Use Azure Pipelines with Azure Machine Learning
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
You can use an Azure DevOps pipeline to automate the machine learning lifecycle. Some of the operations you can automate are:
- Data preparation (extract, transform, load operations)
- Training machine learning models with on-demand scale-out and scale-up
- Deployment of machine learning models as public or private web services
- Monitoring deployed machine learning models (such as for performance or data-drift analysis)
This article teaches you how to create an Azure Pipeline that builds and deploys a machine learning model to Azure Machine Learning.
This tutorial uses Azure Machine Learning Python SDK v2 and Azure CLI ML extension v2.
Prerequisites
- Complete the Create resources to get started to:
- Create a workspace
- Create a cloud-based compute cluster to use for training your model
- Azure Machine Learning extension for Azure Pipelines. This extension can be installed from the Visual Studio marketplace at https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-air-aiagility.azureml-v2.
Step 1: Get the code
Fork the following repo at GitHub:
https://github.com/azure/azureml-examples
Step 2: Sign in to Azure Pipelines
Sign-in to Azure Pipelines. After you sign in, your browser goes to https://dev.azure.com/my-organization-name and displays your Azure DevOps dashboard.
Within your selected organization, create a project. If you don't have any projects in your organization, you see a Create a project to get started screen. Otherwise, select the New Project button in the upper-right corner of the dashboard.
Step 3: Create a service connection
You can use an existing service connection.
You need an Azure Resource Manager connection to authenticate with Azure portal.
In Azure DevOps, select Project Settings and open the Service connections page.
Choose + New service connection and select Azure Resource Manager.
Select the default authentication method, Service principal (automatic).
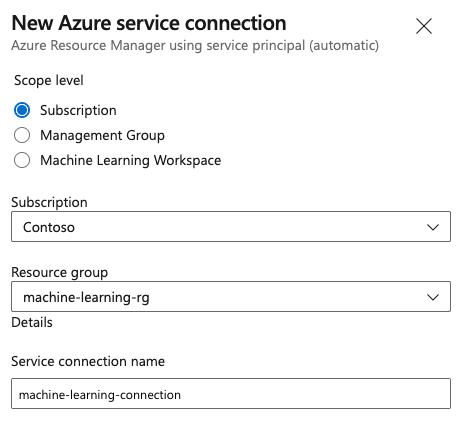
Create your service connection. Set your preferred scope level, subscription, resource group, and connection name.
Step 4: Create a pipeline
Go to Pipelines, and then select New pipeline.
Do the steps of the wizard by first selecting GitHub as the location of your source code.
You might be redirected to GitHub to sign in. If so, enter your GitHub credentials.
When you see the list of repositories, select your repository.
You might be redirected to GitHub to install the Azure Pipelines app. If so, select Approve & install.
Select the Starter pipeline. You'll update the starter pipeline template.
Step 5: Build your YAML pipeline to submit the Azure Machine Learning job
Delete the starter pipeline and replace it with the following YAML code. In this pipeline, you'll:
- Use the Python version task to set up Python 3.8 and install the SDK requirements.
- Use the Bash task to run bash scripts for the Azure Machine Learning SDK and CLI.
- Use the Azure CLI task to submit an Azure Machine Learning job.
Select the following tabs depending on whether you're using an Azure Resource Manager service connection or a generic service connection. In the pipeline YAML, replace the value of variables with your resources.
name: submit-azure-machine-learning-job
trigger:
- none
variables:
service-connection: 'machine-learning-connection' # replace with your service connection name
resource-group: 'machinelearning-rg' # replace with your resource group name
workspace: 'docs-ws' # replace with your workspace name
jobs:
- job: SubmitAzureMLJob
displayName: Submit AzureML Job
timeoutInMinutes: 300
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
displayName: Use Python >=3.8
inputs:
versionSpec: '>=3.8'
- bash: |
set -ex
az version
az extension add -n ml
displayName: 'Add AzureML Extension'
- task: AzureCLI@2
name: submit_azureml_job_task
displayName: Submit AzureML Job Task
inputs:
azureSubscription: $(service-connection)
workingDirectory: 'cli/jobs/pipelines-with-components/nyc_taxi_data_regression'
scriptLocation: inlineScript
scriptType: bash
inlineScript: |
# submit component job and get the run name
job_name=$(az ml job create --file single-job-pipeline.yml -g $(resource-group) -w $(workspace) --query name --output tsv)
# Set output variable for next task
echo "##vso[task.setvariable variable=JOB_NAME;isOutput=true;]$job_name"
Step 6: Wait for Azure Machine Learning job to complete
In step 5, you added a job to submit an Azure Machine Learning job. In this step, you add another job that waits for the Azure Machine Learning job to complete.
If you're using an Azure Resource Manager service connection, you can use the "Machine Learning" extension. You can search this extension in the Azure DevOps extensions Marketplace or go directly to the extension. Install the "Machine Learning" extension.
Important
Don't install the Machine Learning (classic) extension by mistake; it's an older extension that doesn't provide the same functionality.
In the Pipeline review window, add a Server Job. In the steps part of the job, select Show assistant and search for AzureML. Select the AzureML Job Wait task and fill in the information for the job.
The task has four inputs: Service Connection, Azure Resource Group Name, AzureML Workspace Name and AzureML Job Name. Fill these inputs. The resulting YAML for these steps is similar to the following example:
Note
- The Azure Machine Learning job wait task runs on a server job, which doesn't use up expensive agent pool resources and requires no additional charges. Server jobs (indicated by
pool: server) run on the same machine as your pipeline. For more information, see Server jobs. - One Azure Machine Learning job wait task can only wait on one job. You'll need to set up a separate task for each job that you want to wait on.
- The Azure Machine Learning job wait task can wait for a maximum of 2 days. This is a hard limit set by Azure DevOps Pipelines.
- job: WaitForAzureMLJobCompletion
displayName: Wait for AzureML Job Completion
pool: server
timeoutInMinutes: 0
dependsOn: SubmitAzureMLJob
variables:
# We are saving the name of azureMl job submitted in previous step to a variable and it will be used as an inut to the AzureML Job Wait task
azureml_job_name_from_submit_job: $[ dependencies.SubmitAzureMLJob.outputs['submit_azureml_job_task.JOB_NAME'] ]
steps:
- task: AzureMLJobWaitTask@1
inputs:
serviceConnection: $(service-connection)
resourceGroupName: $(resource-group)
azureMLWorkspaceName: $(workspace)
azureMLJobName: $(azureml_job_name_from_submit_job)
Step 7: Submit pipeline and verify your pipeline run
Select Save and run. The pipeline will wait for the Azure Machine Learning job to complete, and end the task under WaitForJobCompletion with the same status as the Azure Machine Learning job. For example:
Azure Machine Learning job Succeeded == Azure DevOps Task under WaitForJobCompletion job Succeeded
Azure Machine Learning job Failed == Azure DevOps Task under WaitForJobCompletion job Failed
Azure Machine Learning job Cancelled == Azure DevOps Task under WaitForJobCompletion job Cancelled
Tip
You can view the complete Azure Machine Learning job in Azure Machine Learning studio.
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use your pipeline, delete your Azure DevOps project. In Azure portal, delete your resource group and Azure Machine Learning instance.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for