Change the redundancy configuration for a storage account
Azure Storage always stores multiple copies of your data to protect it in the face of both planned and unplanned events. These events include transient hardware failures, network or power outages, and massive natural disasters. Data redundancy ensures that your storage account meets the Service-Level Agreement (SLA) for Azure Storage, even in the face of failures.
This article describes the process of changing replication setting(s) for an existing storage account.
Options for changing the replication type
When deciding which redundancy configuration is best for your scenario, consider the tradeoffs between lower costs and higher availability. The factors that help determine which redundancy configuration you should choose include:
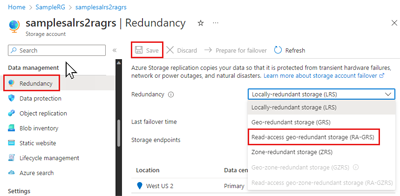
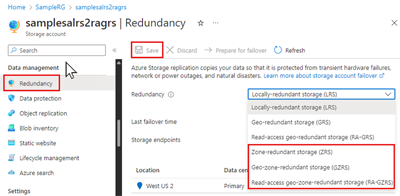
- How your data is replicated within the primary region. Data in the primary region can be replicated locally using locally redundant storage (LRS), or across Azure availability zones using zone-redundant storage (ZRS).
- Whether your data is geo-replicated. Geo-replication provides protection against regional disasters by replicating your data to a second region that is geographically distant to the primary region. Geo-replicated configurations include geo-redundant storage (GRS) and geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS).
- Whether your application requires read access to the replicated data in the secondary region. You can configure your storage account to allow read access to data replicated to the secondary region if the primary region becomes unavailable for any reason. Configurations that provide read access to data in the secondary region include read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) and read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS).
For a detailed overview of all of the redundancy options, see Azure Storage redundancy.
You can change your storage account's redundancy configurations as needed, though some configurations are subject to limitations and downtime requirements. Reviewing these limitations and requirements before making any changes within your environment helps avoid conflicts with your own timeframe and uptime requirements.
There are three ways to change the replication settings:
- Add or remove geo-replication or read access to the secondary region.
- Add or remove zone-redundancy by performing a conversion.
- Perform a manual migration in scenarios where the first two options aren't supported, or to ensure the change is completed within a specific timeframe.
Geo-redundancy and read-access can be changed at the same time. However, any change that also involves zone-redundancy requires a conversion and must be performed separately using a two-step process. These two steps can be performed in any order.
Changing redundancy configuration
The following table provides an overview of how to switch between replication types.
Note
Manual migration is an option for any scenario in which you want to change the replication setting within the limitations for changing replication types. The manual migration option is excluded from the following table for simplification.
| Switching | …to LRS | …to GRS/RA-GRS 6 | …to ZRS | …to GZRS/RA-GZRS 2,6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| …from LRS | N/A | Use Azure portal, PowerShell, or CLI 1,2 | Perform a conversion2,3,4,5 | First, use the Portal, PowerShell, or CLI to switch to GRS/RA-GRS 1, then perform a conversion to GZRS/RA-GZRS 3,4,5 |
| …from GRS/RA-GRS | Use Azure portal, PowerShell, or CLI | N/A | First, use the Portal, PowerShell, or CLI to switch to LRS, then perform a conversion to ZRS 3,5 | Perform a conversion3,5 |
| …from ZRS | Perform a conversion3 | First, use the Portal, PowerShell, or CLI to switch to GZRS/RA-GZRS, then perform a conversion to GRS/RA-GRS3 | N/A | Use Azure portal, PowerShell, or CLI 1 |
| …from GZRS/RA-GZRS | First, use the Portal, PowerShell, or CLI to switch to ZRS, then perform a conversion to LRS 3 | Perform a conversion3 | Use Azure portal, PowerShell, or CLI | N/A |
1 Adding geo-redundancy incurs a one-time egress charge.
2 If your storage account contains blobs in the archive tier, review the access tier limitations before changing the redundancy type to geo- or zone-redundant.
3 The type of conversion supported depends on the storage account type. For more information, see the storage account table.
4 Conversion to ZRS or GZRS for an LRS account resulting from a failover isn't supported. For more information, see Failover and failback.
