Migration guide: Oracle to SQL Server
Applies to:
SQL Server
In this guide, you learn how to migrate your Oracle databases to SQL Server by using SQL Server Migration Assistant for Oracle (SSMA for Oracle).
For other migration guides, see Azure Database Migration Guides.
Important
Try new Database Migration Assessment for Oracle extension in Azure Data Studio for Oracle to SQL pre-assessment and workload categorization. If you are in early phase of Oracle to SQL migration and would need to do a high level workload assessment , interested in sizing Azure SQL target for the Oracle workload or understand feature migration parity, try the new extension. For detailed code assessment and conversion, continue with SSMA for Oracle.
Prerequisites
Before you begin migrating your Oracle database to SQL Server, perform the following steps:
- Verify that your source environment is supported.
- Download and install SQL Server.
- Download and install SSMA for Oracle.
- Get the necessary permissions for SSMA for Oracle and provider.
- Get connectivity and sufficient permissions to access both source and target.
Pre-migration
As you prepare for migrating to the cloud, verify that your source environment is supported and that you meet all other prerequisites. Doing so helps to ensure an efficient and successful migration.
This part of the process involves conducting an inventory of the databases that you need to migrate, assessing them for potential migration issues or blockers, and then resolving any items you might have uncovered.
Discover
To better understand and plan for the migration, use the Microsoft Assessment and Planning (MAP) Toolkit to identify existing data sources and details about the features your organization is using. This process involves scanning the network to identify all your organization's Oracle instances, versions, and features.
To use the MAP Toolkit to perform an inventory scan, perform the following steps:
Open the MAP Toolkit.
On the Overview pane, select Create/Select database.
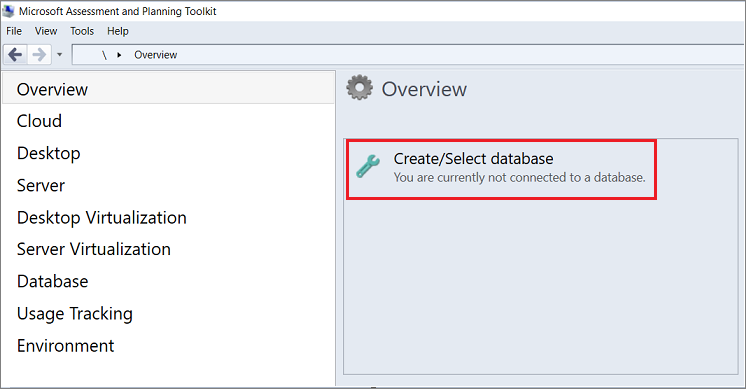
Under Create or select a database, select Create an inventory database, enter a name for the inventory database you're creating, provide a brief description, and then select OK.
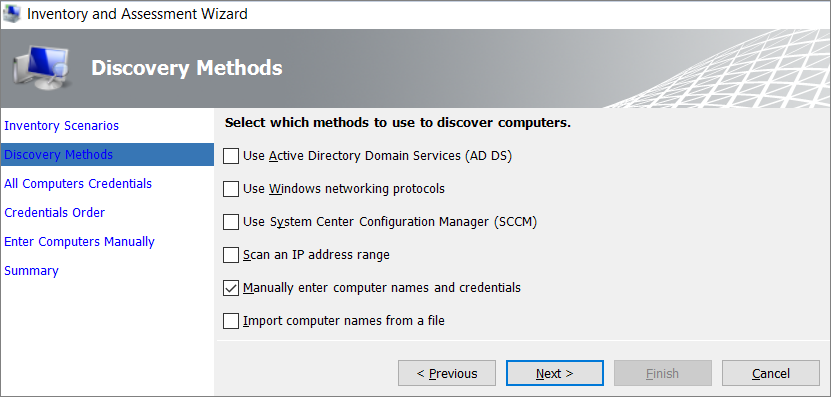
Select Collect inventory data to open the Inventory and Assessment Wizard.
In the wizard, select Oracle, and then select Next.
