Publish NuGet packages with Azure Pipelines (YAML/Classic)
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
In Azure Pipelines, you can use the classic editor or the YAML tasks to publish your NuGet packages within your pipeline, to your Azure Artifacts feed, or to public registries such as nuget.org.
Create a NuGet package
There are various ways to create your NuGet packages such as using Visual Studio to pack your NuGet packages. If you're already using MSBuild or some other task to create your packages, skip this section and jump to the publish NuGet packages section.
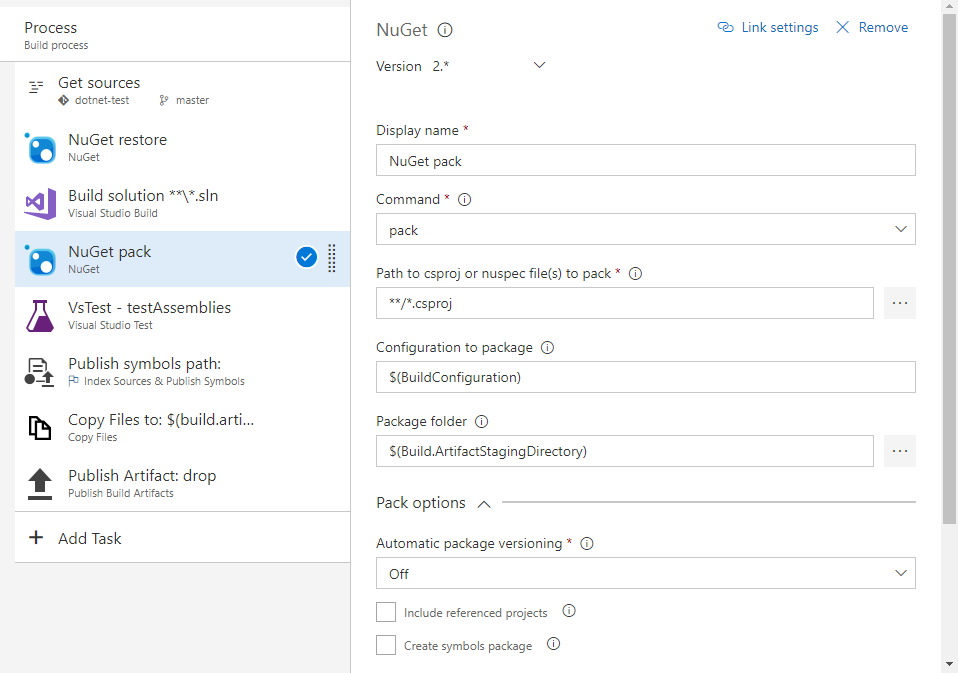
To create a NuGet package, add the following snippet to your pipeline YAML file. For more information, see NuGet task.
- task: NuGetCommand@2
inputs:
command: pack
packagesToPack: '**/*.csproj'
packDestination: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)'
- packagesToPack: pattern to search for csproj directories to pack
- packDestination: directory where packages are created
Package versioning
NuGet packages are distinguished by their names and version numbers. Employing Semantic Versioning is a recommended strategy for effectively managing package versions. Semantic versions consist of three numeric components: Major, Minor, and Patch.
The Patch is incremented after fixing a bug. When you release a new backward-compatible feature, you increment the Minor version and reset the Patch version to 0. When you make a backward-incompatible change, you increment the Major version and reset the Minor and Patch versions to 0.
