Manage session-scoped packages
In addition to pool level packages, you can also specify session-scoped libraries at the beginning of a notebook session. Session-scoped libraries let you specify and use Python, jar, and R packages within a notebook session.
When using session-scoped libraries, it's important to keep the following points in mind:
- When you install session-scoped libraries, only the current notebook has access to the specified libraries.
- These libraries have no impact on other sessions or jobs using the same Spark pool.
- These libraries install on top of the base runtime and pool level libraries, and take the highest precedence.
- Session-scoped libraries don't persist across sessions.
Session-scoped Python packages
Manage session-scoped Python packages through environment.yml file
To specify session-scoped Python packages:
- Navigate to the selected Spark pool and ensure that you have enabled session-level libraries. You can enable this setting by navigating to the Manage > Apache Spark pool > Packages tab.
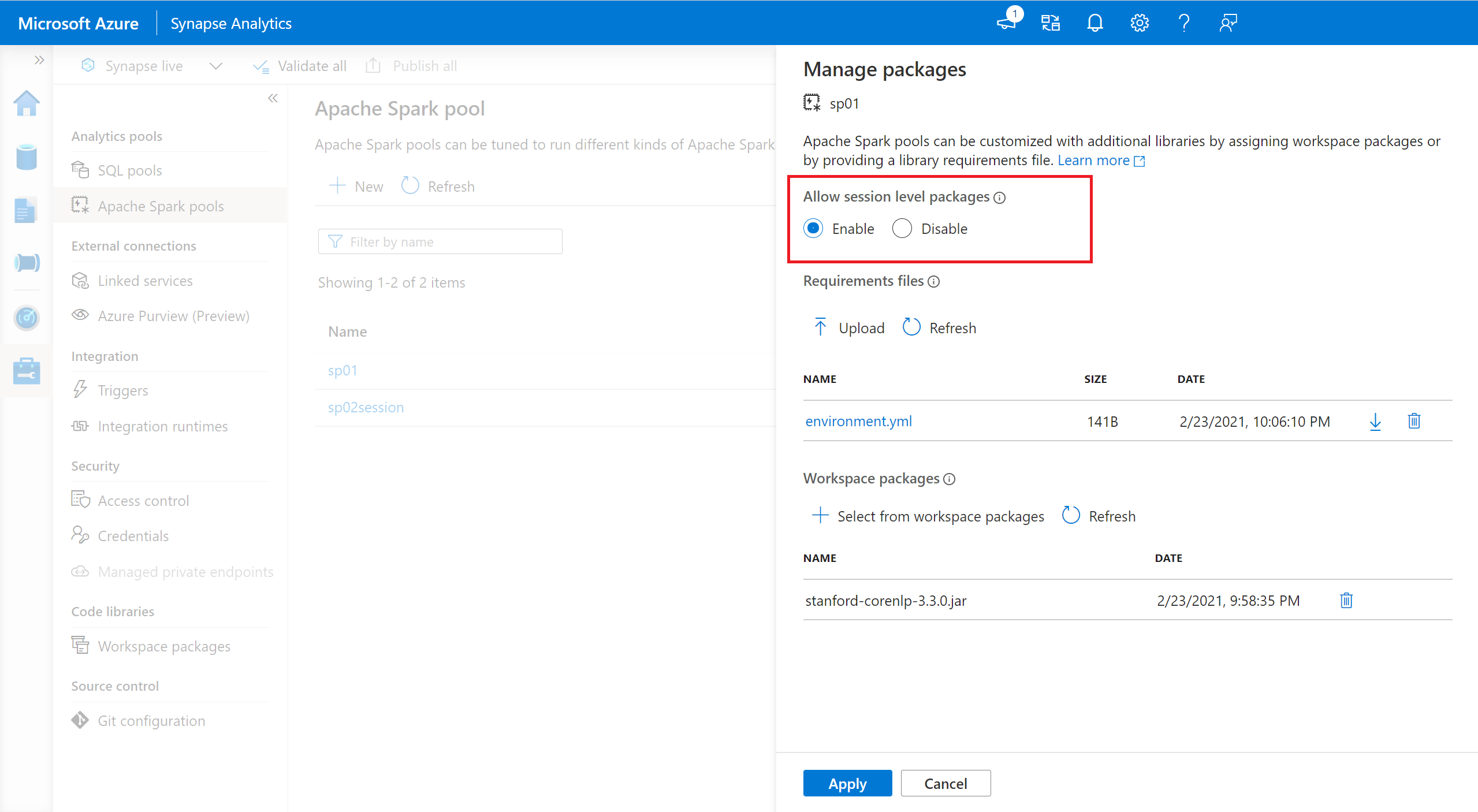
- Once the setting applies, you can open a notebook and select Configure Session> Packages.