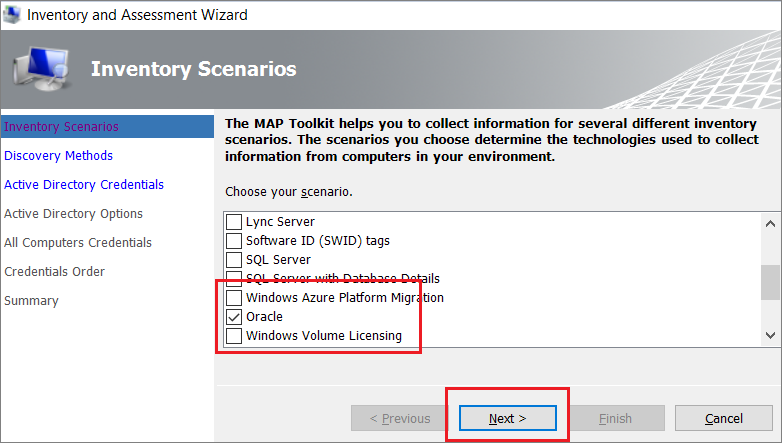
Select the computer search option that best suits your organization's needs and environment, and then select Next.
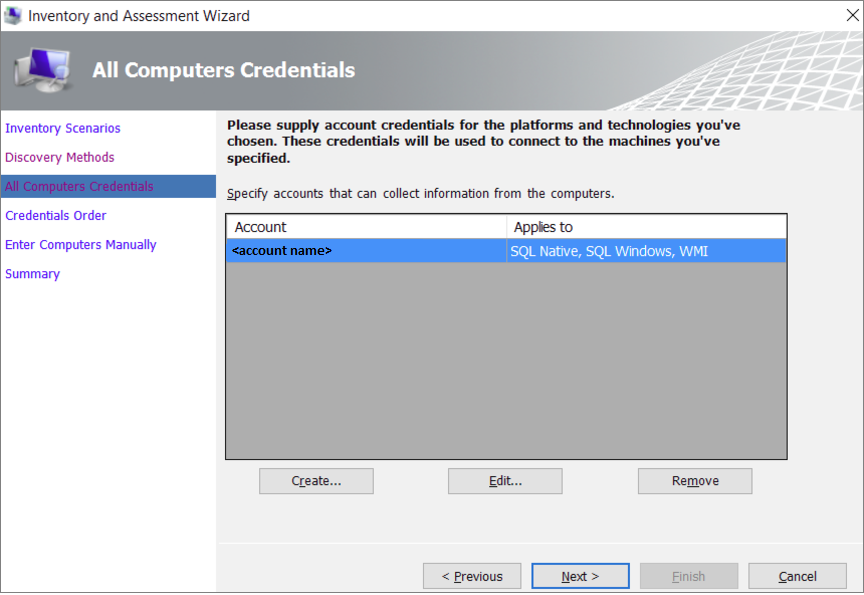
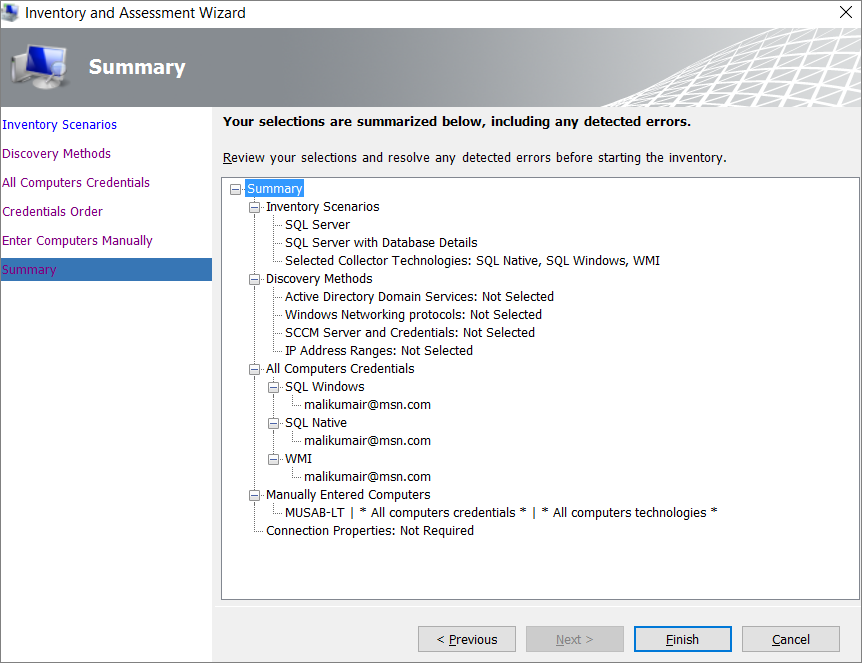
Either enter the current credentials or create new credentials for the systems that you want to explore, and then select Next.
