Known issues/limitations with online migrations from PostgreSQL to Azure Database for PostgreSQL
Known issues and limitations associated with online migrations from PostgreSQL to Azure Database for PostgreSQL are described in the following sections.
Online migration configuration
The source PostgreSQL server must be running version 9.4, 9.5, 9.6, 10, or 11. For more information, see Supported PostgreSQL database versions.
Only migrations to the same or a higher version are supported. For example, migrating PostgreSQL 9.5 to Azure Database for PostgreSQL 9.6 or 10 is supported. Migrating from PostgreSQL 11 to PostgreSQL 9.6 isn't supported.
To enable logical replication in the source PostgreSQL postgresql.conf file, set the following parameters:
- wal_level: Set as logical.
- max_replication_slots: Set at least the maximum number of databases for migration. If you want to migrate four databases, set the value to at least 4.
- max_wal_senders: Set the number of databases running concurrently. The recommended value is 10.
Add DMS agent IP to the source PostgreSQL pg_hba.conf.
Make a note of the DMS IP address after you finish provisioning an instance of Azure Database Migration Service.
Add the IP address to the pg_hba.conf file:
host all 172.16.136.18/10 md5 host replication postgres 172.16.136.18/10 md5
The user must have the REPLICATION role on the server hosting the source database.
The source and target database schemas must match.
Size limitations
- You can migrate up to 1 TB of data from PostgreSQL to Azure Database for PostgreSQL, using a single DMS service.
- DMS allows the users to pick tables inside a database that they want to migrate.
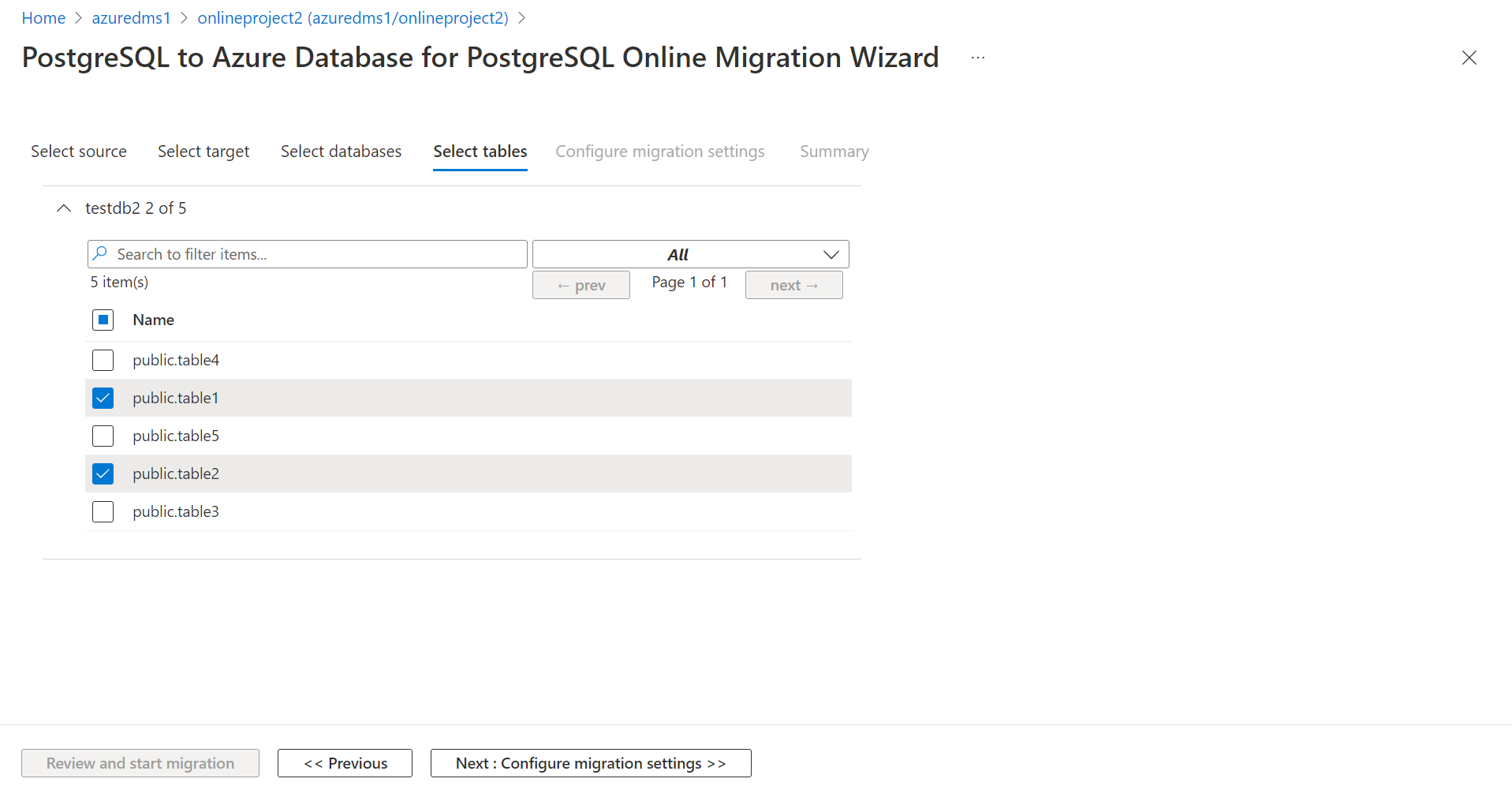
Behind the scenes, there is a pg_dump command that is used to take the dump of the selected tables using one of the following options:
- -T to include the table names picked in the UI
- -t to exclude the table names not picked by the user
There is a max limit of 7500 characters that can be included as part of the pg_dump command following the -t or -T option. The pg_dump command uses the count of the characters for selected or unselected tables , whichever is lower. If the count of characters for the selected and unselected tables exceed 7500, the pg_dump command fails with an error.
For the previous example, the pg_dump command would be:
pg_dump -h hostname -u username -d databasename -T "\"public\".\"table_1\"" -T "\"public\".\"table_2\""
In the previous command, the number of characters is 55 (includes double quotes, spaces, -T and slash)
Datatype limitations
Limitation: If there's no primary key on tables, changes might not be synced to the target database.
Workaround: Temporarily set a primary key for the table for migration to continue. Remove the primary key after data migration is finished.
Limitations with online migration from AWS RDS PostgreSQL
