CoE ALM Accelerator for Power Platform branching and merging (Deprecated)
Note
The CoE CLI is deprecated and will be removed in a future release. Please use the Power Platform Project Setup Wizard to set up and manage your ALM Accelerator for Power Platform projects.
Development as a team of makers, advanced makers, and professional developers often uncovers new concepts. One area of complexity is branching and merging. Using the links below, different personas can review each concept and determine their level of comfort.
Branching and merging - Review approaches to branching and merge changes between team members and push changes to test and production environments.
Pull request - Determine how changes will be reviewed and merged.
Build pipelines - What build pipelines are and how they help automate the integration and deployment process.
The ALM Accelerator for Power Platform (AA4PP) builds on these concepts to allow Power Platform solutions to be managed.
Example
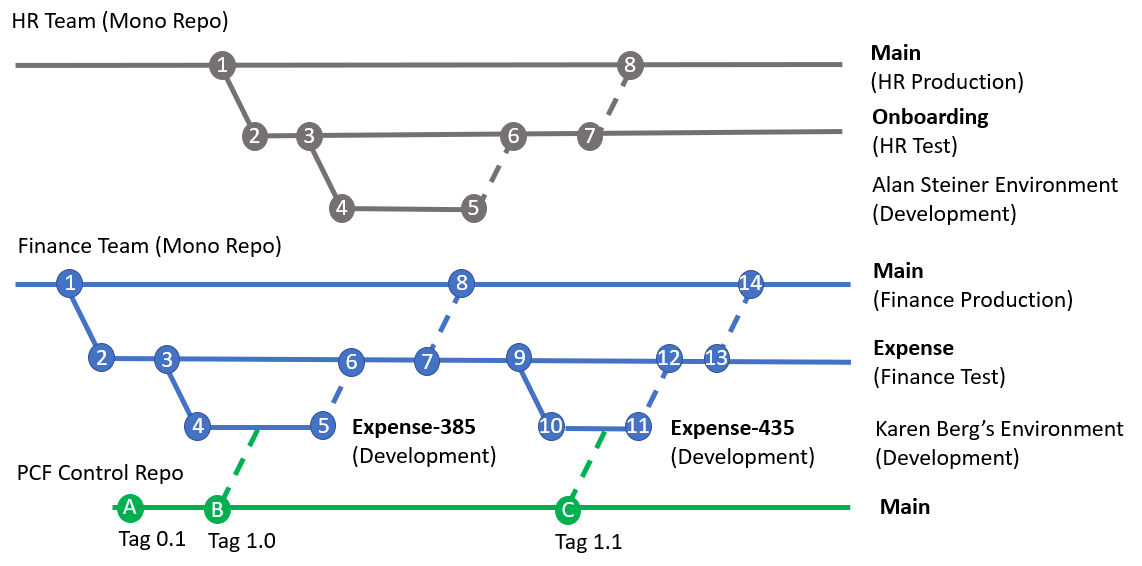
The example below illustrates two parts of the organization the HR and Finance teams use different DevOps projects to manage related solutions for each department.
Human Resources team
The Human Resources team manages one Azure DevOps Git repository that stores each solution as a folder within the repository. This approach allows makers in the HR team to see and collaborate on Human Resources related solutions.
Human Resources team steps
Create a new Azure DevOps project and from the main branch for a new solution branch named Onboarding.
coe alm branch \ -o https://dev.azure.com/contoso \ -p HR \ -r HR-Solutions \ -d Onboarding \ -s validation=https://contoso-hr-validation.crm.dynamics.com,test=https://contoso-hr-test.crm.dynamics.com,https://contoso-hr.crm.dynamics.com
More information: CoE ALM branch
After this command is run, a default branch with Azure Pipelines is created in the repository.
The advanced maker Alan creates an unmanaged solution named Onboarding in the development environment.
Using the AA4PP administration application Alan created a new feature branch and pushes the changes to Git.
Once the initial set of features is complete, select Create Pull Request using the AA4PP Administration application. The validation build pipeline is executed. The pull request is approved and then the feature branch is committed to the solution branch.
The merged commit triggers a continuous deployment to the test environment.
The sets of features are ready for a production deployment. A pull request can be made to merge changes into the main branch.
The build and deployment pipelines can be configured to package the solution to the production environment.
Finance
The Finance team maintains a separate Azure DevOps project for finance related solutions. This Azure DevOps project could be in any of the following locations:
The same Azure DevOps project with a different repository from the HR team. For example, there could be different repositories named HR-Solutions and Fin-Solutions.
A separate Azure DevOps project and repository. This approach of separate projects and repositories could allow different role-based security rights to be defined for team department.
A separate Azure DevOps organization, project, and repository. This configuration would allow different Microsoft Entra tenants to be used.
Finance steps
Karen as the advanced maker in the Finance team follows a similar process to what Alan did inside the HR team.
Karen creates a new Azure DevOps solution branch for the Expense application.
coe alm branch \ -o https://dev.azure.com/contoso \ -p Finance \ -r Finance-Solutions \ -d Expense \ -s validation=https://contoso-fin-validation.crm.dynamics.com,test=https://contoso-fin-test.crm.dynamics.com,https://contoso-fin.crm.dynamics.comMore information: CoE ALM branch command
After this command is run, a default branch with Azure Pipelines is created in the repository.
Karen creates an unmanaged solution named Expense in the development environment.
Using the AA4PP Administration application, Karen creates a new feature branch with the ID of the work item that has been assigned 385 and Push changes to Git.
Once the initial set of features is complete, select Create Pull Request using the AA4PP Administration application. The validation build pipeline is executed. The pull request is approved and then the feature branch is committed to the solution branch.
The merged commit triggers a continuous deployment to the test environment.
When the features are ready for a production deployment, a pull request can be made to merge changes into the main branch.
The build and deployment pipelines can be configured to package the solution to the production environment.
Contribute a new feature to the solution by repeating steps 4 through 8.
PowerApps Component Framework (PCF)
In this example, the finance application makes use of a common component to visually interact with their data.
This PCF component is managed in a separate code repository. As new releases are created, they are tagged with release versions.
A release version is imported into a feature branch for a Power Platform solution. This approach allows different versions of the PCF control to be developed and integrated with different solutions over time. In the finance example, version 1.0 to 1.1, which is committed to the Expense-435 branch to update the PCF control, is used.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for