Sorting Data (C#)
A sorting operation orders the elements of a sequence based on one or more attributes. The first sort criterion performs a primary sort on the elements. By specifying a second sort criterion, you can sort the elements within each primary sort group.
The following illustration shows the results of an alphabetical sort operation on a sequence of characters:
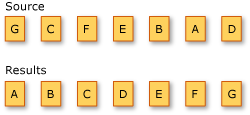
The standard query operator methods that sort data are listed in the following section.
Methods
| Method Name | Description | C# Query Expression Syntax | More Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| OrderBy | Sorts values in ascending order. | orderby |
Enumerable.OrderBy Queryable.OrderBy |
| OrderByDescending | Sorts values in descending order. | orderby … descending |
Enumerable.OrderByDescending Queryable.OrderByDescending |
| ThenBy | Performs a secondary sort in ascending order. | orderby …, … |
Enumerable.ThenBy Queryable.ThenBy |
| ThenByDescending | Performs a secondary sort in descending order. | orderby …, … descending |
Enumerable.ThenByDescending Queryable.ThenByDescending |
| Reverse | Reverses the order of the elements in a collection. | Not applicable. | Enumerable.Reverse Queryable.Reverse |
The following examples in this article use the common data sources for this area:
public enum GradeLevel
{
FirstYear = 1,
SecondYear,
ThirdYear,
FourthYear
};
public class Student
{
public required string FirstName { get; init; }
public required string LastName { get; init; }
public required int ID { get; init; }
public required GradeLevel Year { get; init; }
public required List<int> Scores { get; init; }
public required int DepartmentID { get; init; }
}
public class Teacher
{
public required string First { get; init; }
public required string Last { get; init; }
public required int ID { get; init; }
public required string City { get; init; }
}
public class Department
{
public required string Name { get; init; }
public int ID { get; init; }
public required int TeacherID { get; init; }
}
Each Student has a grade level, a primary department, and a series of scores. A Teacher also has a City property that identifies the campus where the teacher holds classes. A Department has a name, and a reference to a Teacher who serves as the department head.
Primary Ascending Sort
The following example demonstrates how to use the orderby clause in a LINQ query to sort the array of teachers by family name, in ascending order.
IEnumerable<string> query = from teacher in teachers
orderby teacher.Last
select teacher.Last;
foreach (string str in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
The equivalent query written using method syntax is shown in the following code:
IEnumerable<string> query = teachers
.OrderBy(teacher => teacher.Last)
.Select(teacher => teacher.Last);
foreach (string str in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
Primary Descending Sort
The next example demonstrates how to use the orderby descending clause in a LINQ query to sort the teachers by family name, in descending order.
IEnumerable<string> query = from teacher in teachers
orderby teacher.Last descending
select teacher.Last;
foreach (string str in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
The equivalent query written using method syntax is shown in the following code:
IEnumerable<string> query = teachers
.OrderByDescending(teacher => teacher.Last)
.Select(teacher => teacher.Last);
foreach (string str in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
Secondary Ascending Sort
The following example demonstrates how to use the orderby clause in a LINQ query to perform a primary and secondary sort. The teachers are sorted primarily by city and secondarily by their family name, both in ascending order.
IEnumerable<(string, string)> query = from teacher in teachers
orderby teacher.City, teacher.Last
select (teacher.Last, teacher.City);
foreach ((string last, string city) in query)
{
Console.WriteLine($"City: {city}, Last Name: {last}");
}
The equivalent query written using method syntax is shown in the following code:
IEnumerable<(string, string)> query = teachers
.OrderBy(teacher => teacher.City)
.ThenBy(teacher => teacher.Last)
.Select(teacher => (teacher.Last, teacher.City));
foreach ((string last, string city) in query)
{
Console.WriteLine($"City: {city}, Last Name: {last}");
}
Secondary Descending Sort
The next example demonstrates how to use the orderby descending clause in a LINQ query to perform a primary sort, in ascending order, and a secondary sort, in descending order. The teachers are sorted primarily by city and secondarily by their family name.
IEnumerable<(string, string)> query = from teacher in teachers
orderby teacher.City, teacher.Last descending
select (teacher.Last, teacher.City);
foreach ((string last, string city) in query)
{
Console.WriteLine($"City: {city}, Last Name: {last}");
}
The equivalent query written using method syntax is shown in the following code:
IEnumerable<(string, string)> query = teachers
.OrderBy(teacher => teacher.City)
.ThenByDescending(teacher => teacher.Last)
.Select(teacher => (teacher.Last, teacher.City));
foreach ((string last, string city) in query)
{
Console.WriteLine($"City: {city}, Last Name: {last}");
}
See also
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