When you try to perform an online migration from Amazon Web Service (AWS) Relational Database (RDS) PostgreSQL to Azure Database for PostgreSQL, you might encounter the following errors:
Error: The default value of column '{column}' in table '{table}' in database '{database}' is different on source and target servers. It's '{value on source}' on source and '{value on target}' on target.
Limitation: This error occurs when the default value on a column schema differs between the source and target databases.
Workaround: Ensure that the schema on the target matches the schema on the source. For more information on migrating the schema, see the Azure Database for PostgreSQL online migration documentation.
Error: Target database '{database}' has '{number of tables}' tables whereas source database '{database}' has '{number of tables}' tables. The number of tables on source and target databases should match.
Limitation: This error occurs when the number of tables differs between the source and target databases.
Workaround: Ensure that the schema on the target matches the schema on the source. For more information on migrating the schema, see the Azure Database for PostgreSQL online migration documentation.
Error: The source database {database} is empty.
Limitation: This error occurs when the source database is empty. You probably selected the wrong database as the source.
Workaround: Double-check the source database you selected for migration, and then try again.
Error: The target database {database} is empty. Migrate the schema.
Limitation: This error occurs when there's no schema on the target database. Make sure the schema on the target matches the schema on the source.
Workaround: Ensure that the schema on the target matches the schema on the source. For more information on migrating the schema, see the Azure Database for PostgreSQL online migration documentation.
Other limitations
- The database name can't include a semicolon (;).
- A captured table must have a primary key. If a table doesn't have a primary key, the result of DELETE and UPDATE record operations will be unpredictable.
- Updating a primary key segment is ignored. Applying such an update will be identified by the target as an update that didn't update any rows. The result is a record written to the exceptions table.
- If your table has a JSON column, any DELETE or UPDATE operations on this table can lead to a failed migration.
- Migration of multiple tables with the same name but a different case might cause unpredictable behavior and isn't supported. An example is the use of table1, TABLE1, and Table1.
- Change processing of [CREATE | ALTER | DROP | TRUNCATE] table DDLs isn't supported.
- In Database Migration Service, a single migration activity can only accommodate up to four databases.
- Migration of the pg_largeobject table isn't supported.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for