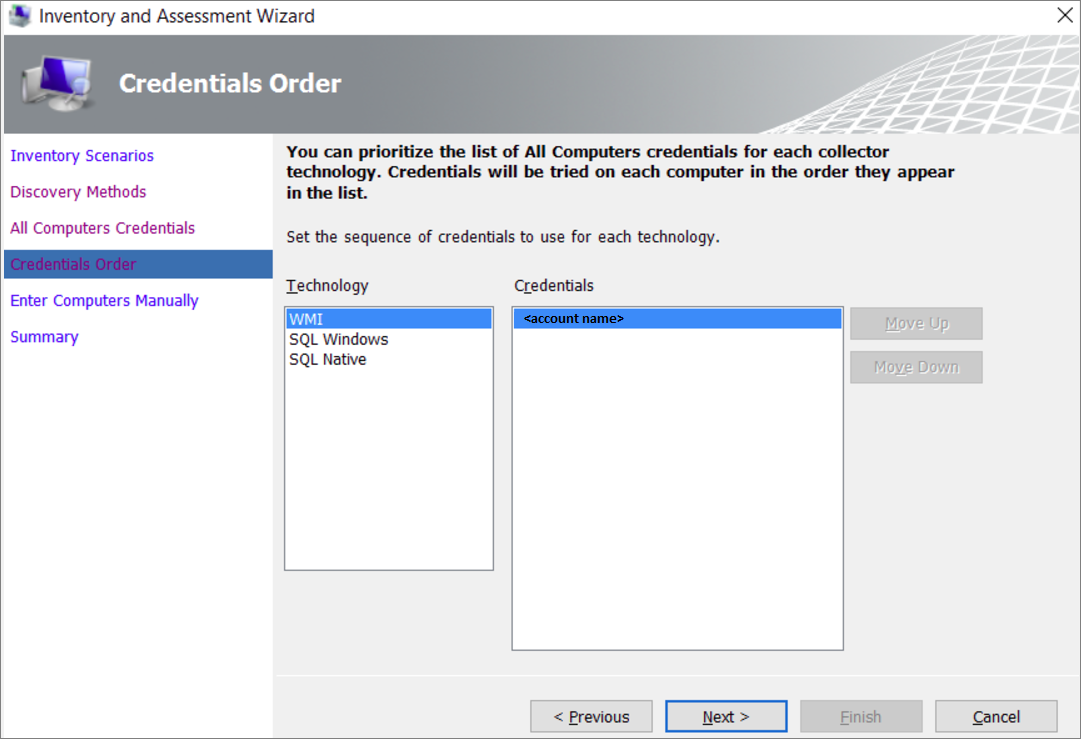
Set the order of the credentials, and then select Next.
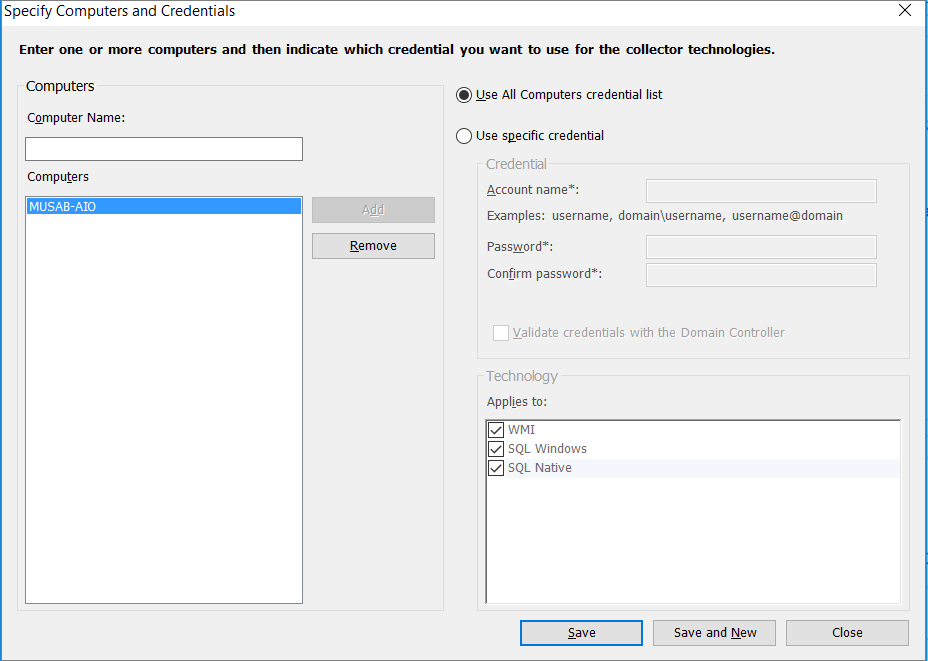
Specify the credentials for each computer you want to discover. You can use unique credentials for every computer or machine, or you can select them from the Computers list.
