SQL warehouse admin settings
This article explains the SQL warehouse settings and access controls available to workspace admins.
Databricks recommends retaining the default settings for all workspace-level configurations for SQL warehouses. These settings assume that workspace admins are responsible for creating and configuring all SQL warehouses and that you use Unity Catalog for data governance.
Workspace administrators can configure the following permissions for an Azure Databricks workspace:
- Revoke all access to SQL warehouses.
- Grant the ability to create SQL warehouses.
- Configure default parameters that control the SQL warehouse compute environment.
- Configure data access policies for SQL warehouses.
Note
By default, all users have access to Databricks SQL. To onboard users to Databricks SQL, you should deploy a SQL warehouse, grant users access to the SQL warehouse, and grant access to data using Unity Catalog.
By default, new workspaces have serverless SQL warehouses enabled in supported regions. See Enable serverless SQL warehouses.
Revoke access to SQL warehouses
You can revoke access to SQL warehouses for a user, service principal, or group by unassigning the Databricks SQL access entitlement. See Manage entitlements.
Grant SQL warehouse creation privileges
You can grant SQL warehouse creation privileges to a user, service principal, or group by assigning the Allow unrestricted cluster creation entitlement. See Manage entitlements.
Configure SQL parameters
To configure all warehouses with SQL parameters:
Click your username in the top bar of the workspace and select Admin Settings from the drop down.
Click Manage next to SQL warehouses.
In the SQL Configuration Parameters textbox, specify one key-value pair per line. Separate the name of the parameter from its value using a space. For example, to enable
ANSI_MODE: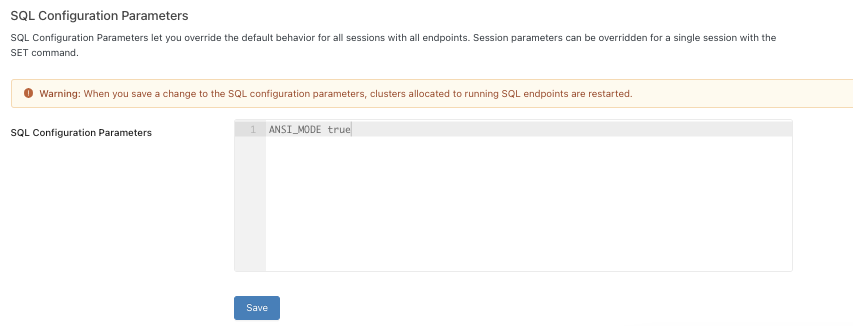
For a list of all parameters that are supported at the global scope, see Configuration parameters.
Click Save.
Important
When you change a SQL configuration parameter, all running SQL warehouses are automatically restarted.
For a general overview of the available SQL configuration parameters, see Configuration parameters.
To configure all SQL warehouses using the REST API, see SQL Warehouses API.
Configure data access policies for SQL warehouses
Databricks recommends managing data access policies using Unity Catalog.
Some data sources might require additional privileges. See Enable data access configuration.
Note
When you configure data access policies other than Unity Catalog, legacy table ACLs also apply. See Enable Hive metastore table access control on a cluster (legacy).
Transfer ownership of a SQL warehouse
The user you transfer ownership of a SQL warehouse to must have the Allow unrestricted cluster creation entitlement.
- As a workspace admin, log in to your Azure Databricks workspace.
- Click SQL Warehouses in the sidebar.
- In a warehouse row, click the
 kebab menu at the far right and select Permissions. The SQL warehouse permissions display.
kebab menu at the far right and select Permissions. The SQL warehouse permissions display. - Click on the gear icon at the top right and click Assign new owner.
- Select the user to assign ownership to. Service principals and groups cannot be assigned ownership of a SQL warehouse.
- Click Confirm.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for