5 Converting from LRS to ZRS isn't supported if the NFSv3 protocol support is enabled for Azure Blob Storage or if the storage account contains Azure Files NFSv4.1 shares.
6 Even though enabling geo-redundancy appears to occur instantaneously, failover to the secondary region can't be initiated until data synchronization between the two regions is complete.
Change the replication setting
Depending on your scenario from the changing redundancy configuration section, use one of the following methods to change your replication settings.
Change the redundancy configuration using Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI
In most cases you can use the Azure portal, PowerShell, or the Azure CLI to change the geo-redundant or read access (RA) replication setting for a storage account.
Changing how your storage account is replicated in the Azure portal doesn't result in down time for your applications, including changes that require a conversion.
To change the redundancy option for your storage account in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Perform a conversion
A redundancy "conversion" is the process of changing the zone-redundancy aspect of a storage account.
During a conversion, there's no data loss or application downtime required.
There are two ways to initiate a conversion:
Tip
Microsoft recommends using a customer-initiated conversion instead of support-initiated conversion whenever possible. A customer-initiated conversion allows you to initiate the conversion and monitor its progress directly from within the Azure portal. Because the conversion is initiated by the customer, there is no need to create and manage a support request.
Customer-initiated conversion
Instead of opening a support request, customers in most regions can start a conversion and monitor its progress. This option eliminates potential delays related to creating and managing support requests. For help determining the regions in which customer-initiated conversion is supported, see the region limitations article.
Customer-initiated conversion can be completed in supported regions using the Azure portal, PowerShell, or the Azure CLI. After initiation, the conversion could still take up to 72 hours to begin.
Important
There is no SLA for completion of a conversion.
If you need more control over when a conversion begins and finishes, consider a Manual migration. Generally, the more data you have in your account, the longer it takes to replicate that data to other zones or regions.
For more information about the timing of a customer-initiated conversion, see Timing and frequency.
To add or modify a storage account's zonal-redundancy within the Azure portal, perform these steps:
Monitoring customer-initiated conversion progress
As the conversion request is evaluated and processed, the status should progress through the list shown in the following table:
| Status | Explanation |
|---|---|
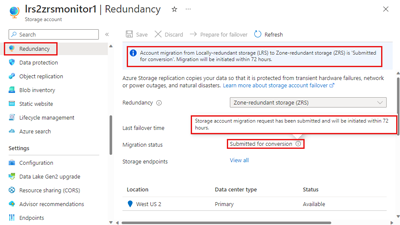
| Submitted for conversion | The conversion request was successfully submitted for processing. |
| In Progress1 | The conversion is in progress. |
| Completed - or -Failed2 |
The conversion is completed successfully. - or -The conversion failed. |
1 Once initiated, the conversion could take up to 72 hours to begin. If the conversion doesn't enter the "In Progress" status within 96 hours of initiating the request, submit a support request to Microsoft to determine why. For more information about the timing of a customer-initiated conversion, see Timing and frequency.
2 If the conversion fails, submit a support request to Microsoft to determine the reason for the failure.
Note
While Microsoft handles your request for a conversion promptly, there's no guarantee as to when it will complete. If you need your data converted by a certain date, Microsoft recommends that you perform a manual migration instead.
Generally, the more data you have in your account, the longer it takes to replicate that data to other zones in the region.
The status of your customer-initiated conversion is displayed on the Redundancy page of the storage account:
Support-initiated conversion
Customers can still request a conversion by opening a support request with Microsoft.
Tip
If you need to convert more than one storage account, create a single support ticket and specify the names of the accounts to convert on the Additional details tab.
Follow these steps to request a conversion from Microsoft:
In the Azure portal, navigate to a storage account that you want to convert.
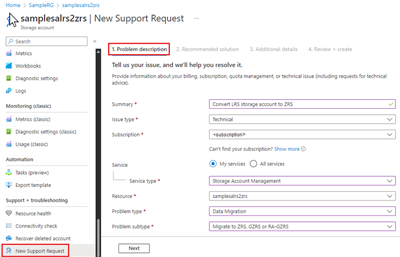
Under Support + troubleshooting, select New Support Request.
Complete the Problem description tab based on your account information:
- Summary: (some descriptive text).
