ToolboxNew Products for IT Pros
Greg Steen
Manage Boot Configuration Data
VistaBootPRO
Every IT pro I know has at least one or two multi-boot machines. Today, those systems usually include an instance of Windows Vista® or Windows Server® 2008, formerly code-named "Longhorn." If you are running a multi-boot system with one of these operating systems, you might want to take a look at VistaBootPRO from PROnetworks.
As you probably know, starting with Windows Vista and moving forward, Microsoft has changed the way boot configuration is managed. Instead of using a readable text file like Boot.ini, you now get the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) store. This provides a more secure and firmware-independent approach to managing boot environment details. There are three basic ways you can look at and modify your BCD. The first is to use MSConfig, which gives you basic access to read, modify, and re-order entries in the BCD. System administrators are likely most familiar with the second option, which is to use the command-line tool BCDEdit. With this tool, you can create a new BCD store, modify existing stores, and import or export stores for archiving and reuse. The third option is to manage the BCD programmatically using its Windows® Management Instrumentation (WMI) API.
All three of these methods get the job done, but none of them are particularly user-friendly. This is where VistaBootPRO comes in, with a friendlier GUI for modifying the boot configuration on your machine running Windows Vista. The tool lets you easily rename OS entries, add new entries, change the boot drive, and configure timeout options with just a click or two. In addition, VistaBootPRO lets you select an OS entry and set startup parameters, such as limiting the CPUs available to the OS, enabling or disabling Data Execution Prevention for Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 entries, reducing the physical memory available to the OS and running the boot process in debug mode.
Before you make any changes to your BCD using this tool, you should back up your current store in case something goes awry. The application will warn you if you haven't made a backup, and it provides an easy way to export the current configuration. And, of course, VistaBootPRO lets you restore backed up configurations.
All in all, VistaBootPRO is a simple-to-use, well-featured application for managing your BCD. Best of all, it's free.
Price: Free.
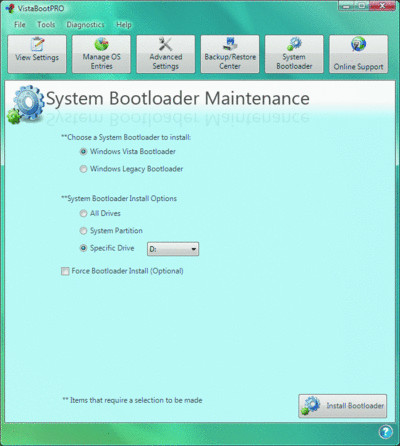
Figure vistabootpro (Click the image for a larger view)
Monitor Services and Devices
NetGong
Ahhh, monitoring tools—I can't seem to get enough of them. If you're in the market for a new network service and device monitor, or you just like to dabble with monitoring utilities, check out NetGong.
The application runs in your system tray, launching when you start Windows. A simple right-click on the icon provides an option to quickly start or stop monitoring. Double-clicking the icon brings up the main configuration UI where you can set up, review, and see events for your monitored hosts.
Setting up a host monitor is easy. Just enter the host, the TCP port you want to monitor, the interval at which the tests should be conducted, and the alert type you want to receive. You can also add a meaningful description and modify the default Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) settings, such as the timeout, packet size, and number of retries. By default, NetGong requires the monitored host to respond to ICMP requests, but you can also override that option with a checkbox for silent hosts that don't accept ICMP requests on your network.
The application gives you four alert categories: sounds, e-mail, messages, and file. For sounds, you can specify the WAV file you want to use. For messages, you can define a text message, force it to be the top-most window, and choose whether to close the window automatically or manually. E-mail alerts let you specify an SMTP server and the details of the message to be sent. And the file alert option allows you to run an executable (or batch file) with configurable parameters, window mode, and start up directory. For each of the alert types, you can configure a schedule that defines when to send the first alert, the maximum number of alerts to send, and the failure interval (number of failures) between alerts. You can also choose to be notified upon recovery of the service.
NetGong also keeps log files of the results. You can choose to log events to an event log, text file, or dynamically created HTML page. The app lets you view monitoring results on pages served through its built-in Web server listening on a user-specified port. And you can send a query string parameter with a refresh interval to have the Web page refresh with the latest monitoring event details.
Price: $79.95 direct per machine (corporate license), $59.95 direct per machine (academic license), $39.95 direct per machine (home license).