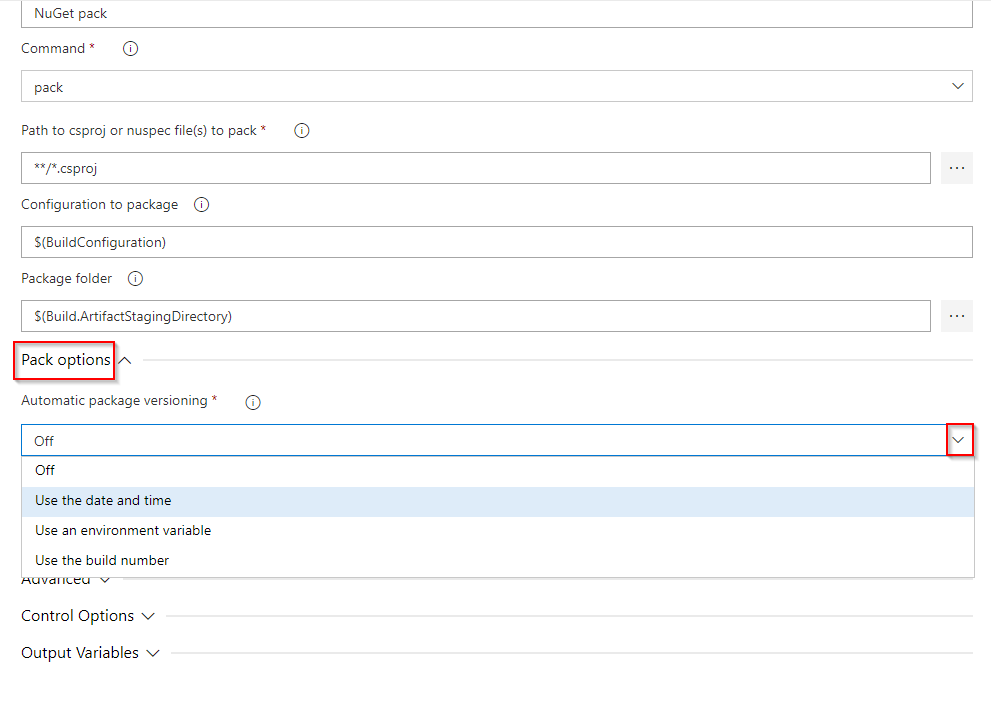
With Semantic Versioning, you can also use prerelease labels to tag your packages. To do so, enter a hyphen followed by your prerelease tag: E.g.1.0.0-beta. Semantic Versioning is supported in Azure Pipelines and can be configured in your NuGet task as follows:
Use the date and time (Classic): byPrereleaseNumber (YAML). Your package version is in the format: Major.Minor.Patch-ci-datetime where you have the flexibility to choose the values of your Major, Minor, and Patch.
Use an environment variable (Classic): byEnvVar (YAML). Your package version is set to the value of the environment variable you specify.
Use the build number (Classic): byBuildNumber (YAML). Your package version is set to the build number. Make sure you set your build number format under your pipeline Options to
$(BuildDefinitionName)_$(Year:yyyy).$(Month).$(DayOfMonth)$(Rev:.r). To do set the format in YAML, add a propertyname:at the root of your pipeline and add your format.
The following example shows how to use the date and time versioning option to generate a SemVer compliant version formatted as: Major.Minor.Patch-ci-datetime.
variables:
Major: '1'
Minor: '0'
Patch: '0'
steps:
- task: NuGetCommand@2
inputs:
command: pack
versioningScheme: byPrereleaseNumber
majorVersion: '$(Major)'
minorVersion: '$(Minor)'
patchVersion: '$(Patch)'
Note
DotNetCore and DotNetStandard packages should be packaged with the DotNetCoreCLI@2 task to avoid System.InvalidCastExceptions. For more information, see .NET Core CLI task.