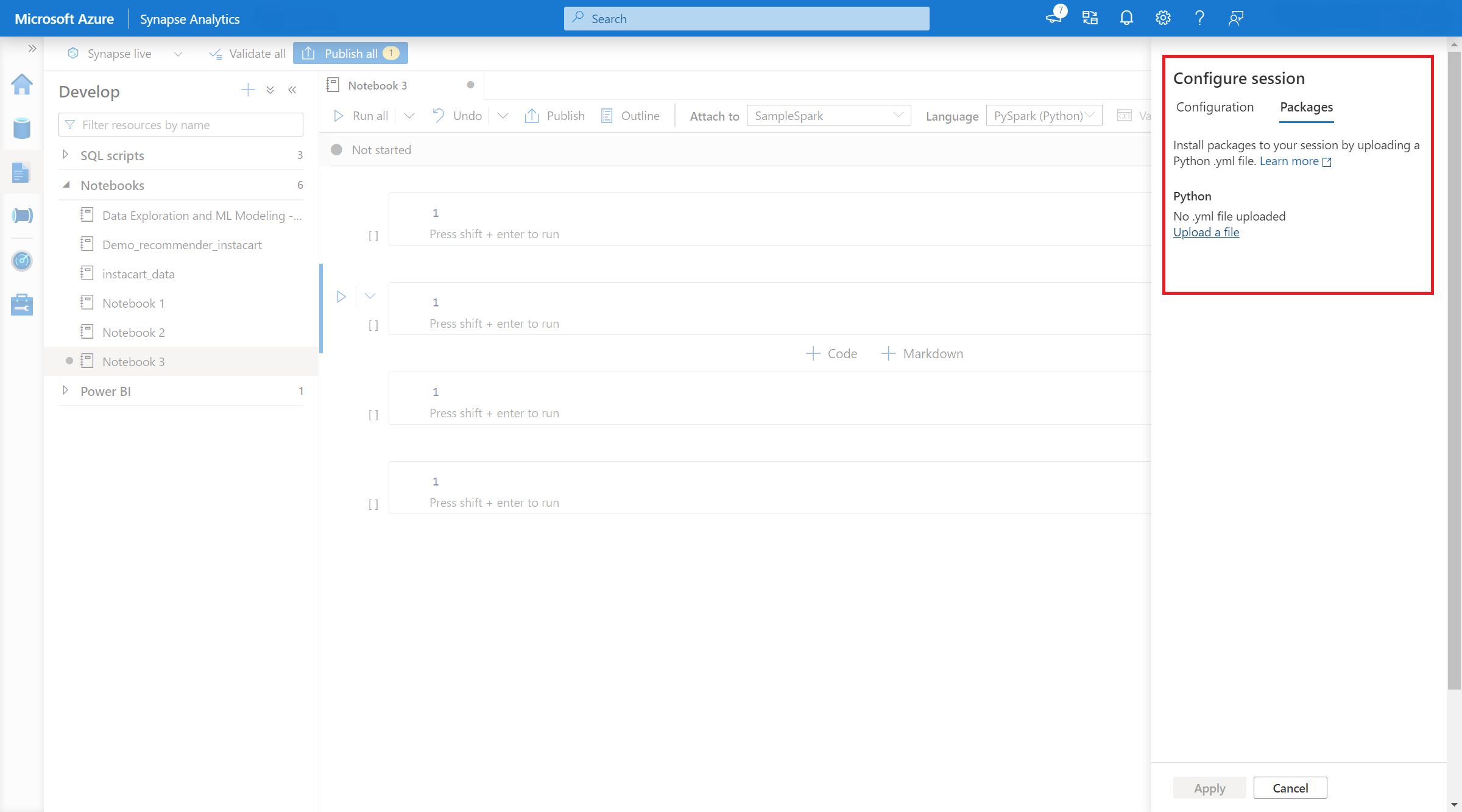
- Here, you can upload a Conda environment.yml file to install or upgrade packages within a session.The specified libraries are present once the session starts. These libraries will no longer be available after session ends.
Manage session-scoped Python packages through %pip and %conda commands
You can use the popular %pip and %conda commands to install additional third party libraries or your custom libraries during your Apache Spark notebook session. In this section, we use %pip commands to demonstrate several common scenarios.
Note
- We recommend to put the %pip and %conda commands at the first cell of your notebook if you want to install new libraries. The Python interpreter will be restarted after the session-level library being managed to bring the changes effective.
- These commands of managing Python libraries will be disabled when running pipeline jobs. If you want to install a package within a pipeline, you must leverage the library management capabilities at the pool level.
- Session-scoped Python libraries are automatically installed across both the driver and worker nodes.
- The following %conda commands are not supported: create, clean, compare, activate, deactivate, run, package.
- You can refer to %pip commands and %conda commands for the full list of commands.
Install a third party package
You can easily install a Python library from PyPI.