Verify your selection summary, and then select Finish.
After the scan is completed, view the Data Collection summary report. The scan might take a few minutes, depending on the number of databases. When you're finished, select Close.
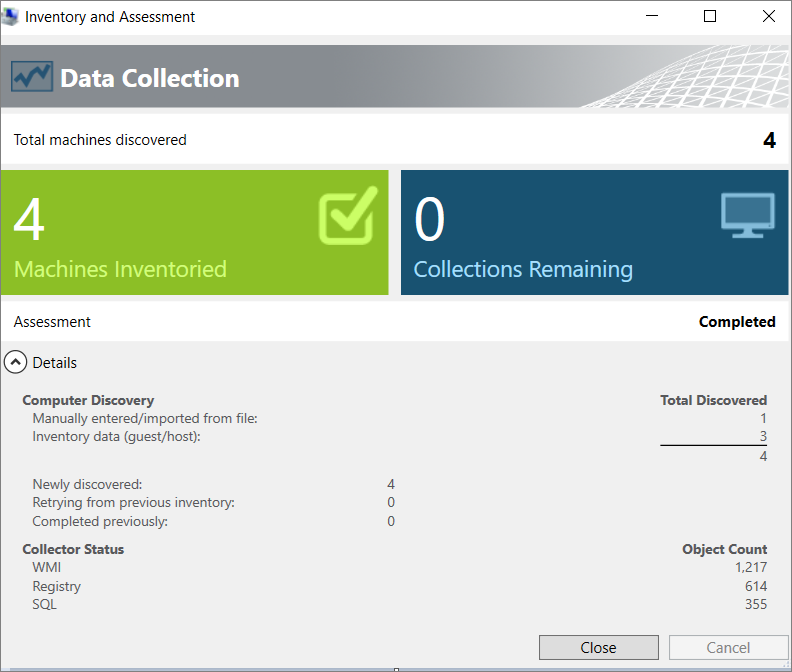
Select Options to generate a report about the Oracle Assessment and database details. Select both options (one at a time) to generate the report.
Assess
After you identify the data sources, use SSMA for Oracle to assess the Oracle instance you're migrating to the SQL Server virtual machine so that you understand the gaps between the two. By using the migration assistant, you can review the database objects and data, assess the databases for migration, migrate the database objects to SQL Server, and then migrate the data to SQL Server.
To create an assessment, perform the following steps:
Open SSMA for Oracle.
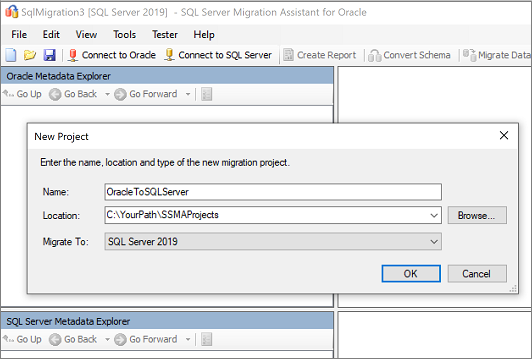
Select File, and then select New Project.
Provide a project name and location and then, in the dropdown list, select a SQL Server migration target. Select OK.
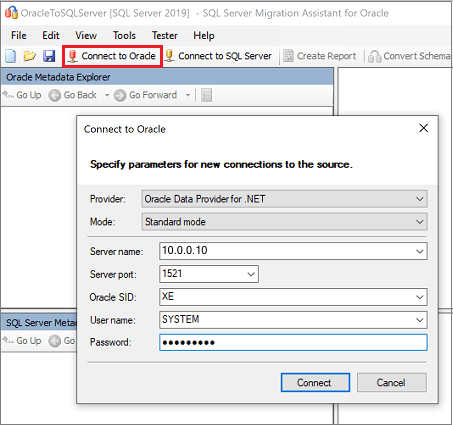
Select Connect to Oracle, enter the Oracle connection details, and then select Connect.
On the Filter objects pane, select the Oracle schemas you want to migrate, and then select OK.