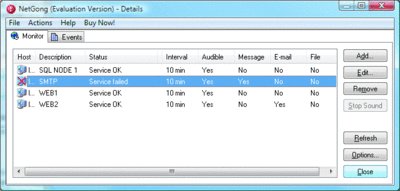
Figure steen.toolbox.netgong (Click the image for a larger view)
Book Review
Windows PowerShell: TFM
Sure, you've already heard of Windows PowerShell™. Everybody seems to be talking about it. TechNet Magazine even has a column dedicated to it (which happens to be written by one of the authors of this book). But have you really delved into it?
Windows PowerShell can be an extremely effective automation and productivity tool once you get a handle on how to use it. Whether you are just getting into scripting or you are a VBScript ninja looking to expand into this new admin-focused scripting language and command-line toolset, Windows PowerShell: TFM, by Don Jones and Jeffery Hicks, is a great place to start. This very approachable book is geared toward the system administrator and does a good job of focusing on what will be useful for most administrators.
The first section of the book introduces the Windows PowerShell environment, covering the parameters that all of the cmdlets have in common and the basics of the syntax and semantics of the scripting language. The concepts of redirection, execution pipelining, functions, variables, and running multiple shells are also presented. Since Windows PowerShell is based on the Microsoft® .NET Framework, it inherits the benefits of managed code. (Note that Windows PowerShell requires the .NET Framework 2.0 or later.) So the book also provides some insight into the essentials of the Framework, from the security context within which scripts run to the concepts of reflection, assemblies, and classes.
After explaining how to tie Windows PowerShell into Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), the authors discuss the Windows PowerShell scripting language structure in detail, providing examples that help you understand the function of objects and their associated properties and methods. You'll also see how to use the different types of operators, from basic arithmetic operators to bitwise comparison operators, as well as powerful regular expressions to parse strings for items like IP addresses and domain controller names. This is a particularly useful foundation for anyone serious about mastering Windows PowerShell.
The chapters on managing Windows and database scripting demonstrate some of the hardcore capabilities Windows PowerShell has to offer. You'll see how to work with event logs, processes, the registry, the file system, and directory services as well how to connect to and execute queries on databases.
Other sections cover outputting and formatting data, making your scripts modular, error handling, and debugging. The authors even offer a suggested set of best practices for Windows PowerShell scripting that includes naming conventions, commenting your code, and using indentation to make your code more readable.
You'll certainly want to keep the book handy for easy access to the material in the appendices, one of which is a reference for all of the 133 Windows PowerShell cmdlets, while the other is a reference for the most commonly used types (and the methods and properties associated with these types). Besides providing a quick look-up of how to use a specific cmdlet, these references give you an instant preview of the breadth of the capabilities Windows PowerShell offers.
Price: $49.99 list.
Test Your Cables
SMARTest Compact Network Cable Tester
Cables, cables, everywhere! As IT pros, most of us are surrounded by CAT5 cable. Lots of CAT5 cable: hundreds of strands, spanning thousands of feet. And if you are responsible for these cables, a good, easy-to-carry cable tester isn't just handy, it's essential. For that reason, you might want to take a look at the SMARTest Compact Network Cable Tester from Hobbes.
The SMARTest device is a pen-style cable tester. It's compatible with CAT 3, 4, 5, 5e, and 6 network cables and can help you detect common cable wiring issues. Specifically, you can check for open, shorted, reversed, mis-wires, split pairs, and grounding issues within a cable strand.
The device runs on four small watch-style batteries, so your cables don't need to be connected to test; nor should you connect SMARTest to an active network connection. To test a cable, you simply have to plug one end of the strand into the Main unit and the other into the detachable Remote unit. The SMARTest unit has an interface with both RJ45 socket and plug (female and male) connectors, so you can test any kind of cable setup. You can even use the SMARTest device to check the wiring or your patch panels and wall sockets.
Another cool feature is that the device has built-in tone generation so you can send an audio signal through the cable you're testing. You can then pick up the signal with a compatible signal probe, such as the Cable Tracer Probe also available from Hobbes.
The SMARTest with tone-generation costs around $80-$90, depending on the retailer. There is also an optional F connector adapter for testing coax cable.
Price: $99.99 list.

Figure steen.toolbox.smartest (Click the image for a larger view)
Greg Steen is a technology professional, entrepreneur, and enthusiast. He is always on the hunt for new tools and methods to help make operations and development easier for IT professionals.
© 2008 Microsoft Corporation and CMP Media, LLC. All rights reserved; reproduction in part or in whole without permission is prohibited.