# Install vega_datasets
%pip install altair vega_datasets
To verify the installing result, you can run the following code to visualize vega_datasets
# Create a scatter plot
# Plot Miles per gallon against the horsepower across different region
import altair as alt
from vega_datasets import data
cars = data.cars()
alt.Chart(cars).mark_point().encode(
x='Horsepower',
y='Miles_per_Gallon',
color='Origin',
).interactive()
Install a wheel package from storage account
In order to install library from storage, you need to mount to your storage account by running following commands.
from notebookutils import mssparkutils
mssparkutils.fs.mount(
"abfss://<<file system>>@<<storage account>.dfs.core.windows.net",
"/<<path to wheel file>>",
{"linkedService":"<<storage name>>"}
)
And then, you can use the %pip install command to install the required wheel package
%pip install /<<path to wheel file>>/<<wheel package name>>.whl
Install another version of built-in library
You can use the following command to see what's the built-in version of certain package. We use pandas as an example
%pip show pandas
The result is as following log:
Name: pandas
Version: **1.2.3**
Summary: Powerful data structures for data analysis, time series, and statistics
Home-page: https://pandas.pydata.org
... ...
You can use the following command to switch pandas to another version, let's say 1.2.4
%pip install pandas==1.2.4
Uninstall a session-scoped library
If you want to uninstall a package, which installed on this notebook session, you may refer to following commands. However, you cannot uninstall the built-in packages.
%pip uninstall altair vega_datasets --yes
Using %pip command to install libraries from a requirement.txt file
%pip install -r /<<path to requirement file>>/requirements.txt
Session-scoped Java or Scala packages
To specify session-scoped Java or Scala packages, you can use the %%configure option:
%%configure -f
{
"conf": {
"spark.jars": "abfss://<<file system>>@<<storage account>.dfs.core.windows.net/<<path to JAR file>>",
}
}
Note
- We recommend you to run the %%configure at the beginning of your notebook. You can refer to this document for the full list of valid parameters.
Session-scoped R packages (Preview)
Azure Synapse Analytics pools include many popular R libraries out-of-the-box. You can also install extra third party libraries during your Apache Spark notebook session.
Note
- These commands of managing R libraries will be disabled when running pipeline jobs. If you want to install a package within a pipeline, you must leverage the library management capabilities at the pool level.
- Session-scoped R libraries are automatically installed across both the driver and worker nodes.
Install a package
You can easily install an R library from CRAN.
# Install a package from CRAN
install.packages(c("nycflights13", "Lahman"))
You can also use CRAN snapshots as the repository to ensure to download the same package version each time.
install.packages("highcharter", repos = "https://cran.microsoft.com/snapshot/2021-07-16/")
Using devtools to install packages
The devtools library simplifies package development to expedite common tasks. This library is installed within the default Azure Synapse Analytics runtime.
You can use devtools to specify a specific version of a library to install. These libraries will be installed across all nodes within the cluster.
# Install a specific version.
install_version("caesar", version = "1.0.0")
Similarly, you can install a library directly from GitHub.
# Install a GitHub library.
install_github("jtilly/matchingR")
Currently, the following devtools functions are supported within Azure Synapse Analytics:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| install_github() | Installs an R package from GitHub |
| install_gitlab() | Installs an R package from GitLab |
| install_bitbucket() | Installs an R package from BitBucket |
| install_url() | Installs an R package from an arbitrary URL |
| install_git() | Installs from an arbitrary git repository |
| install_local() | Installs from a local file on disk |
| install_version() | Installs from a specific version on CRAN |
View installed libraries
You can query all the libraries installed within your session using the library command.
library()
You can use the packageVersion function to check the version of the library:
packageVersion("caesar")
Remove an R package from a session
You can use the detach function to remove a library from the namespace. These libraries stay on disk until they're loaded again.
# detach a library
detach("package: caesar")
To remove a session-scoped package from a notebook, use the remove.packages() command. This library change has no impact on other sessions on the same cluster. Users can't uninstall or remove built-in libraries of the default Azure Synapse Analytics runtime.
remove.packages("caesar")
Note
You can't remove core packages like SparkR, SparklyR, or R.
Session-scoped R libraries and SparkR
Notebook-scoped libraries are available on SparkR workers.
install.packages("stringr")
library(SparkR)
str_length_function <- function(x) {
library(stringr)
str_length(x)
}
docs <- c("Wow, I really like the new light sabers!",
"That book was excellent.",
"R is a fantastic language.",
"The service in this restaurant was miserable.",
"This is neither positive or negative.")
spark.lapply(docs, str_length_function)
Session-scoped R libraries and SparklyR
With spark_apply() in SparklyR, you can use any R package inside Spark. By default, in sparklyr::spark_apply(), the packages argument sets to FALSE. This copies libraries in the current libPaths to the workers, allowing you to import and use them on workers. For example, you can run the following to generate a caesar-encrypted message with sparklyr::spark_apply():
install.packages("caesar", repos = "https://cran.microsoft.com/snapshot/2021-07-16/")
spark_version <- "3.2"
config <- spark_config()
sc <- spark_connect(master = "yarn", version = spark_version, spark_home = "/opt/spark", config = config)
apply_cases <- function(x) {
library(caesar)
caesar("hello world")
}
sdf_len(sc, 5) %>%
spark_apply(apply_cases, packages=FALSE)
Next steps
- View the default libraries: Apache Spark version support
- Manage the packages outside Synapse Studio portal: Manage packages through Az commands and REST APIs
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for