Supported composite data types for Electronic reporting formulas
This article provides information about the composite data types that are supported in Electronic reporting (ER) expressions. The composite data types are class, container, record, record list, and object.
Class
The class data type refers to a public application class. In ER, it's represented as a record that contains a separate field for every public method of the referenced class. When the call of the method is parameterized, you must also specify the required arguments of the appropriate types in an ER expression that is configured to call the method.
In ER mapping and format components, you can add the Class data source that is presented as a data source and that returns a value of the class type. This data source exposes public methods of the class that can be called at runtime.
Note
Only methods that return a value can be called from ER expressions.
Only methods that have a range of zero to eight arguments can be called from ER expressions.
The default value of a class is null.
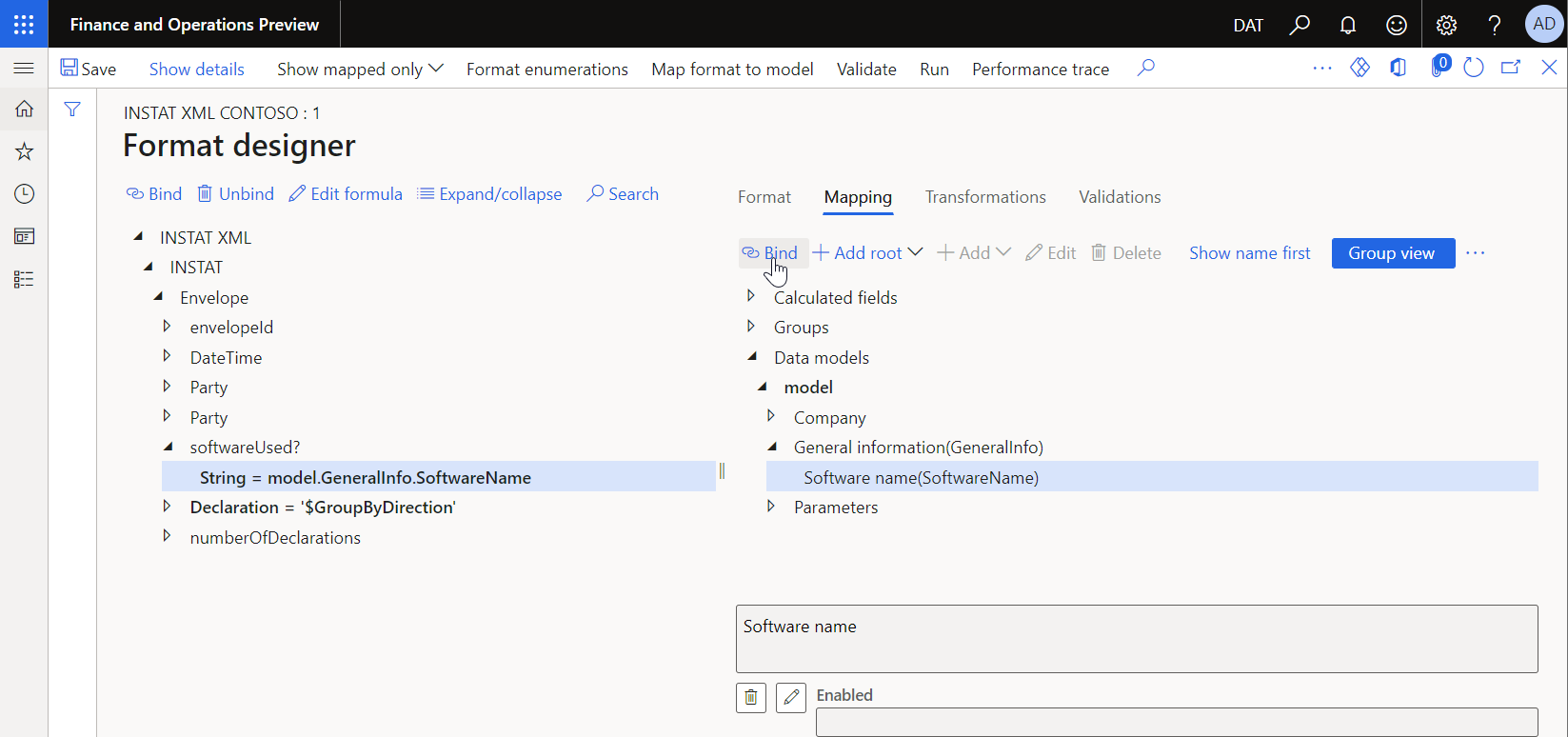
The following illustration shows how the System information(xInfo) data source of the Class type is added to make the instance of the xInfo application class and call its productName() method to receive the name of the current application. The name of the current application is fetched at runtime by execution of the xInfo.productName binding that was configured for the Software name(SoftwareName) field of the ER data model. This binding calls the productName() method of the xInfo application class that is represented in the current model mapping as the System information(xInfo) data source.