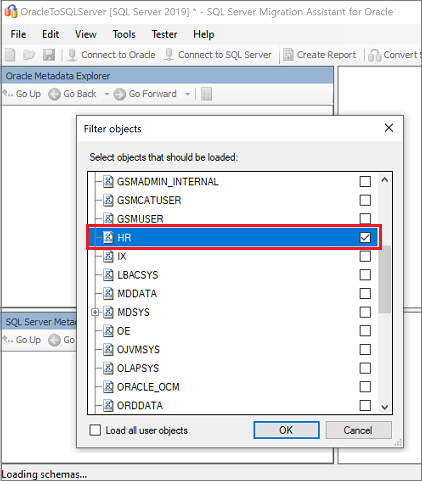
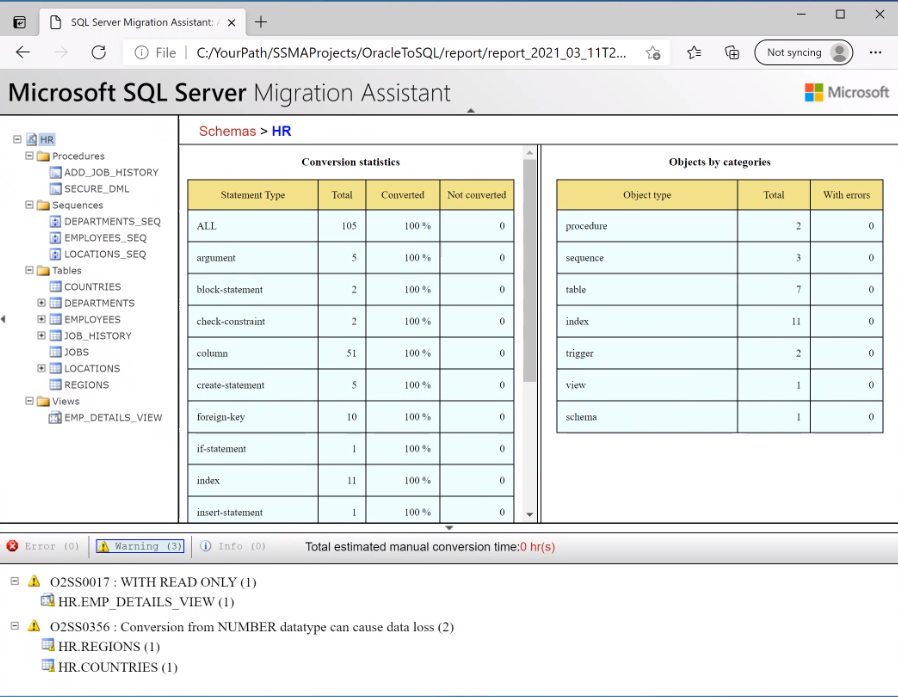
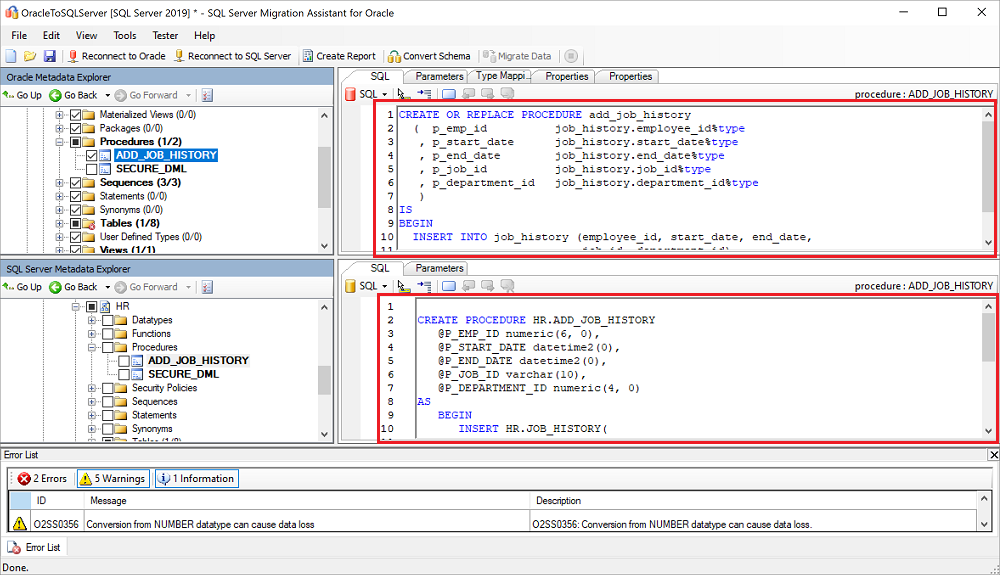
On the Oracle Metadata Explorer pane, select the Oracle schemas you're working with, and then select Create Report to generate an HTML report with conversion statistics and errors or warnings, if any. Alternatively, you can select the Create Report tab at the upper right.
