Known limitations and troubleshooting with virtual tables
This article describes the known limitations and troubleshooting tips when working with virtual tables in Microsoft Dataverse.
Known limitations
The following is a list of known limitations for virtual tables created using the virtual connector provider.
General
- The table or list used must include at least one string field to be used as the primary field, and one GUID field. Without these string fields, the virtual table can't be created and an error will be generated during the table details retrieval stage.
- SharePoint uses the hidden numeric ID field present in all lists
- SQL can use a GUID or integer field
- Excel must have a GUID field
- Dataverse can only create columns that include data types compatible with Dataverse. This includes the following data types:
- String
- Multiline text (memo)
- Whole Number/Integer
- Decimal
- Float
- Date/time
- Yes/No (boolean)
- Choices (multi-value select)
- Hyperlink/Url
- Data types not supported for virtual tables:
- File and attachments
- Image
- Lookup
- Maximum length of characters allowed for a text column in a virtual table is 4,000 characters. If the source table has a maximum character limit greater than this value, any create/update operation exceeding the max character limit results in a validation error, and the operation fails.
- Virtual table queries are limited to return 1,000 records. If you have a 1:N or N custom multi-table (polymorphic) relationship with a virtual table, any query exceeding this limit fails and provides an error. Use filtering in your query to reduce the record set as a workaround to this limitation.
- Audit functionality isn't available for Virtual Tables, this is because Dataverse can only perform and store audit data for locally stored data.
- Rollups and calculated fields can't be calculated for virtual tables. This is because rollups are a server side calculation in Dataverse, which requires the data to be stored locally.
- The Microsoft Entra ID virtual table provided by Microsoft only allows read access.
- Dataverse virtual tables can display values in fields that exceed the normal maximum values of Dataverse. This behavior is because the values being presented aren't stored locally. For example, the Dataverse integer maximum value is 100,000,000,000, but it could retrieve and display 9,000,000,000,000 from SharePoint. However, if the user attempts to edit the number to a size larger than the max accepted size in Dataverse an error is provided indicating the record can't be saved because it exceeds the maximum size.
- Import and export functionality of table data isn't supported for virtual tables.
For each data source
The following are limitations for each data source.
- SQL virtual tables can use a GUID or an Integer field for the Primary Key for functionality.
- SQL Server tables without primary keys: Any nonstring field can be selected as the primary key. The virtual table should be created successfully. RetrieveMultiple works, the other operations fail with the following error message (coming from SQL connector): "APIM request wasn't successful: BadRequest: No primary key exists in table". For functionality a GUID or integer field must be used as the primary key.
- SQL Server tables using a string primary key: The SQL string primary key is the only option available for the virtual table primary key. SQL Server string primary keys are supported only if the values can be parsed as GUID. If they can't be parsed as a GUID, the virtual table creation succeeds, but fails at runtime with the following errors:
- Maker Portal: "We weren't able to open your table. Try reloading or reopening."
- Network trace: "String primary keys are supported only if they can be parsed as GUID."
- SQL Server tables without nonprimary key string fields for use as the Primary Name: If the SQL table doesn't have a string field available to use as the Primary Name, we display the following error in the Configuration step: "The table doesn't have a primary field"
- SQL views can be used to create a virtual table but they'll only provide read operations.
- For SQL Server Connector limitations, go to SQL Server connector reference.
- SQL data type bigint columns in the source table is mapped as a decimal data type in Dataverse virtual tables. When platform support is available for bigint mapping to a whole number, previously created columns in the virtual table need to be deleted, and new columns should be created.
- The following column types can't be included in a virtual table at this time:
- Time
- Datetime2
- Image
- Geometry
- Geography
- RowVersion
- The following column types are included in a virtual table but are only shown as text fields:
- HierarchyID
- XML
- Sqlvariant
Troubleshooting
There's only one (1) record in your virtual table even though you have more in your source table.
