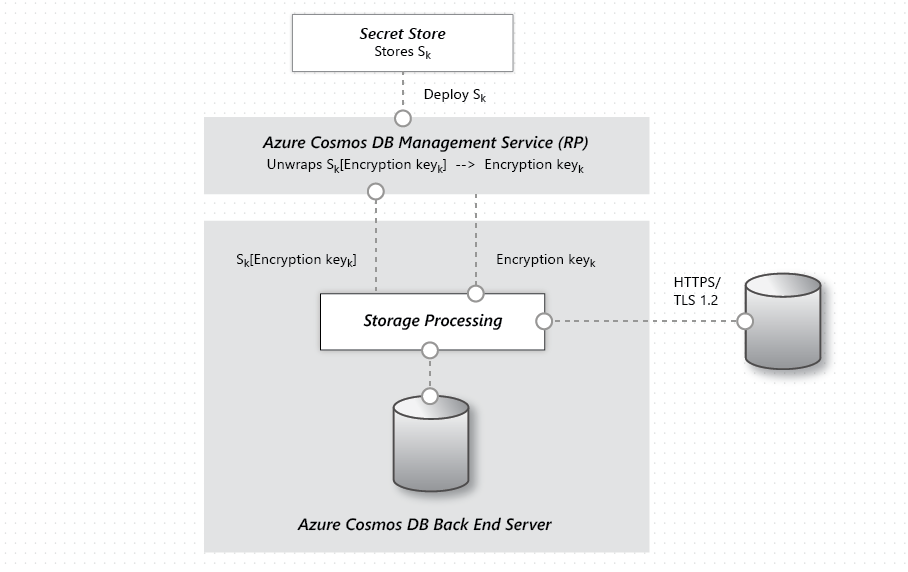
The basic flow of a user request is:
- The user database account is made ready, and storage keys are retrieved via a request to the Management Service Resource Provider.
- A user creates a connection to Azure Cosmos DB via HTTPS/secure transport. (The SDKs abstract the details.)
- The user sends a JSON document to be stored over the previously created secure connection.
- The JSON document is indexed unless the user has turned off indexing.
- Both the JSON document and index data are written to secure storage.
- Periodically, data is read from the secure storage and backed up to the Azure Encrypted Blob Store.
Frequently asked questions
Find answers to commonly asked questions about encryption.
How much more does Azure Storage cost if Storage Service Encryption is enabled?
There's no extra cost.
Who manages the encryption keys?
Data stored in your Azure Cosmos DB account is automatically and seamlessly encrypted with keys managed by Microsoft by using service-managed keys. Optionally, you can choose to add a second layer of encryption with keys you manage by using customer-managed keys.
How often are encryption keys rotated?
Microsoft has a set of internal guidelines for encryption key rotation, which Azure Cosmos DB follows. The specific guidelines aren't published. Microsoft does publish the Security Development Lifecycle, which is seen as a subset of internal guidance and has useful best practices for developers.
Can I use my own encryption keys?
Yes, this feature is available for new Azure Cosmos DB accounts. It should be deployed at the time of account creation. For more information, see the customer-managed keys document.
Warning
The following field names are reserved on Cassandra API tables in accounts by using customer-managed keys:
idttl_ts_etag_rid_self_attachments_epk
When customer-managed keys aren't enabled, only field names beginning with __sys_ are reserved.
What regions have encryption turned on?
All Azure Cosmos DB regions have encryption turned on for all user data.
Does encryption affect the performance latency and throughput SLAs?
There's no effect or changes to the performance SLAs because encryption at rest is now enabled for all existing and new accounts. To see the latest guarantees, see SLA for Azure Cosmos DB.
Does the local emulator support encryption at rest?
The emulator is a standalone dev/test tool and doesn't use the key management services that the managed Azure Cosmos DB service uses. We recommend that you enable BitLocker on drives where you're storing sensitive emulator test data. The emulator supports changing the default data directory and using a well-known location.
Next steps
- To learn more about adding a second layer of encryption with your own keys, see the customer-managed keys article.
- For an overview of Azure Cosmos DB security and the latest improvements, see Azure Cosmos DB database security.
- For more information about Microsoft certifications, see the Azure Trust Center.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for