Update IoT Edge
Applies to: ![]() IoT Edge 1.4
IoT Edge 1.4
Important
IoT Edge 1.4 is the supported release. If you are on an earlier release, see Update IoT Edge.
As the IoT Edge service releases new versions, update your IoT Edge devices for the latest features and security improvements. This article provides information about how to update your IoT Edge devices when a new version is available.
Two logical components of an IoT Edge device need to be updated if you want to move to a newer version.
Security subsystem - Although the architecture of the security subsystem changed between version 1.1 and 1.2, its responsibilities remained the same. It runs on the device, handles security-based tasks, and starts the modules when the device starts. The security subsystem can only be updated from the device itself.
IoT Edge runtime - The IoT Edge runtime is made up of the IoT Edge hub (
edgeHub) and IoT Edge agent (edgeAgent) modules. Depending on how you structure your deployment, the runtime can be updated from either the device or remotely.
How to update
Use the sections of this article to update both the security subsystem and runtime containers on a device.
Patch releases
When you upgrade between patch releases, for example 1.4.1 to 1.4.2, the update order isn't important. You can upgrade the security subsystem or the runtime containers before or after the other. To update between patch releases:
You can troubleshoot the upgrade process at any time.
Major or minor releases
When you upgrade between major or minor releases, for example from 1.1 to 1.4, update both the security subsystem and the runtime containers. Before a release, we test the security subsystem and the runtime container version combination. To update between major or minor product releases:
On the device, stop IoT Edge using the command
sudo systemctl stop iotedgeand uninstall.On the device, upgrade your container engine, either Docker or Moby.
On the device, install IoT Edge.
If you're importing an old configuration using
iotedge config import, then modify the [agent.config] image of the generated/etc/aziot/config.tomlfile to use the 1.4 image for edgeAgent.For more information, see Configure IoT Edge device settings.
In IoT Hub, update the module deployment to reference the newest system modules.
On the device, start the IoT Edge using
sudo iotedge config apply.
You can troubleshoot the upgrade process at any time.
Update the security subsystem
The IoT Edge security subsystem includes a set of native components that need to be updated using the package manager on the IoT Edge device.
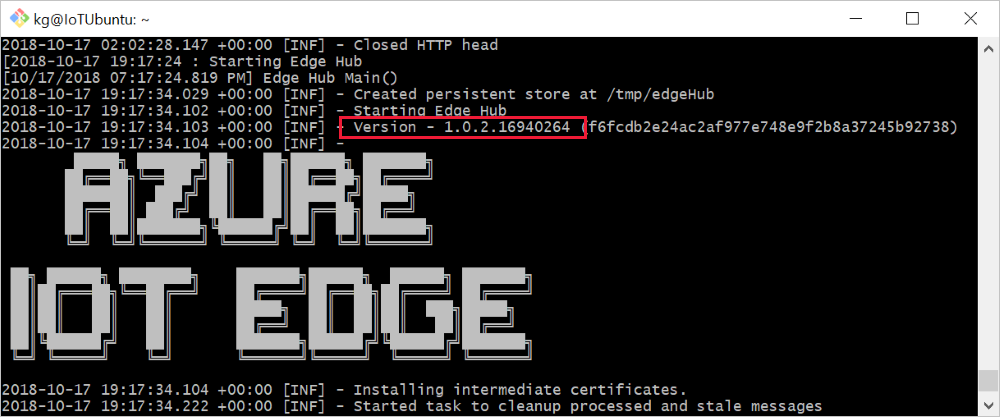
Check the version of the security subsystem running on your device by using the command iotedge version. If you're using IoT Edge for Linux on Windows, you need to SSH into the Linux virtual machine to check the version.
Important
If you are updating a device from version 1.0 or 1.1 to the latest release, there are differences in the installation and configuration processes that require extra steps. For more information, see the steps later in this article: Special case: Update from 1.0 or 1.1 to latest release.
On Linux x64 devices, use apt-get or your appropriate package manager to update the security subsystem to the latest version.
Update apt:
sudo apt-get update
Note
For instructions to get the latest repository configuration from Microsoft see the preliminary steps to Install IoT Edge.
Check to see which versions of IoT Edge are available:
apt list -a aziot-edge
Update IoT Edge:
sudo apt-get install aziot-edge defender-iot-micro-agent-edge
Running apt-get install aziot-edge upgrades the security subsystem and installs the identity service, aziot-identity-service, as a required dependency.