- Issue type: Select Technical.
- Subscription: Select your subscription from the drop-down.
- Service: Select My Services, then Storage Account Management for the Service type.
- Resource: Select a storage account to convert. If you need to specify multiple storage accounts, you can do so on the Additional details tab.
- Problem type: Choose Data Migration.
- Problem subtype: Choose Migrate to ZRS, GZRS, or RA-GZRS.
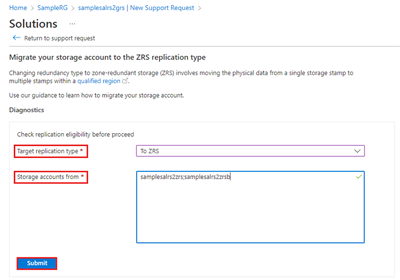
Select Next. The Recommended solution tab might be displayed briefly before it switches to the Solutions page. On the Solutions page, you can check the eligibility of your storage account(s) for conversion:
- Target replication type: (choose the desired option from the drop-down)
- Storage accounts from: (enter a single storage account name or a list of accounts separated by semicolons)
- Select Submit.
Take the appropriate action if the results indicate your storage account isn't eligible for conversion. Otherwise, select Return to support request.
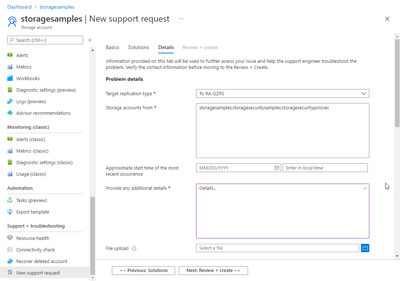
Select Next. If you have more than one storage account to migrate, on the Details tab, specify the name for each account, separated by a semicolon.
Provide the required information on the Additional details tab, then select Review + create to review and submit your support ticket. An Azure support agent reviews your case and contacts you to provide assistance.
Manual migration
A manual migration provides more flexibility and control than a conversion. You can use this option if you need your data moved by a certain date, or if conversion isn't supported for your scenario. Manual migration is also useful when moving a storage account to another region. For more detail, see Move an Azure Storage account to another region.
You must perform a manual migration if:
- You want to migrate your storage account to a different region.
- Your storage account is a block blob account.
- Your storage account includes data in the archive tier and rehydrating the data isn't desired.
Important
A manual migration can result in application downtime. If your application requires high availability, Microsoft also provides a conversion option. A conversion is an in-place migration with no downtime.
With a manual migration, you copy the data from your existing storage account to a new storage account. To perform a manual migration, you can use one of the following options:
- Copy data by using an existing tool such as AzCopy, one of the Azure Storage client libraries, or a reliable non-Microsoft tool.
- If you're familiar with Hadoop or HDInsight, you can attach both the source storage account and destination storage account to your cluster. Then, parallelize the data copy process with a tool like DistCp.
For more detailed guidance on how to perform a manual migration, see Move an Azure Storage account to another region.
Limitations for changing replication types
Important
Boot diagnostics doesn't support premium storage accounts or zone-redundant storage accounts. When either premium or zone-redundant storage accounts are used for boot diagnostics, users receive a StorageAccountTypeNotSupported error upon starting their virtual machine (VM).
Limitations apply to some replication change scenarios depending on:
Region
Make sure the region where your storage account is located supports all of the desired replication settings. For example, if you're converting your account to zone-redundant (ZRS, GZRS, or RA-GZRS), make sure your storage account is in a region that supports it. See the lists of supported regions for Zone-redundant storage and Geo-zone-redundant storage.
Important
Customer-initiated conversion from LRS to ZRS is available in all public regions that support ZRS except for the following:
- (Europe) Italy North
- (Europe) UK South
- (Europe) Poland Central
- (Europe) West Europe
- (Middle East) Israel Central
- (North America) Canada Central
- (North America) East US
- (North America) East US 2
Customer-initiated conversion from existing ZRS accounts to LRS is available in all public regions.
Feature conflicts
Some storage account features aren't compatible with other features or operations. For example, the ability to fail over to the secondary region is the key feature of geo-redundancy, but other features aren't compatible with failover. For more information about features and services not supported with failover, see Unsupported features and services. The conversion of an account to GRS, GZRS, or RA-GZRS might be blocked if a conflicting feature is enabled, or it might be necessary to disable the feature later before initiating a failover.