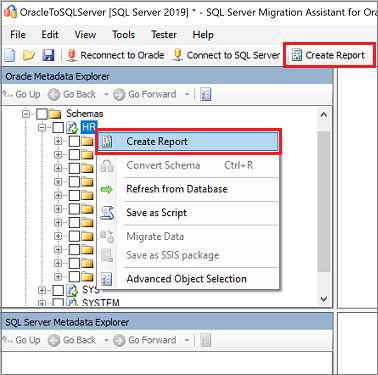
Review the HTML report to understand the conversion statistics and any errors or warnings. You can also open the report in Excel to get an inventory of Oracle objects and the effort required to perform schema conversions. The default location for the report is the report folder within SSMAProjects. For example:
drive:\<username>\Documents\SSMAProjects\MyOracleMigration\report\report_2016_11_12T02_47_55\
Validate data types
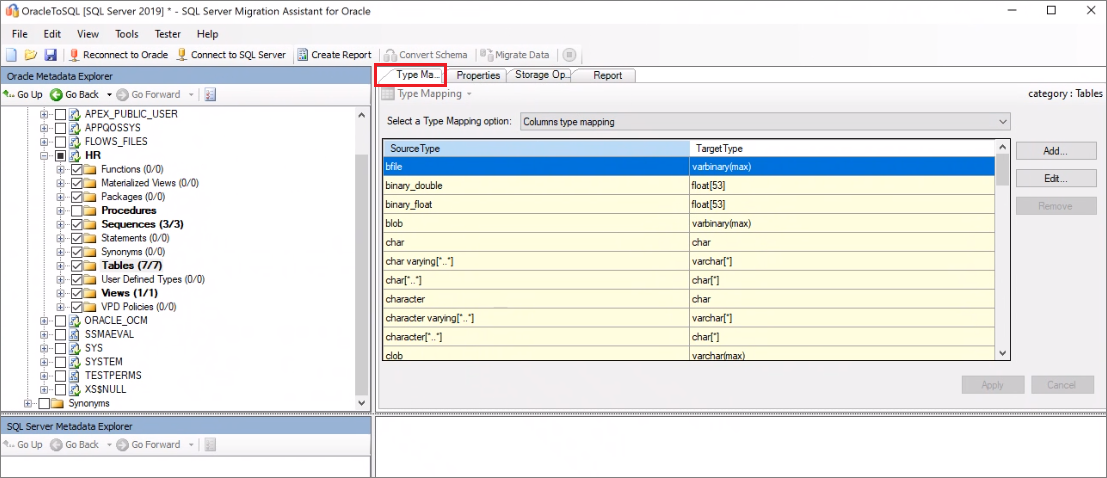
Validate the default data-type mappings and change them based on requirements if necessary. To do so:
Select Tools, and then select Project Settings.
Select the Type Mapping tab.
You can change the type mapping for each table by selecting the table name on the Oracle Metadata Explorer pane.
Convert schema
To convert the schema, perform the following steps:
(Optional) To convert dynamic or specialized queries, right-click the node, and then select Add statement.
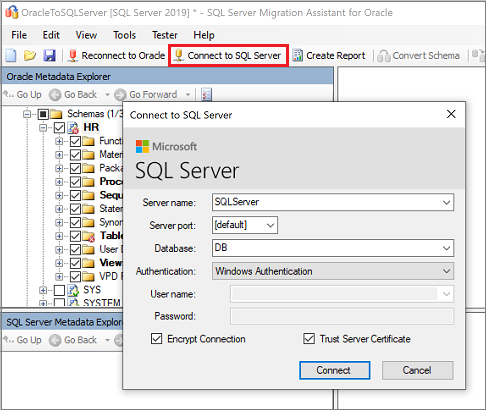
Select the Connect to SQL Server tab, and then enter the connection details for your SQL Server instance.
In the Database dropdown list, select your target database, or provide a new name to create a database on the target server.
Provide authentication details.
Select Connect.
On the Oracle Metadata Explorer pane, right-click the schema you're working with, and then select Convert Schema. Alternatively, you can select the Convert Schema tab at the upper right.