It's recommended to install the micro agent with the Edge agent to enable security monitoring and hardening of your Edge devices. To learn more about Microsoft Defender for IoT, see What is Microsoft Defender for IoT for device builders.
Then, reapply configuration to ensure system is fully updated.
sudo iotedge config apply
Update the runtime containers
The way that you update the IoT Edge agent and IoT Edge hub containers depends on whether you use rolling tags (like 1.1) or specific tags (like 1.1.1) in your deployment.
Check the version of the IoT Edge agent and IoT Edge hub modules currently on your device using the commands iotedge logs edgeAgent or iotedge logs edgeHub. If you're using IoT Edge for Linux on Windows, you need to SSH into the Linux virtual machine to check the runtime module versions.
Understand IoT Edge tags
The IoT Edge agent and IoT Edge hub images are tagged with the IoT Edge version that they're associated with. There are two different ways to use tags with the runtime images:
Rolling tags - Use only the first two values of the version number to get the latest image that matches those digits. For example, 1.1 is updated whenever there's a new release to point to the latest 1.1.x version. If the container runtime on your IoT Edge device pulls the image again, the runtime modules are updated to the latest version. Deployments from the Azure portal default to rolling tags. This approach is suggested for development purposes.
Specific tags - Use all three values of the version number to explicitly set the image version. For example, 1.1.0 won't change after its initial release. You can declare a new version number in the deployment manifest when you're ready to update. This approach is suggested for production purposes.
Update a rolling tag image
If you use rolling tags in your deployment (for example, mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-hub:1.1) then you need to force the container runtime on your device to pull the latest version of the image.
Delete the local version of the image from your IoT Edge device. On Windows machines, uninstalling the security subsystem also removes the runtime images, so you don't need to take this step again.
docker rmi mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-hub:1.1
docker rmi mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-agent:1.1
You may need to use the force -f flag to remove the images.
The IoT Edge service pulls the latest versions of the runtime images and automatically starts them on your device again.
Update a specific tag image
If you use specific tags in your deployment (for example, mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-hub:1.4) then all you need to do is update the tag in your deployment manifest and apply the changes to your device.
In the IoT Hub in the Azure portal, select your IoT Edge device, and select Set Modules.
On the Modules tab, select Runtime Settings.
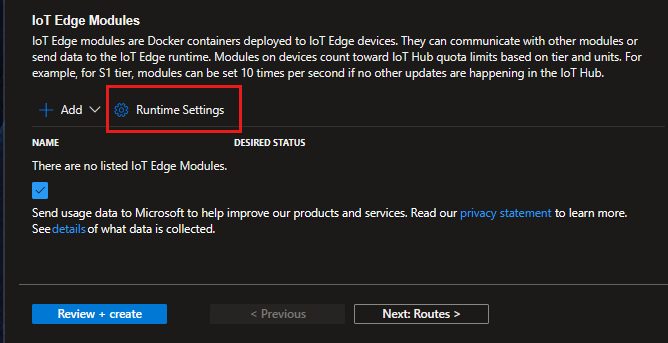
In Runtime Settings, update the Image URI value in the Edge Agent section with the desired version. Don't select Apply yet.
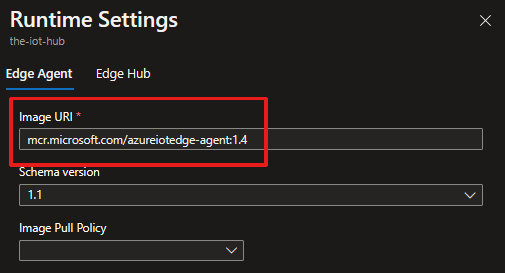
Select the Edge Hub tab and update the Image URI value with the same desired version.
Select Apply to save changes.
Select Review + create, review the deployment as seen in the JSON file, and select Create.
Verify versions match
On your device, use
iotedge versionto check the security subsystem version. The output includes the major, minor, and revision version numbers. For example, iotedge 1.4.2.In your device deployment runtime settings, verify the edgeHub and edgeAgent image URI versions match the major and minor version of the security subsystem. If the security subsystem version is 1.4.2, the image versions would be 1.4. For example, mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-hub:1.4 and mcr.microsoft.com/azureiotedge-agent:1.4.
Note
Update the IoT Edge security subsystem and runtime containers to the same supported release version. While mismatched versions are supported, we haven't tested all version combinations.
