Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The following diagram shows how NAP is deployed with a DHCP Server.
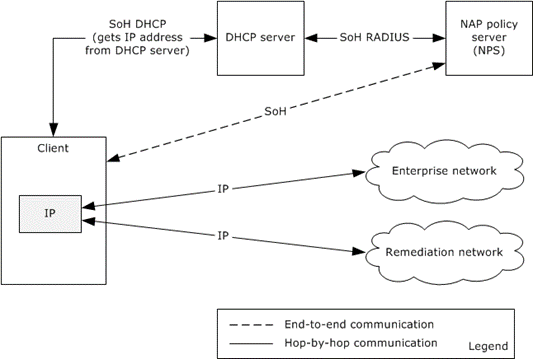
Figure 6: NAP deployment with DHCP server
Some enterprise networks control network access at Layer Three by controlling IP address assignment with DHCP ([RFC2131]). In this scenario, the SoH/SoHR is transported from the client to the DHCP server by using a DHCP option ([MS-DHCPN]). The DHCP server uses RADIUS to communicate with the NPS. Based on the policy evaluation by the NPS, the DHCP server can grant the client an IP address to use on the enterprise network, refuse to grant an IP address, or assign an IP address to a remediation network. The remediation network has servers that allow the client to perform remediation for updated software, new virus signatures used by anti-virus checkers, or scripts to configure host based firewalls on the client.
If the NPS determines that the client requires remediation, the DHCP server can give the client an IP address that has limited access to network resources to enable the client to access resources required to perform remediation. These resources can include software distribution servers, Group Policy servers, or configuration file servers. After remediation, the client retries accessing the network to obtain a new IP address that has full access to the enterprise network.