How to use the IoT Central REST API to control devices
The IoT Central REST API lets you develop client applications that integrate with IoT Central applications. You can use the REST API to control devices in your IoT Central application. The REST API lets you:
- Read the last known telemetry value from a device.
- Read property values from a device.
- Set writable properties on a device.
- Call commands on a device.
This article describes how to use the /devices/{device_id} API to control individual devices. You can also use jobs to control devices in bulk.
A device can group the properties, telemetry, and commands it supports into components and modules.
Every IoT Central REST API call requires an authorization header. To learn more, see How to authenticate and authorize IoT Central REST API calls.
For the reference documentation for the IoT Central REST API, see Azure IoT Central REST API reference.
Tip
You can use Postman to try out the REST API calls described in this article. Download the IoT Central Postman collection and import it into Postman. In the collection, you'll need to set variables such as your app subdomain and admin token.
To learn how to control devices by using the IoT Central UI, see
- Use properties in an Azure IoT Central solution.
- How to use commands in an Azure IoT Central solution().
Components and modules
Components let you group and reuse device capabilities. To learn more about components and device models, see the IoT Plug and Play modeling guide.
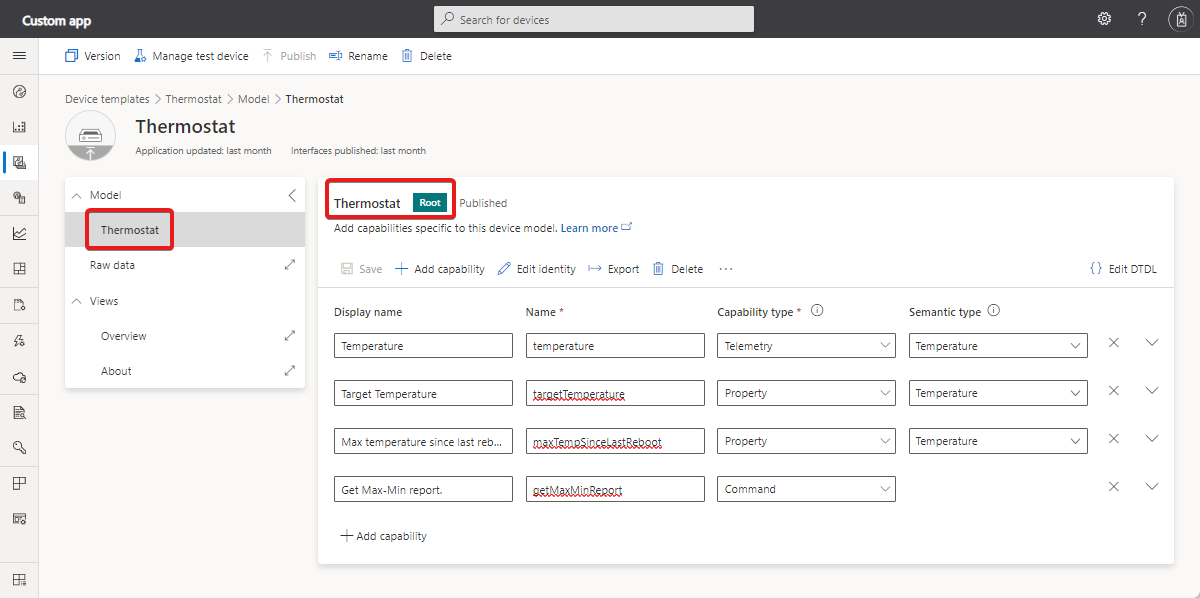
Not all device templates use components. The following screenshot shows the device template for a simple thermostat where all the capabilities are defined in a single interface called the Root component:
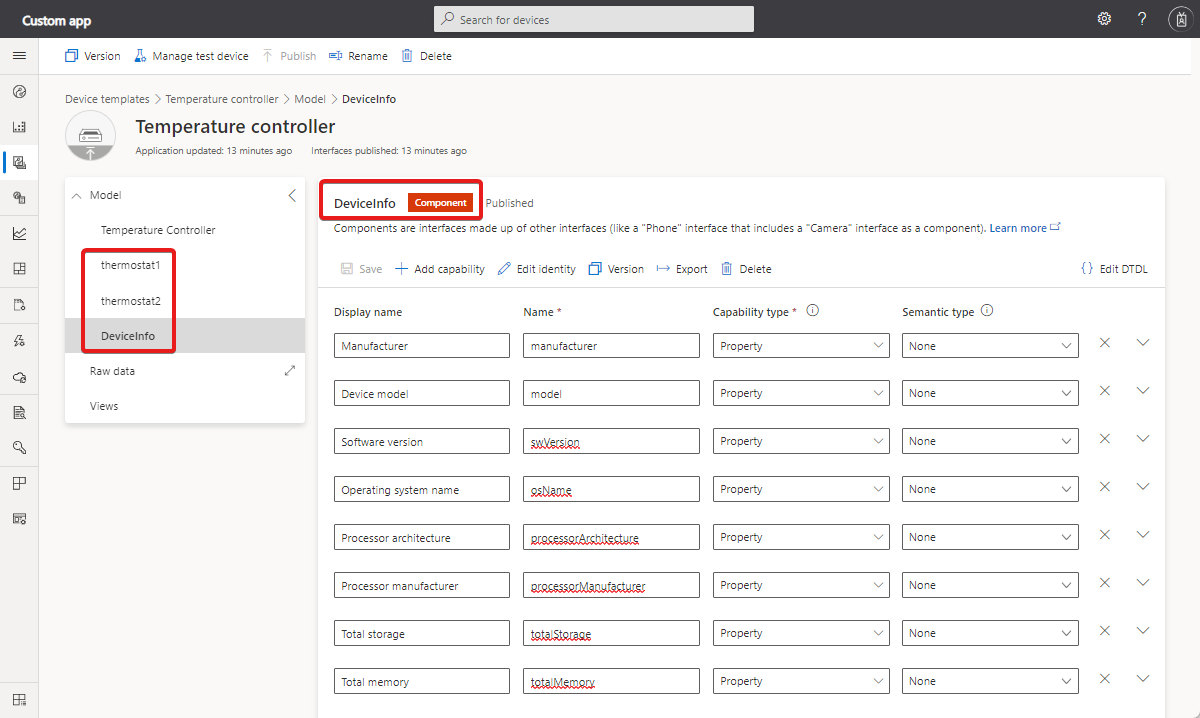
The following screenshot shows a temperature controller device template that uses components. The temperature controller has two thermostat components and a device information component:
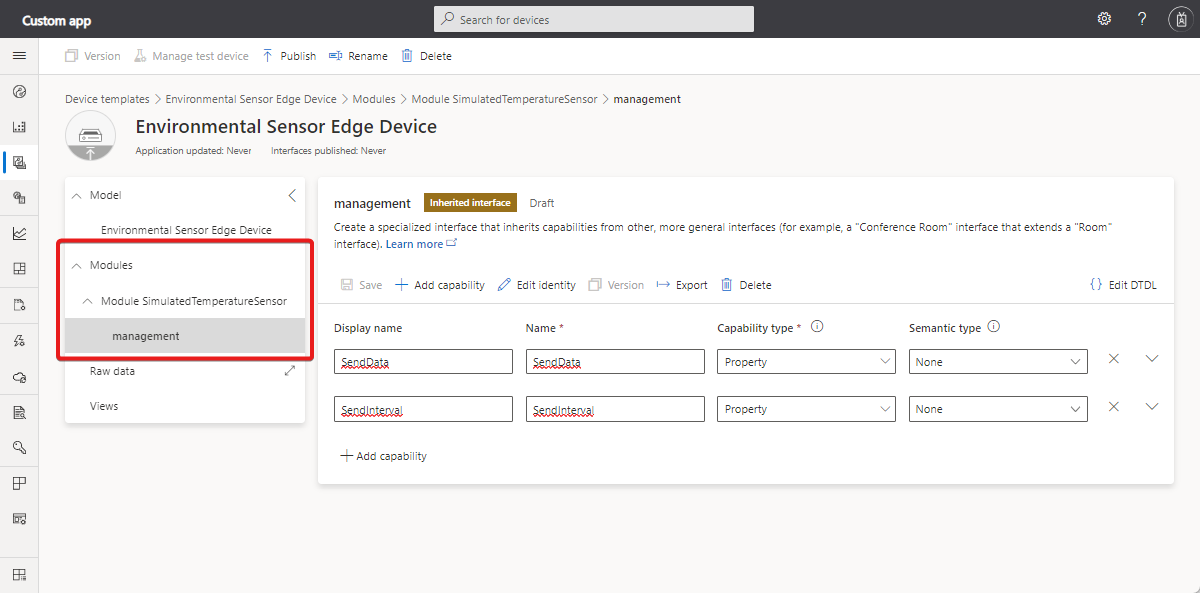
In IoT Central, a module refers to an IoT Edge module running on a connected IoT Edge device. A module can have a simple model such as the thermostat that doesn't use components. A module can also use components to organize a more complex set of capabilities. The following screenshot shows an example of a device template that uses modules. The environmental sensor device has a module called SimulatedTemperatureSensor and an inherited interface called management:
Get a device component
Use the following request to retrieve the components from a device called temperature-controller-01:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/temperature-controller-01/components?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example. The value array contains details of each device component:
{
"value": [
{
"@type": "Component",
"name": "thermostat1",
"displayName": "Thermostat One",
"description": "Thermostat One of Two."