To find the latest version of Azure IoT Edge, see Azure IoT Edge releases.
Special case: Update from 1.0 or 1.1 to latest release
Starting with version 1.2, the IoT Edge service uses a new package name and has some differences in the installation and configuration processes. If you have an IoT Edge device running version 1.0 or 1.1, use these instructions to learn how to update to the latest release.
Some of the key differences between the latest release and version 1.1 and earlier include:
- The package name changed from iotedge to aziot-edge.
- The libiothsm-std package is no longer used. If you used the standard package provided as part of the IoT Edge release, then your configurations can be transferred to the new version. If you used a different implementation of libiothsm-std, then any user-provided certificates like the device identity certificate, device CA, and trust bundle need to be reconfigured.
- A new identity service, aziot-identity-service was introduced as part of the 1.2 release. This service handles the identity provisioning and management for IoT Edge and for other device components that need to communicate with IoT Hub, like Device Update for IoT Hub.
- The default config file has a new name and location. Formerly
/etc/iotedge/config.yaml, your device configuration information is now expected to be in/etc/aziot/config.tomlby default. Theiotedge config importcommand can be used to help migrate configuration information from the old location and syntax to the new one.- The import command can't detect or modify access rules to a device's trusted platform module (TPM). If your device uses TPM attestation, you need to manually update the /etc/udev/rules.d/tpmaccess.rules file to give access to the aziottpm service. For more information, see Give IoT Edge access to the TPM.
- The workload API in the latest version saves encrypted secrets in a new format. If you upgrade from an older version to the latest version, the existing master encryption key is imported. The workload API can read secrets saved in the prior format using the imported encryption key. However, the workload API can't write encrypted secrets in the old format. Once a module re-encrypts a secret, it's saved in the new format. Secrets encrypted in the latest version are unreadable by the same module in version 1.1. If you persist encrypted data to a host-mounted folder or volume, always create a backup copy of the data before upgrading to retain the ability to downgrade if necessary.
- For backward compatibility when connecting devices that don't support TLS 1.2, you can configure Edge Hub to still accept TLS 1.0 or 1.1 via the SslProtocols environment variable. Support for TLS 1.0 and 1.1 in IoT Hub is considered legacy and may also be removed from Edge Hub in future releases. To avoid future issues, use TLS 1.2 as the only TLS version when connecting to Edge Hub or IoT Hub.
- The preview for the experimental MQTT broker in Edge Hub 1.2 has ended and isn't included in Edge Hub 1.4. We're continuing to refine our plans for an MQTT broker based on feedback received. In the meantime, if you need a standards-compliant MQTT broker on IoT Edge, consider deploying an open-source broker like Mosquitto as an IoT Edge module.
- Starting with version 1.2, when a backing image is removed from a container, the container keeps running and it persists across restarts. In 1.1, when a backing image is removed, the container is immediately recreated and the backing image is updated.
Before automating any update processes, validate that it works on test machines.
When you're ready, follow these steps to update IoT Edge on your devices:
Update apt.
sudo apt-get updateUninstall the previous version of IoT Edge, leaving your configuration files in place.
sudo apt-get remove iotedgeInstall the most recent version of IoT Edge, along with the IoT identity service and the Microsoft Defender for IoT micro agent for Edge.
sudo apt-get install aziot-edge defender-iot-micro-agent-edge
It's recommended to install the micro agent with the Edge agent to enable security monitoring and hardening of your Edge devices. To learn more about Microsoft Defender for IoT, see What is Microsoft Defender for IoT for device builders.
Import your old config.yaml file into its new format, and apply the configuration info.
sudo iotedge config import
Now that the latest IoT Edge service is running on your devices, you also need to Update the runtime containers to the latest version. The updating process for runtime containers is the same as the updating process for the IoT Edge service.
Troubleshooting
You can view logs of your system at any time by running the following commands from your device.
Start troubleshooting using the check command. It runs a collection of configuration and connectivity tests for common issues.
sudo iotedge check --verboseTo view the status of the IoT Edge system, run:
sudo iotedge system statusTo view host component logs, run:
sudo iotedge system logsTo check for recurring issues reported with edgeAgent and edgeHub, run:
Be sure to replace
<module>with your own module name. If there are no issues, you see no output.sudo iotedge logs <module>
For more information, see Troubleshoot your IoT Edge device.
Next steps
View the latest Azure IoT Edge releases.
Stay up-to-date with recent updates and announcements in the Internet of Things blog
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for