Azure Stream Analytics resource model
Azure Stream Analytics is a fully managed platform-as-a-service (PaaS) for stream processing. This article describes the resource model for Stream Analytics by introducing the concept of a Stream Analytics cluster, job and the components of a job.
Stream Analytics job
A Stream Analytics job is the fundamental unit in Stream Analytics that allows you to define and run your stream processing logic. A job consists of 3 main components:
- Input
- Output
- Query
Input
A job can have one or more inputs to continuously read data from. These streaming input data sources could be an Azure Event Hubs, Azure IoT Hub or Azure Storage. Stream Analytics also supports reading static or slow changing input data (called reference data) which is often used to enrich streaming data. Adding these inputs to your job is a zero-code operation.
Output
A job can have one or more outputs to continuously write data to. Stream Analytics supports 12 different output sinks including Azure SQL Database, Azure Data Lake Storage, Azure Cosmos DB, Power BI and more. Adding these outputs to your job is also a zero-code operation.
Query
You can implement your stream processing logic by writing a SQL query in your job. The rich SQL language support allows you to tackle scenarios such as parsing complex JSON, filtering values, computing aggregates, performing joins, and even more advanced use cases such as geospatial analytics and anomaly detection. You can also extend this SQL language with JavaScript user-defined-functions (UDF) and user-defined-aggregates (UDA). Stream Analytics also allows you to easily adjust for late and out-of-order events through simple configurations in your job's settings. You can also choose to execute your query based on input event's arrival time at the input source or when the event was generated at the event source.
Running a job
Once you have developed your job by configuring inputs, output and a query, you can start your job by specifying number of Streaming Units. Once your job has started, it goes into a Running state and will stay in that state until explicitly stopped or it runs into an unrecoverable failure. When the job is in a running state, it continuously pulls data from your input sources, executes the query logic which produces results that get written to your output sinks with milliseconds end-to-end latency.
When your job is started, the Stream Analytics service takes care of compiling your query and assigns certain amount of compute and memory based on the number of Streaming Units configured in your job. You don't have to worry about any underlying infrastructure as cluster maintenance, security patches as that is automatically taken care by the platform. When running jobs in the Standard SKU, you are charged for the Streaming Units only when the job runs.
Stream Analytics cluster
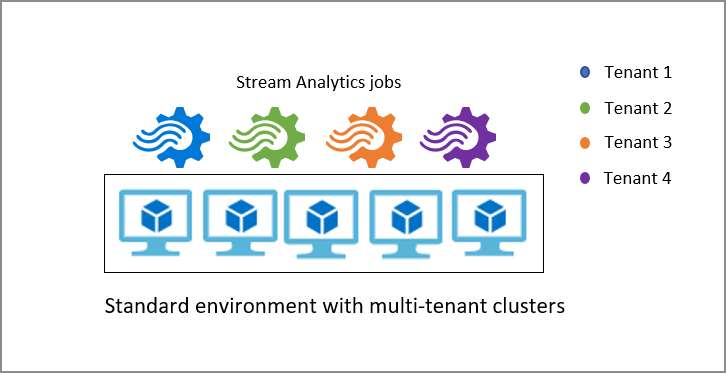
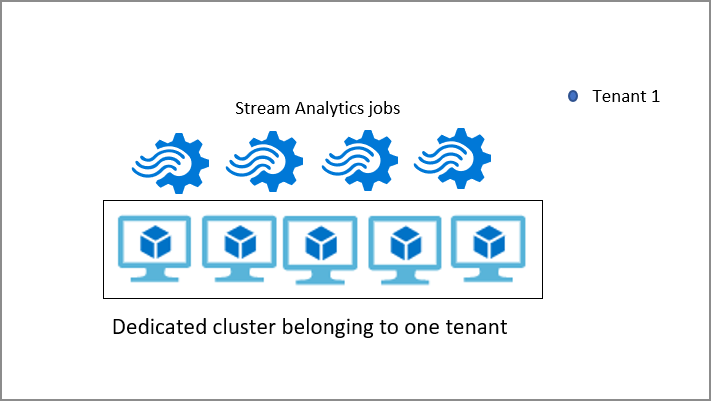
By default, Stream Analytics jobs run in the Standard multi-tenant environment which forms the Standard SKU. Stream Analytics also provides a Dedicated SKU where you can provision an entire Stream Analytics cluster that belongs to you. Doing so gives you full control of which jobs run on your cluster. The minimum size of a Stream Analytics cluster is 12 Streaming Units and you are charged for the entire cluster capacity from when it gets provisioned. You can learn more about the benefits of Stream Analytics clusters and when to use it.
Next steps
Learn how to manage your Azure Stream Analytics and other concepts:
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for