},
{
"@type": "Component",
"name": "thermostat2",
"displayName": "Thermostat Two",
"description": "Thermostat Two of Two."
},
{
"@type": "Component",
"name": "deviceInformation",
"displayName": "Device Information interface",
"description": "Optional interface with basic device hardware information."
}
]
}
Get a device module
Use the following request to retrieve a list of modules running on a connected IoT Edge device called environmental-sensor-01:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/environmental-sensor-01/modules?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example. The array of modules only includes custom modules running on the IoT Edge device, not the built-in $edgeAgent and $edgeHub modules:
{
"value": [
{
"@type": [
"Relationship",
"EdgeModule"
],
"name": "SimulatedTemperatureSensor",
"displayName": "SimulatedTemperatureSensor"
}
]
}
Use the following request to retrieve a list of the components in a module called SimulatedTemperatureSensor:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/environmental-sensor-01/modules?api-version=2022-07-31
Read telemetry
Use the following request to retrieve the last known telemetry value from a device that doesn't use components. In this example, the device is called thermostat-01 and the telemetry is called temperature:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/thermostat-01/telemetry/temperature?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"timestamp": "2021-03-24T12:33:15.223Z",
"value": 40.10993804456927
}
Use the following request to retrieve the last known telemetry value from a device that does use components. In this example, the device is called temperature-controller-01, the component is called thermostat2, and the telemetry is called temperature:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/temperature-controller-01/components/thermostat2/telemetry/temperature?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"timestamp": "2021-03-24T12:43:44.968Z",
"value": 70.29168040339141
}
If the device is an IoT Edge device, use the following request to retrieve the last known telemetry value from a module. This example uses a device called environmental-sensor-01 with a module called SimulatedTemperatureSensor and telemetry called ambient. The ambient telemetry type has temperature and humidity values:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/environmental-sensor-01/modules/SimulatedTemperatureSensor/telemetry/ambient?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"timestamp": "2021-03-25T15:44:34.955Z",
"value": {
"temperature": 21.18032378129676,
"humidity": 25
}
}
Tip
To access the telemetry from a component in a module, use /api/devices/{deviceId}/modules/{moduleName}/components/{componentName}/telemetry/{telemetryName}.
Read properties
Use the following request to retrieve the property values from a device that doesn't use components. In this example, the device is called thermostat-01:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/thermostat-01/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example. It shows the device is reporting a single property value:
{
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": 93.95907131817654,
"$metadata": {
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T12:47:46.7571438Z"
}
}
}
Use the following request to retrieve property values from all components. In this example, the device is called temperature-controller-01:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/temperature-controller-01/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"serialNumber": "Explicabo animi nihil qui facere sit explicabo nisi.",
"$metadata": {
"serialNumber": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
}
},
"thermostat1": {
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": 79.7290121339184,
"$metadata": {
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
}
}
},
"thermostat2": {
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": 54.214860556320424,
"$metadata": {
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
}
}
},
"deviceInformation": {
"manufacturer": "Eveniet culpa sed sit omnis.",
"$metadata": {
"manufacturer": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
},
"model": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
},
"swVersion": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
},
"osName": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
},
"processorArchitecture": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
},
"processorManufacturer": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
},
"totalStorage": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
},
"totalMemory": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T13:58:52.5999859Z"
}
},
"model": "Necessitatibus id ab dolores vel eligendi fuga.",
"swVersion": "Ut minus ipsum ut omnis est asperiores harum.",
"osName": "Atque sit omnis eum sapiente eum tenetur est dolor.",
"processorArchitecture": "Ratione enim dolor iste iure.",
"processorManufacturer": "Aliquam eligendi sit ipsa.",
"totalStorage": 36.02825898541592,
"totalMemory": 55.442695395750505
}
}
Use the following request to retrieve a property value from an individual component. In this example, the device is called temperature-controller-01 and the component is called thermostat2:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/temperature-controller-01/components/thermostat2/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": 24.445128131004935,
"$metadata": {
"maxTempSinceLastReboot": {
"lastUpdateTime": "2021-03-24T14:03:53.787491Z"
}
}
}
If the device is an IoT Edge device, use the following request to retrieve property values from a module. This example uses a device called environmental-sensor-01 with a module called SimulatedTemperatureSensor:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/environmental-sensor-01/modules/SimulatedTemperatureSensor/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"$metadata": {
"SendData": {
"desiredValue": true,
"desiredVersion": 1
},
"SendInterval": {
"desiredValue": 10,
"desiredVersion": 1
}
}
}
Tip
To access the properties from a component in a module, use /devices/{deviceId}/modules/{moduleName}/components/{componentName}/properties.