The following illustration shows how the ER format is configured to put the provided application name in generated documents. The Software name(SoftwareName) field of the used data model was bound to the String component that is nested under the softwareUsed XML element of the ER format. So, the name of the current application is placed at runtime to the softwareUsed XML element of a generated document in XML format.
Container
The container data type holds binary content. A container value can be used to pass specific information from storage to a generated document. In the ER framework, this data type is frequently used to put media content such as a company logo in generated documents.
Note
Although every media item can be represented as a container value, not every container value represents a media item. Therefore, if you configure an ER format so that it uses a container to put an image in generated documents, but the referenced container doesn't return media content, an exception that resembles the following example might be thrown: "Error executing code: Binary (object), method constructFromContainer called with invalid parameters."
The default value of a container is null.
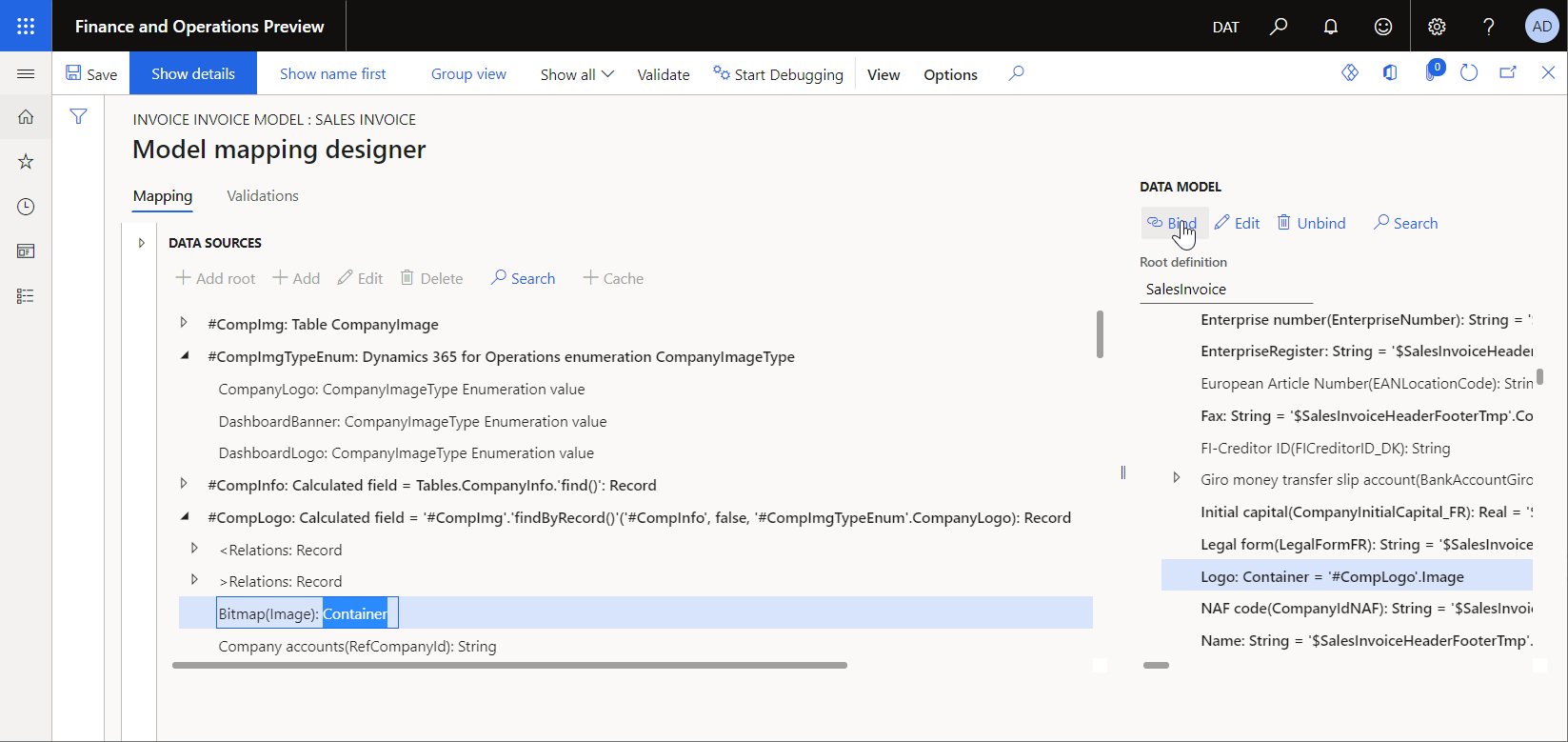
The following illustration shows how the Bitmap(Image) field of the Container type is bound to the data model Logo field of the Container type in the Sales invoice model mapping. This binding makes the company logo available to any ER format that is designed for the SalesInvoice root definition and that uses this model mapping at runtime.