Solution: Check your source table and make sure it has primary key defined.I get one of the following errors when Power Apps (make.powerapps.com) is retrieving my table list or when I select Finish to create my table:
- "Resource not found for the segment
msdyn_get_required_fields" - “Error calling... please verify that connection... exists in environment”
- "Sequence matches no element for
msdyn_get_required_fields"
Solution: In some cases you might not have the most up to date solution for the virtual connector provider. To determine whether your virtual connector provider solution needs an update:
- Select Solutions on the left navigation pane. If the item isn’t in the side panel pane, select …More and then select the item you want.
- Select the History tab.
- Search for ConnectorProvider.
- View the information to see whether the solution needs to be updated.
- If the history indicates an update is needed, go to the Microsoft commercial marketplace search for Virtual Connector Provider, and then select Get it now to import the solution into your environment.
- Follow the steps to create the virtual table again.
- "Resource not found for the segment
A message is displayed “Connection ‘xyz’ not found in current environment.” when retrieving the list of connections.
Solution: This occurs when there are a large number of connections in the user's Dataverse environment. This is fixed with version 1,029 of the Connector Provider solution. The updated version should be in all regions by February 20, 2023. To determine whether your virtual connector provider solution needs an update:- Select Solutions on the left navigation pane. If the item isn’t in the side panel pane, select …More and then select the item you want.
- Select the History tab.
- Search for ConnectorProvider.
- View the information to see whether the solution needs to be updated.
- If the history indicates an update is needed, go to the Microsoft commercial marketplace search for Virtual Connector Provider, and then select Get it now to import the solution into your environment.
- Follow the steps to create the virtual table again.
I get notified that a timeout occurred during the virtual table creation.
Solution: This can occur when other existing jobs cause the virtual table creation to be delayed. Wait for a few minutes and try again.I get notified that "An unexpected error occurred"
Solution: This occurs when the virtual table data source was created with invalid values. To resolve this, you'll need to locate the virtual table data source that is causing the error, delete it, and then recreate the virtual table.- Select Settings (gear icon) > Advanced settings from Power Apps.
- In the top menu, select Settings.
- Go to Solutions. If the item isn’t in the side panel pane, select …More and then select the item you want.
- Go to the solution that includes your virtual table (if you weren't using a solution then go to Common Data Services Default Solution).
- In the left hand panel, select Virtual table data sources.
- Double-click on each data source (they all start with VCP_DS_..."), when you locate the one with the error, delete that data source.
- Recreate your virtual table.
A message is displayed "This table already exists, you're recreating the table. Primary field and Schema name can't be changed."
Solution: This table has previously been created. Continuing with the creation will re-create the table, this results in any table changes made at the data source to be updated in the virtual table (this includes addition or removal of fields). The custom name and primary field values won't be editable.Error message: “primary_key_name can't be empty”
Solution: You have chosen a table or list that doesn't include a GUID value for the primary key. You'll need to add an additional GUID column in your source table in order to create a virtual table.I created an Excel virtual table but I can't see it in "Tables".
Solution: Since the virtual table creation is asynchronous, you can check the status of the process in System Jobs. Look for system jobs with a Name startingMicrosoft.Wrm.DataProvider.Connector.Plugins.ConnectorGenerateVEPluginand a Regarding column's value equal to the name of the new virtual table. If status is still In Progress, just wait for the job to complete. If there's an error, you can get details by clicking the system, job name hyperlink. In this example, table creation is still pending: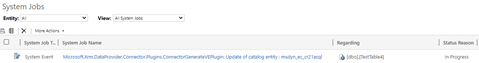
Here, table creation failed due to 429 "Too Many Requests" error:
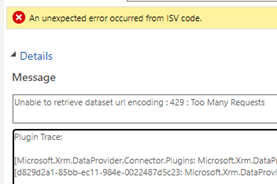
Table creation's system job succeeded but I'm getting runtime errors related to invalid or missing columns
Solution: If a failure occurs while creating a table's field, the table creation process won't fail and try to continue with the remaining fields. This is because we don't want to block the virtual table creation when some column types are unsupported. To get details on the error, you can enable logging in Administration> System Settings > Customizations > Enable logging to plug-in trace log, then delete the virtual table and try to create it again.
Next steps
Create virtual tables using the virtual connector provider (preview)
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for