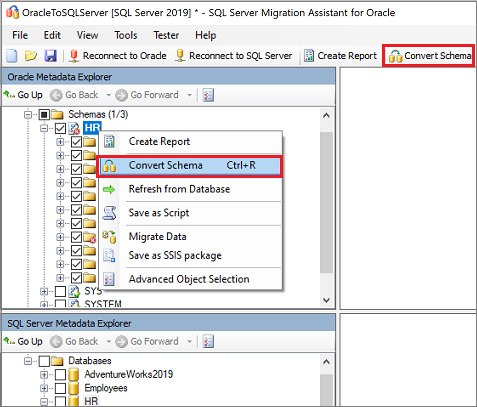
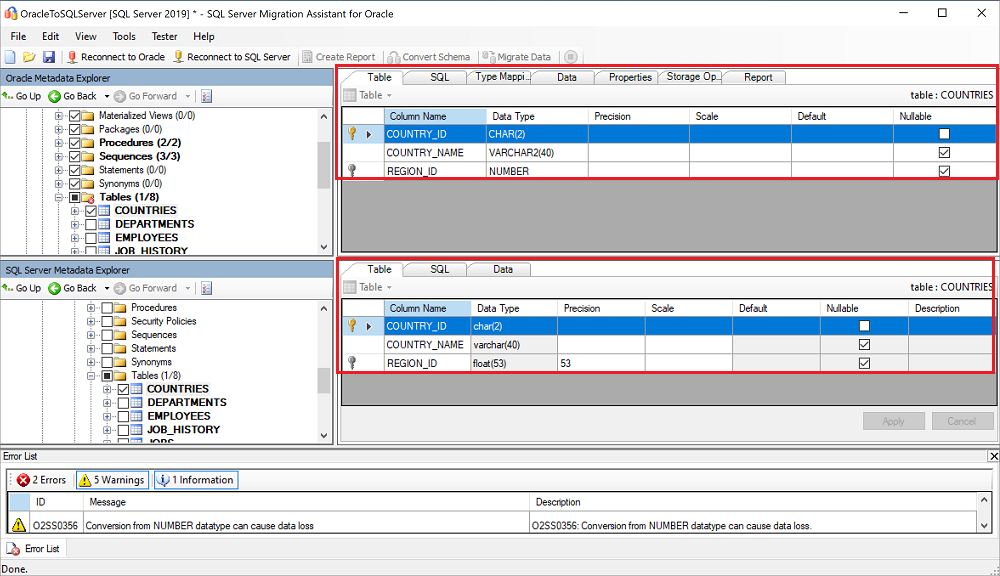
After the conversion is completed, compare the converted objects to the original objects to identify potential problems, and address them based on the recommendations.
Compare the converted Transact-SQL text to the original code, and review the recommendations.
On the output pane, select the Review results icon, and then review any errors on the Error list pane.
For an offline schema remediation exercise, save the project locally by selecting File > Save Project. Doing so gives you an opportunity to evaluate the source and target schemas offline and remediate them before you publish the schema to your SQL Server instance.
Migrate database
After you've satisfied the prerequisites and completed the tasks associated with the pre-migration stage, you're ready to perform the schema and database migration. Migration involves two steps: publishing the schema and migrating the database.
To publish your schema and migrate the database, perform the following steps:
Publish the schema. On the SQL Server Metadata Explorer pane, right-click the database, and then select Synchronize with Database. This action publishes the Oracle schema to your SQL Server instance.
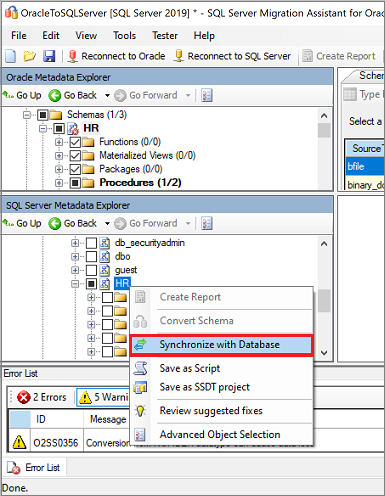
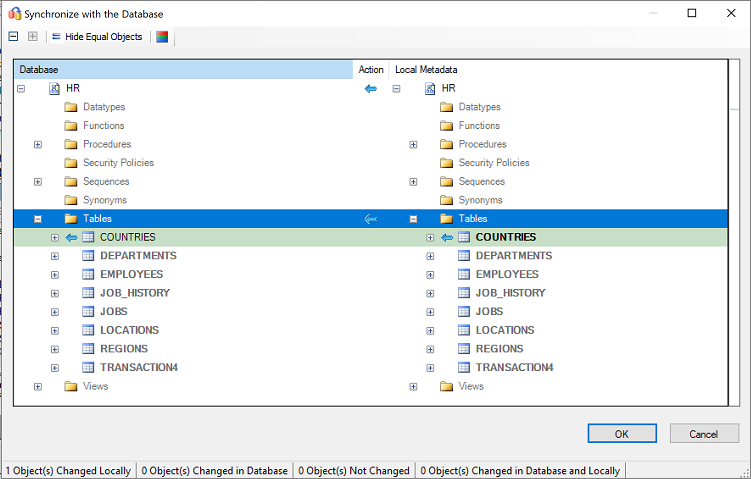
Review the mapping between your source project and your target, as shown here:
Migrate the data. On the Oracle Metadata Explorer pane, right-click the schema or object you want to migrate, and then select Migrate Data. Alternatively, you can select the Migrate Data tab at the upper right.