Storage account type
When planning to change your replication settings, consider the following limitations related to the storage account type.
Some storage account types only support certain redundancy configurations, which affect whether they can be converted or migrated and, if so, how. For more information on Azure storage account types and the supported redundancy options, see the storage account overview.
The following table provides an overview of redundancy options available for storage account types and whether conversion and manual migration are supported:
| Storage account type | Supports LRS | Supports ZRS | Supports conversion (from the portal) |
Supports conversion (by support request) |
Supports manual migration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard general purpose v2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Premium file shares | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ 1 | ✅ | |
| Premium block blob | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ||
| Premium page blob | ✅ | ||||
| Managed disks2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Standard general purpose v1 | ✅ | 3 | ✅ | ||
| ZRS Classic4 (available in standard general purpose v1 accounts) |
✅ |
1 Conversion for premium file shares is only available by opening a support request; Customer-initiated conversion isn't currently supported.
2 Managed disks are available for LRS and ZRS, though ZRS disks have some limitations. If an LRS disk is regional (no zone specified), it can be converted by changing the SKU. If an LRS disk is zonal, then it can only be manually migrated by following the process in Migrate your managed disks. You can store snapshots and images for standard SSD managed disks on standard HDD storage and choose between LRS and ZRS options. For information about integration with availability sets, see Introduction to Azure managed disks.
3 If your storage account is v1, you need to upgrade it to v2 before performing a conversion. To learn how to upgrade your v1 account, see Upgrade to a general-purpose v2 storage account.
4 ZRS Classic storage accounts are deprecated. For information about converting ZRS Classic accounts, see Converting ZRS Classic accounts.
Converting ZRS Classic accounts
Important
ZRS Classic accounts were deprecated on March 31, 2021. Customers can no longer create ZRS Classic accounts. If you still have some, you should upgrade them to general purpose v2 accounts.
ZRS Classic was available only for block blobs in general-purpose V1 (GPv1) storage accounts. For more information about storage accounts, see Azure storage account overview.
ZRS Classic accounts asynchronously replicated data across data centers within one to two regions. Replicated data wasn't available unless Microsoft initiated a failover to the secondary. A ZRS Classic account can't be converted to or from LRS, GRS, or RA-GRS. ZRS Classic accounts also don't support metrics or logging.
To change ZRS Classic to another replication type, use one of the following methods:
- Upgrade it to ZRS first
- Manually migrate the data directly to another replication type
To upgrade your ZRS Classic storage account to ZRS, use the Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI in regions where ZRS is available:
To upgrade to ZRS in the Azure portal, navigate to the Configuration settings of the account and choose Upgrade:
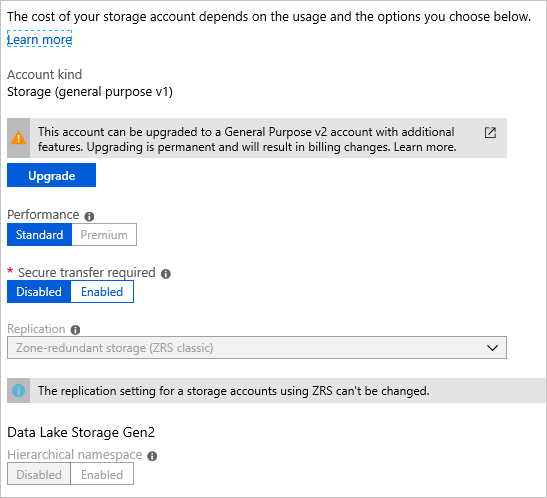
To manually migrate your ZRS Classic account data to another type of replication, follow the steps to perform a manual migration.
If you want to migrate your data into a zone-redundant storage account located in a region different from the source account, you must perform a manual migration. For more information, see Move an Azure Storage account to another region.