Record
A record is a collection of named fields, each of which is associated with a value of either a primitive data type or a composite data type. Usually, a record is used to represent a single record of a record list. In this case, every item represents individual fields, methods, and relations.
The default value of a record is empty.
Note
When you get the value of a field of an empty record, the default value of the appropriate data type is returned.
A record can be obtained by using the following functions:
For more information about the transformation of record values, see List of ER functions in the list category.
Record list
A record list is a list of items of the record type. Usually, a record list is used to represent the list of records that has been fetched from a database table.
By default, records of a record list are accessed sequentially. To access a specific record, you can use the INDEX function and specify the integer index.
The default value of a record list is empty. You can use the ISEMPTY function to evaluate whether a record list is empty.
Note
If a record list is empty, any attempt to get a field value for a record in it causes an exception to be thrown at runtime. To learn how you can help prevent runtime exceptions of this type, see Consideration of empty list cases.
A record list can be initiated by using the following functions:
For more information about the transformation of record list values, see List of ER functions in the list category. To learn how to introduce record list items, fill them with application data, and then use the data to generate business documents, see Design a new ER solution to print a custom report.
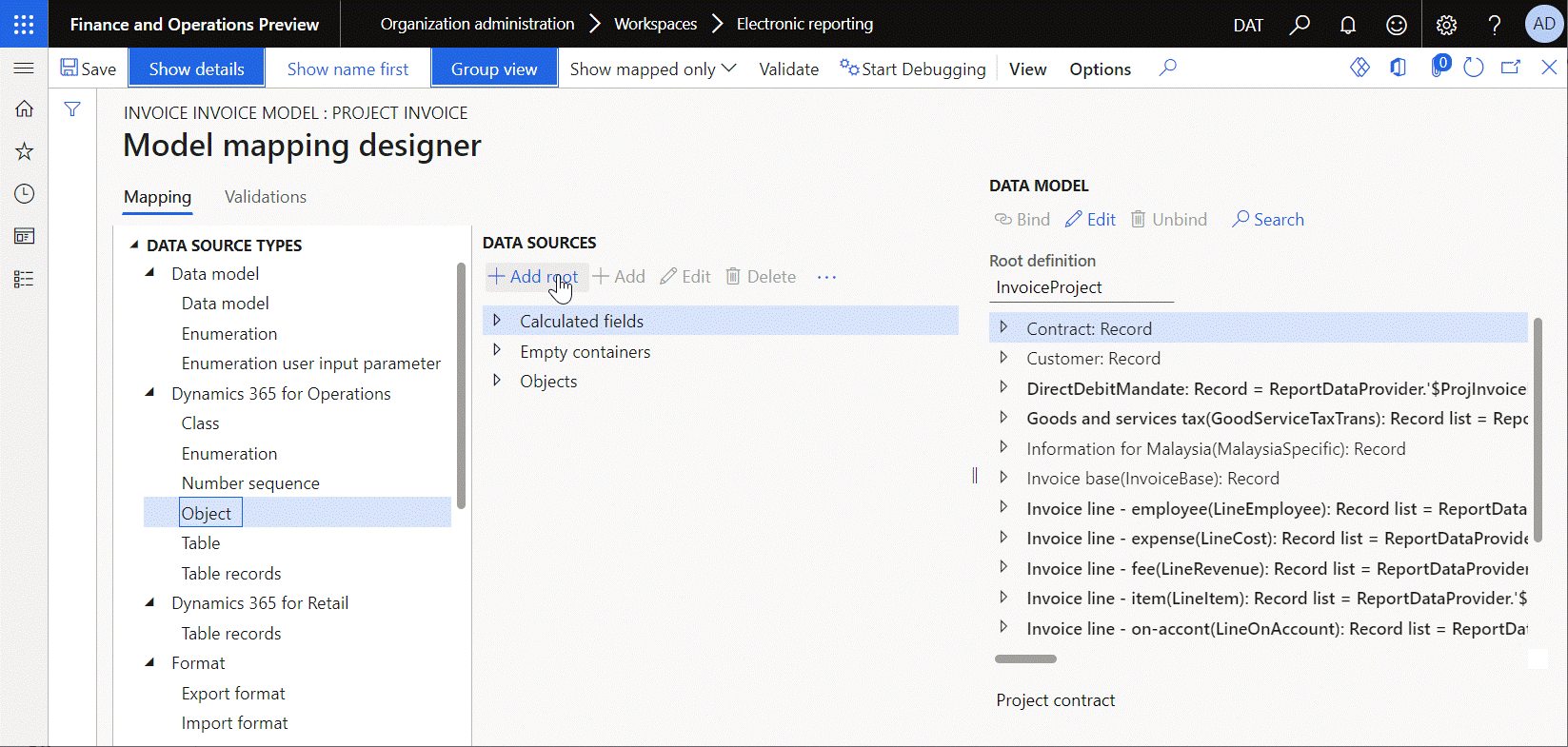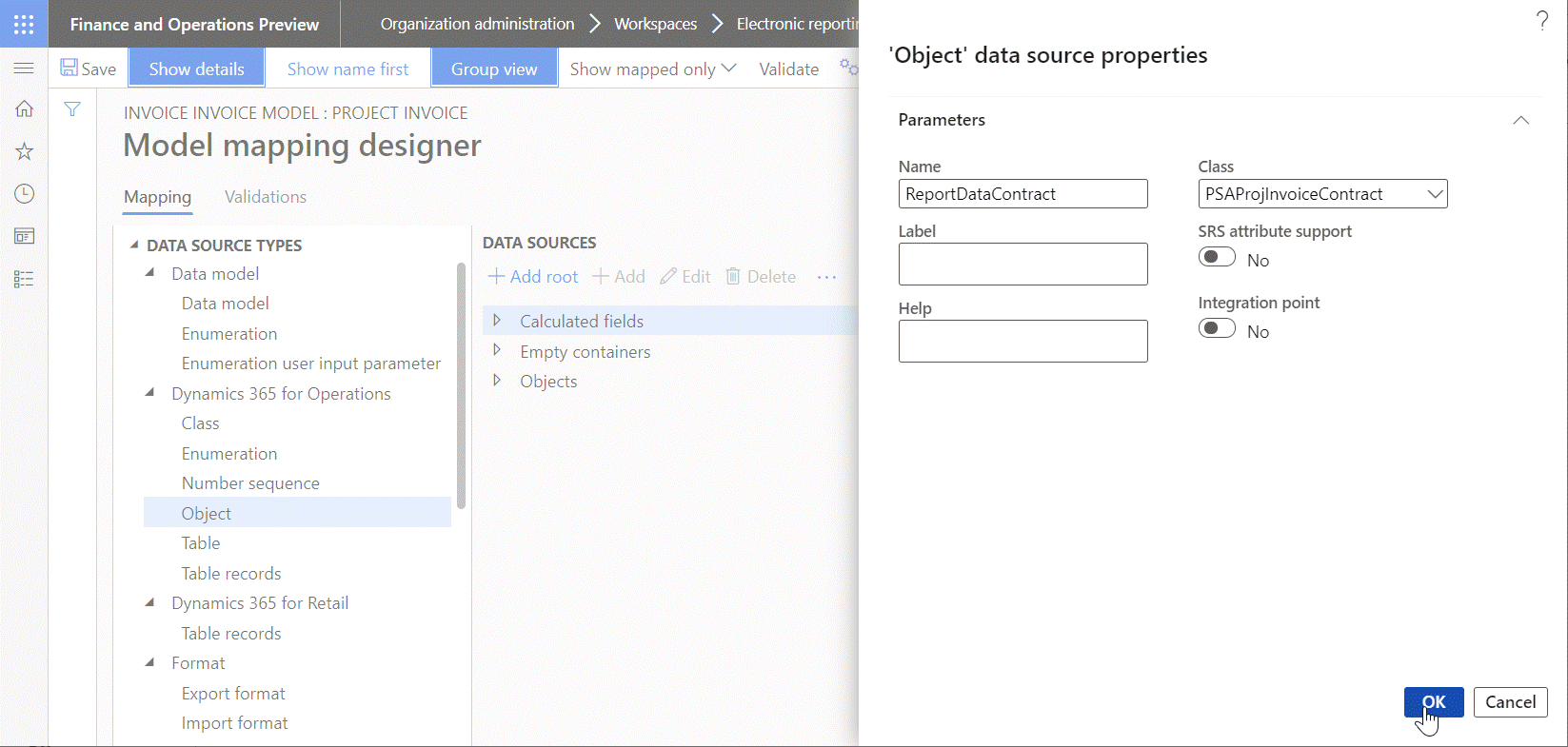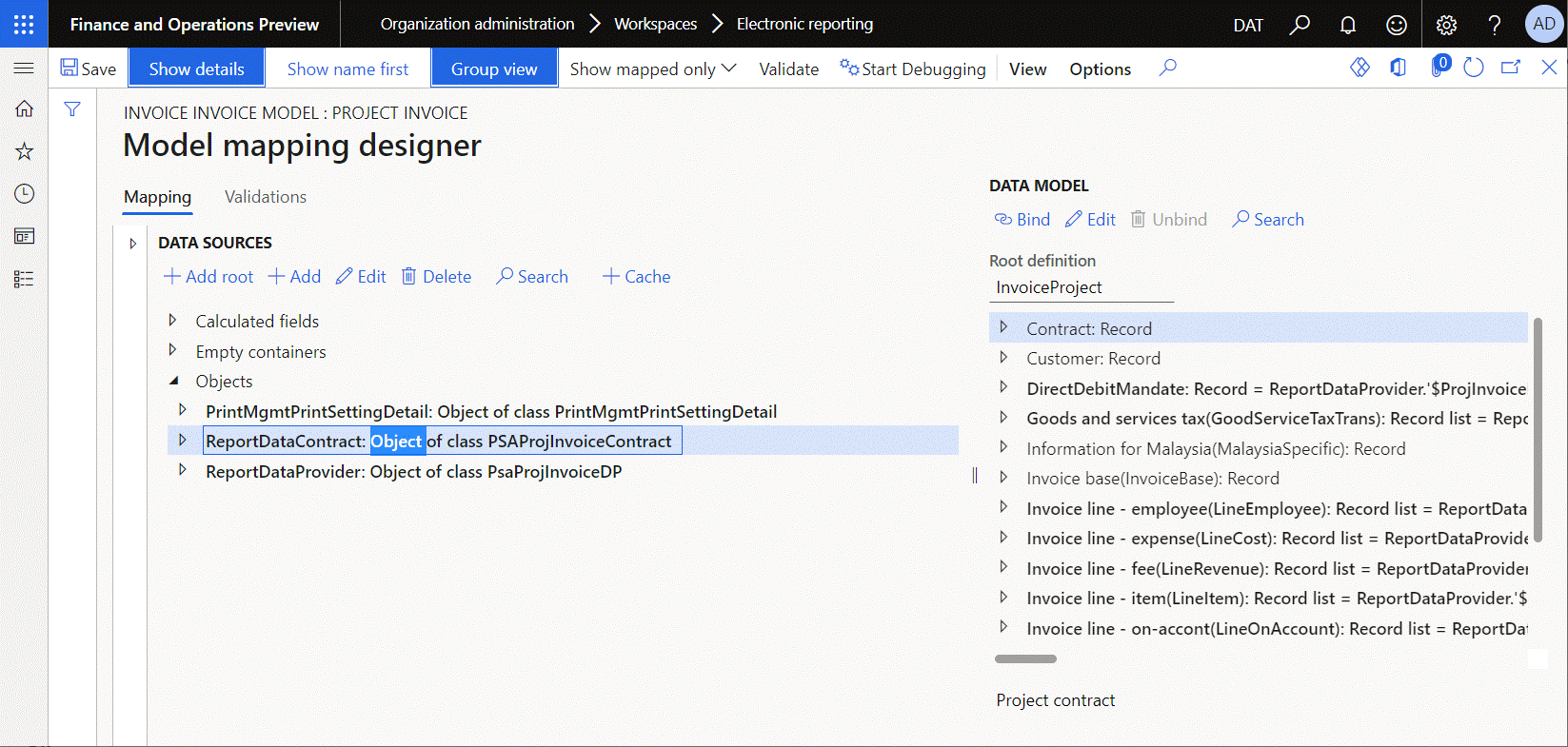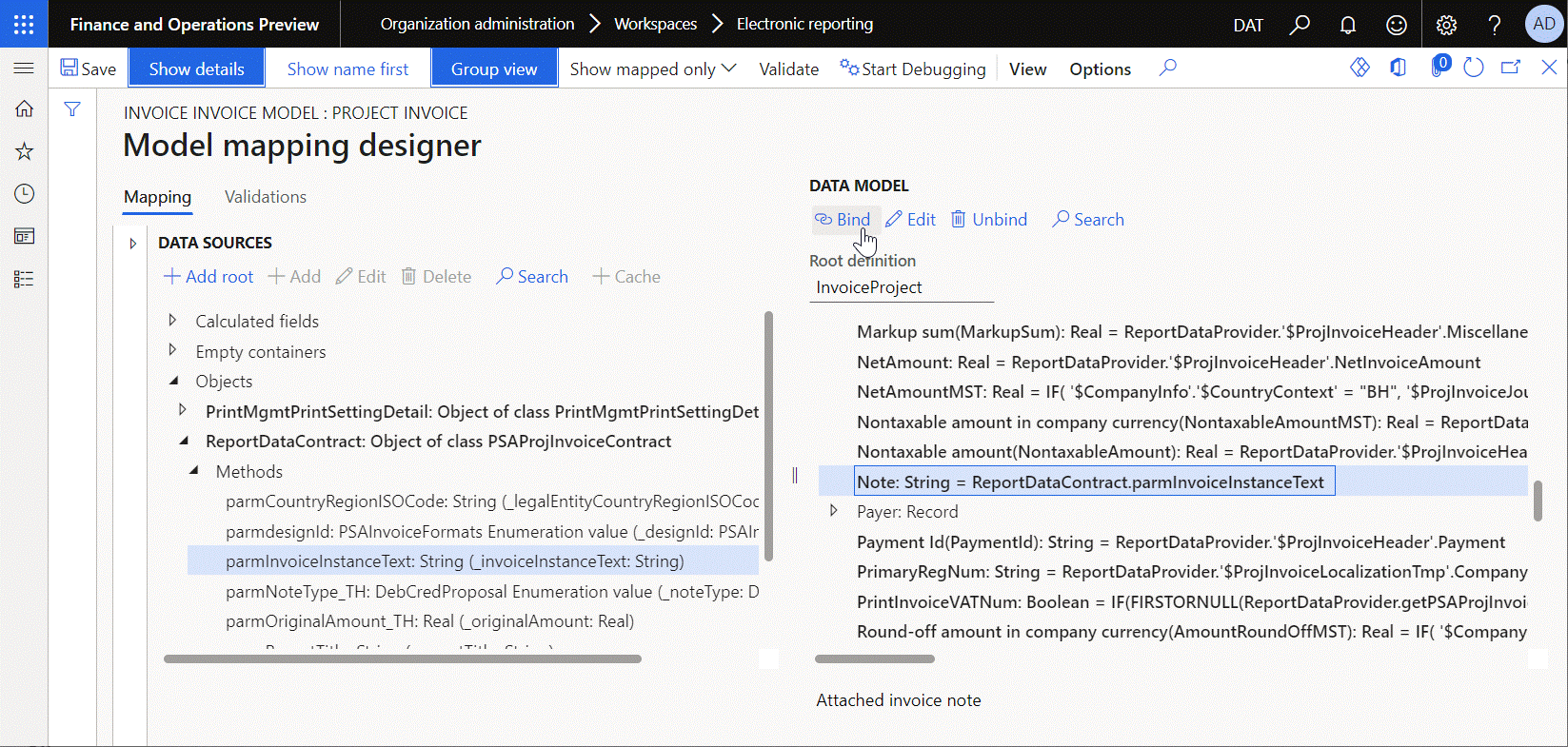
Object
An object refers to a stateful instance of a class. Usually, an object is initiated in source code. It's then passed to an ER model mapping and provides details of the execution context.
The default value of an object is null.
The following illustration shows how the ReportDataContract data source of the Object type is added to pass information about a generated invoice from source code to the Project invoice model mapping. For example, the invoice instance text is passed as part of the execution context. This text is taken from source code at runtime by execution of the ReportDataContract.parmInvoiceInstanceText binding that was configured for the Note field of the ER data model. This binding calls the parmInvoiceInstanceText() method of the PSAProjInvoiceContract application class that is represented in the current model mapping as the ReportDataContract data source.
To learn how to pass details of the execution context from source code to the running ER solution, see Develop application artefacts to call the designed report.
Additional resources
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for