Write properties
Some properties are writable. In the example thermostat model, the targetTemperature property is a writable property.
Use the following request to write an individual property value to a device that doesn't use components. In this example, the device is called thermostat-01:
PATCH https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/thermostat-01/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
The request body looks like the following example:
{
"targetTemperature": 65.5
}
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"$metadata": {
"targetTemperature": {
"desiredValue": 65.5
}
}
}
Tip
To update all the properties on a device, use PUT instead of PATCH.
Use the following request to write an individual property value to a device that does use components. In this example, the device is called temperature-controller-01 and the component is called thermostat2:
PATCH https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/temperature-controller-01/components/thermostat2/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
The request body looks like the following example:
{
"targetTemperature": 65.5
}
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"$metadata": {
"targetTemperature": {
"desiredValue": 65.5
}
}
}
Tip
To update all the properties on a component, use PUT instead of PATCH.
If the device is an IoT Edge device, use the following request to write an individual property value to a module. This example uses a device called environmental-sensor-01, a module called SimulatedTemperatureSensor, and a property called SendInterval:
PUT https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/environmental-sensor-01/modules/SimulatedTemperatureSensor/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
The request body looks like the following example:
{
"SendInterval": 20
}
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"$metadata": {
"SendInterval": {
"desiredValue": 20
}
}
}
Tip
To update all the properties on a module, use PUT instead of PATCH.
Update module properties
If you're using an IoT Edge device, use the following request to retrieve property values from a module:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/{deviceId}/modules/{moduleName}/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
If you're using an IoT Edge device, use the following request to retrieve property values from a component in a module:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/{deviceId}/modules/{moduleName}/components/{componentName}/properties?api-version=2022-07-31
Call commands
You can use the REST API to call device commands and retrieve the command history.
Use the following request to call a command on device that doesn't use components. In this example, the device is called thermostat-01 and the command is called getMaxMinReport:
POST https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/thermostat-01/commands/getMaxMinReport?api-version=2022-07-31
The request body looks like the following example:
{
"request": "2021-03-24T12:55:20.789Z"
}
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"response": {
"maxTemp": 21.002000799562367,
"minTemp": 73.09674605264892,
"avgTemp": 59.54553991653756,
"startTime": "2022-02-28T15:02:56.789Z",
"endTime": "2021-05-05T03:50:56.412Z"
},
"responseCode": 200
}
To view the history for this command, use the following request:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/thermostat-01/commands/getMaxMinReport?api-version=2022-07-31
The response to this request looks like the following example:
{
"value": [
{
"response": {
"maxTemp": 71.43744908819954,
"minTemp": 51.29986610160005,
"avgTemp": 39.577384387771744,
"startTime": "2021-06-20T00:38:17.620Z",
"endTime": "2022-01-07T22:30:41.104Z"
},
"responseCode": 200
}
]
}
Use the following request to call a command on device that does use components. In this example, the device is called temperature-controller-01, the component is called thermostat2, and the command is called getMaxMinReport:
POST https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/temperature-controller-01/components/thermostat2/commands/getMaxMinReport?api-version=2022-07-31
The formats of the request payload and response are the same as for a device that doesn't use components.
To view the history for this command, use the following request:
GET https://{your app subdomain}.azureiotcentral.com/api/devices/temperature-controller-01/components/thermostat2/commands/getMaxMinReport?api-version=2022-07-31
Tip
To call commands in a component in a module, use /devices/{deviceId}/modules/{moduleName}/components/{componentName}/commands/{commandName}.
Next steps
Now that you've learned how to control devices with the REST API, a suggested next step is to learn How to use the IoT Central REST API to create and manage jobs.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for