Access tier
Make sure the desired redundancy option supports the access tiers currently used in the storage account. For example, ZRS, GZRS and RA-GZRS storage accounts don't support the archive tier. For more information, see Hot, Cool, and Archive access tiers for blob data. To convert an LRS, GRS or RA-GRS account to one that supports zone-redundancy, first move the archived blobs to a storage account that supports blobs in the archive tier. Then convert the source account to ZRS, GZRS and RA-GZRS.
An LRS storage account containing blobs in the archive tier can be switched to GRS or RA-GRS after rehydrating all archived blobs to the Hot or Cool tier. You can also perform a manual migration.
Tip
Microsoft recommends that you avoid changing the redundancy configuration for a storage account that contains archived blobs if at all possible, because rehydration operations can be costly and time-consuming. But if you must change it, a manual migration can save you the expense of rehydration.
Protocol support
You can't convert storage accounts to zone-redundancy (ZRS, GZRS or RA-GZRS) if either of the following cases are true:
- NFSv3 protocol support is enabled for Azure Blob Storage
- The storage account contains Azure Files NFSv4.1 shares
Failover and failback
After an account failover to the secondary region, it's possible to initiate a failback from the new primary back to the new secondary with PowerShell or Azure CLI (version 2.30.0 or later). Initiate the failover.
If you performed a customer-managed account failover to recover from an outage for your GRS or RA-GRS account, the account becomes locally redundant (LRS) in the new primary region after the failover. Conversion to ZRS or GZRS for an LRS account resulting from a failover isn't supported, even for so-called failback operations. For example, if you perform an account failover from RA-GRS to LRS in the secondary region, and then configure it again as RA-GRS, it remains LRS in the new secondary region (the original primary). If you then perform another account failover to failback to the original primary region, it remains LRS again in the original primary. In this case, you can't perform a conversion to ZRS, GZRS or RA-GZRS in the primary region. Instead, perform a manual migration to add zone-redundancy.
Downtime requirements
During a conversion, you can access data in your storage account with no loss of durability or availability. The Azure Storage SLA is maintained during the migration process and no data is lost during a conversion. Service endpoints, access keys, shared access signatures, and other account options remain unchanged after the migration.
If you choose to perform a manual migration, downtime is required but you have more control over the timing of the migration process.
Timing and frequency
If you initiate a zone-redundancy conversion from the Azure portal, the conversion process could take up to 72 hours to begin. It could take longer to start if you request a conversion by opening a support request. If a customer-initiated conversion doesn't enter the "In Progress" status within 96 hours of initiating the request, submit a support request to Microsoft to determine why. To monitor the progress of a customer-initiated conversion, see Monitoring customer-initiated conversion progress.
Important
There is no SLA for completion of a conversion. If you need more control over when a conversion begins and finishes, consider a Manual migration. Generally, the more data you have in your account, the longer it takes to replicate that data to other zones or regions.
After a zone-redundancy conversion, you must wait at least 72 hours before changing the redundancy setting of the storage account again. The temporary hold allows background processes to complete before making another change, ensuring the consistency and integrity of the account. For example, going from LRS to GZRS is a 2-step process. You must add zone redundancy in one operation, then add geo-redundancy in a second. After going from LRS to ZRS, you must wait at least 72 hours before going from ZRS to GZRS.
Costs associated with changing how data is replicated
Azure Storage offers several options for configuring replication. These options, ordered by least- to most-expensive, include:
- LRS
- ZRS
- GRS
- RA-GRS
- GZRS
- RA-GZRS
The costs associated with changing how data is replicated in your storage account depend on which aspects of your redundancy configuration you change. A combination of data storage and egress bandwidth pricing determines the cost of making a change. For details on pricing, see Azure Storage Pricing page.
If you add zone-redundancy in the primary region, there's no initial cost associated with making that conversion, but the ongoing data storage cost is higher due to the increased replication and storage space required.
Geo-redundancy incurs an egress bandwidth charge at the time of the change because your entire storage account is being replicated to the secondary region. All subsequent writes to the primary region also incur egress bandwidth charges to replicate the write to the secondary region.
If you remove geo-redundancy (change from GRS to LRS), there's no cost for making the change, but your replicated data is deleted from the secondary location.
Important
If you remove read access to the secondary region (RA) (change from RA-GRS to GRS or LRS), that account is billed as RA-GRS for an additional 30 days beyond the date that it was converted.
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for