task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
inputs:
command: pack
versioningScheme: byPrereleaseNumber
majorVersion: '$(Major)'
minorVersion: '$(Minor)'
patchVersion: '$(Patch)'
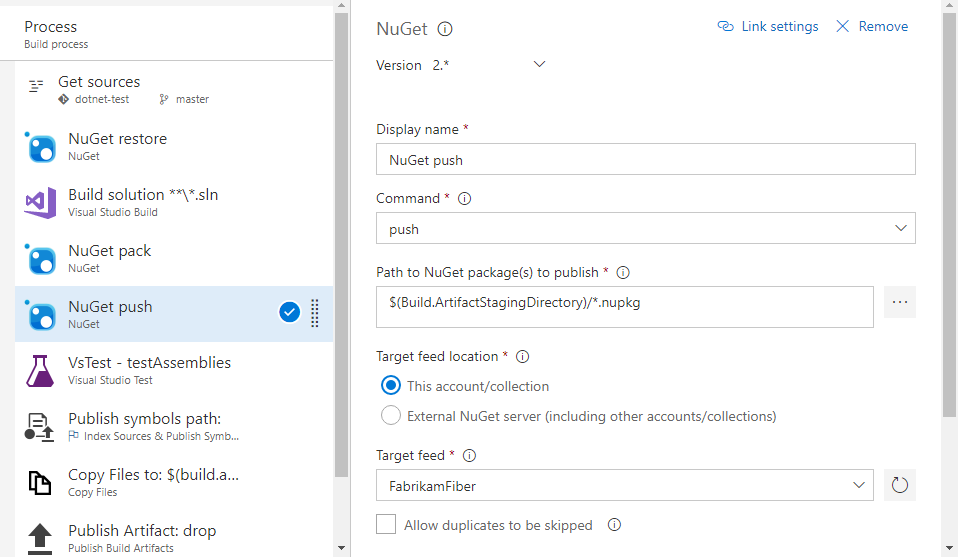
Publish NuGet packages
To publish packages to an Azure Artifacts feed from your pipeline, the pipeline identity must have the Feed Publisher (Contributor) role on the feed. For more information, see Pipelines permissions.
steps:
- task: NuGetAuthenticate@1
displayName: 'NuGet Authenticate'
- task: NuGetCommand@2
displayName: 'NuGet push'
inputs:
command: push
publishVstsFeed: '<projectName>/<feed>'
allowPackageConflicts: true
To publish a package to an external NuGet feed, you must first create a service connection to connect to that feed. To create a service connection:
- Go to Project settings > Service connections > New service connection.
- Select NuGet, and then select Next.
- Fill out the form and then select Save when you're done.
For more information, see Manage service connections.
Note
The NuGetAuthenticate@1 task supports a service connection using basic authenication. The task doesn't support NuGet API key authentication. If your service connection uses ApiKey, you must use the NuGetCommand@2 task and specify the NuGet API key in the arguments field. For more information, see NuGet task.
To publish a package to an external NuGet feed, add the following snippet to your YAML pipeline.
Using the Command line task (with NuGet.exe):
- task: NuGetAuthenticate@1
inputs:
nuGetServiceConnections: <NAME_OF_YOUR_SERVICE_CONNECTION>
- script: |
nuget push <PACKAGE_PATH> -src https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/<ORGANIZATION_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/_packaging/<FEED_NAME>/nuget/v3/index.json -ApiKey <ANY_STRING>
displayName: "Push"
Using the Command line task (with dotnet):
- task: NuGetAuthenticate@1
inputs:
nuGetServiceConnections: <NAME_OF_YOUR_SERVICE_CONNECTION>
- script: |
dotnet build <CSPROJ_PATH> --configuration <CONFIGURATION>
dotnet pack <CSPROJ_PATH> -p:PackageVersion=<YOUR_PACKAGE_VERSION> --output <OUTPUT_DIRECTORY> --configuration <CONFIGURATION>
dotnet nuget push <PACKAGE_PATH> --source https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/<ORGANIZATION_NAME>/<PROJECT_NAME>/_packaging/<FEED_NAME>/nuget/v3/index.json --api-key <ANY_STRING>
displayName: "Build, pack and push"
Note
The ApiKey is required, but you can use any arbitrary value when pushing to Azure Artifacts feeds.
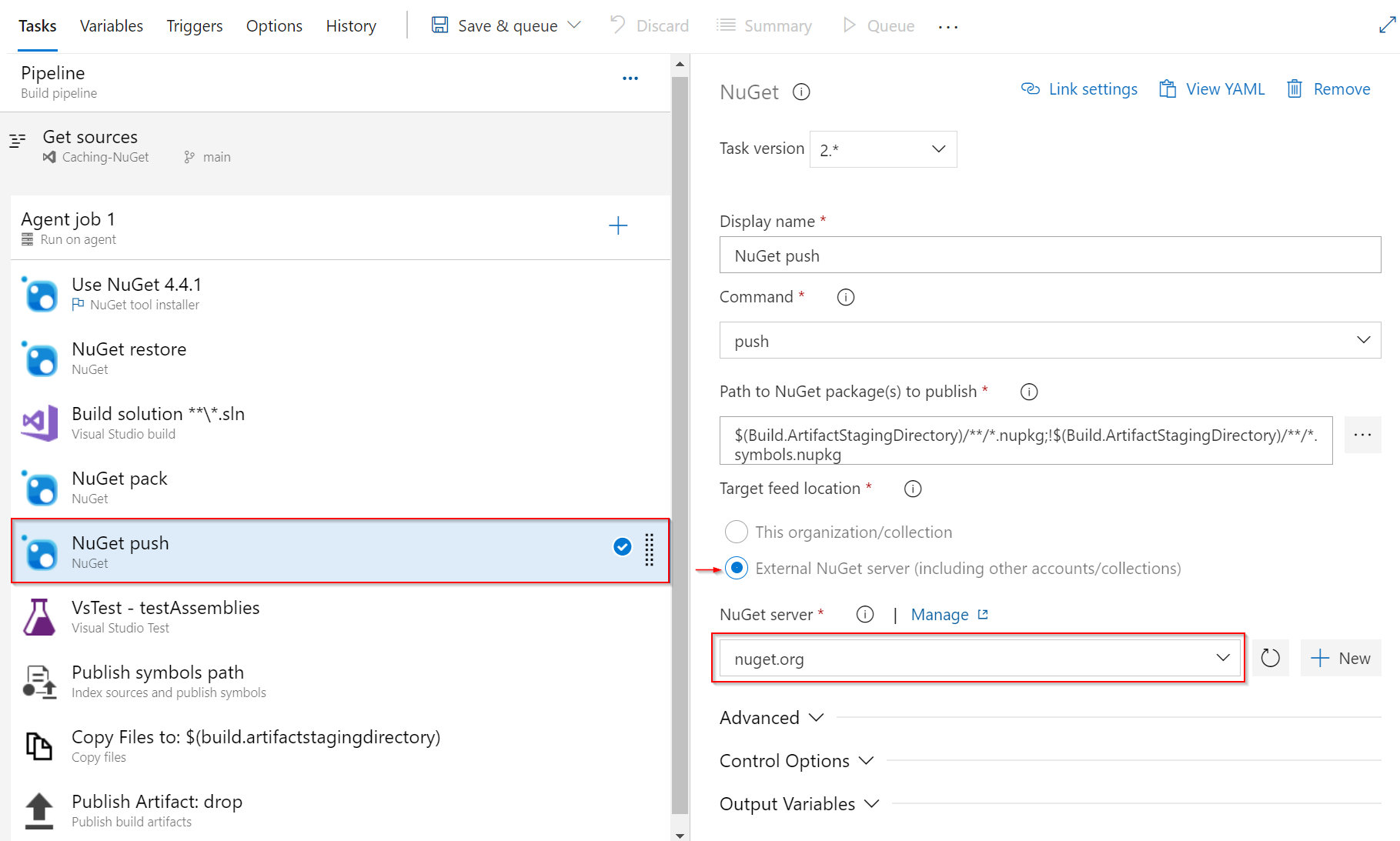
Publish to NuGet.org
Navigate to your Azure DevOps project and then select
 Project settings.
Project settings.Select Service Connections, and then select New service connection.
Select NuGet, and then select Next.
Select ApiKey as your authentication method. Use the following url for your Feed URL: https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json.
Enter the ApiKey you generated earlier, and then enter a Service connection name.
Select Grant access permission to all pipelines, and then select Save when you're done. To select this option, you need the service connection Administrator role.
Add the following YAML snippet to your pipeline definition:
steps:
- task: NuGetCommand@2
displayName: 'NuGet push'
inputs:
command: push
nuGetFeedType: external
publishFeedCredentials: nuget.org
Related articles
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for