To migrate data for an entire database, select the check box next to the database name. To migrate data from individual tables, expand the database, expand Tables, and then select the check box next to the table. To omit data from individual tables, clear the check box.
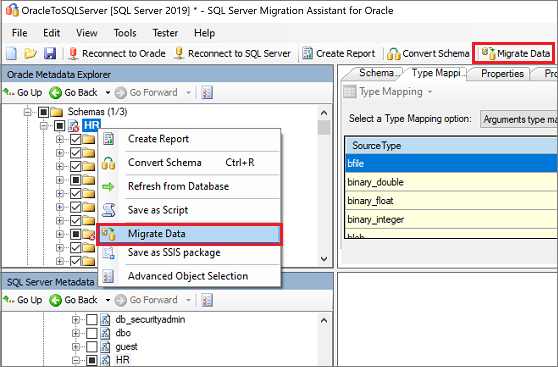
On the Migrate Data pane, enter the connection details for both Oracle and SQL Server.
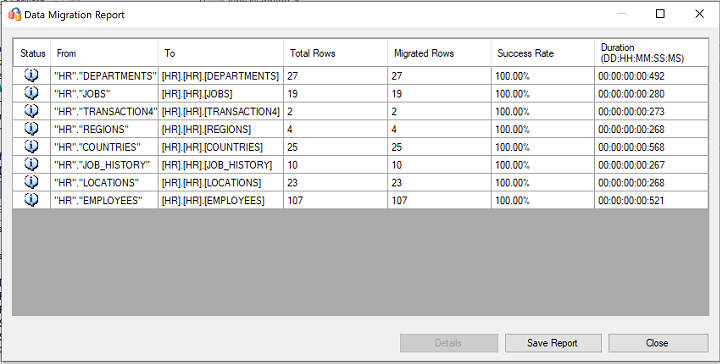
After the migration is completed, view the Data Migration Report.
Connect to your SQL Server instance by using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), and then validate the migration by reviewing the data and schema.
 In addition to using SSMA, you can use SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) to migrate the data. To learn more, see:
In addition to using SSMA, you can use SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) to migrate the data. To learn more, see:
- SQL Server Integration Services (article)
- SQL Server Integration Services: SSIS for Azure and Hybrid Data Movement (technical white paper)
Post-migration
After you successfully complete the migration stage, you need to complete a series of post-migration tasks to ensure that everything is functioning as smoothly and efficiently as possible.
Remediate applications
After you migrate the data to the target environment, all the applications that formerly consumed the source need to start consuming the target. Accomplishing this step can require changes to the applications.
The Data Access Migration Toolkit is an extension for Visual Studio Code with which you can analyze your Java source code and detect data-access API calls and queries. The toolkit gives you a single-pane view of the items to be addressed to support the new database back end. To learn more, see the Migrate our Java application from Oracle blog.
Perform tests
The test approach to database migration consists of the following activities:
Develop validation tests: To test the database migration, you need to use SQL queries. You must create the validation queries to run against both the source and target databases. Your validation queries should cover the scope you defined.
Set up a test environment: The test environment should contain a copy of the source database and the target database. Be sure to isolate the test environment.
Run validation tests: Run validation tests against the source and the target, and then analyze the results.
Run performance tests: Run performance tests against the source and the target, and then analyze and compare the results.
Optimize
The post-migration phase is crucial for reconciling any data accuracy issues, verifying completeness, and addressing performance issues with the workload.
For more information about these issues and the steps to mitigate them, see the Post-migration Validation and Optimization Guide.
Migration assets
For more assistance with completing this migration scenario, see the following resources. They were developed in support of a real-world migration project engagement.
| Title | Description |
|---|---|
| Data workload assessment model and tool | Provides suggested "best fit" target platforms, cloud readiness, and application/database remediation levels for specified workloads. It offers simple, one-click calculation, and report generation that helps to accelerate large estate assessments by providing an automated, uniform target-platform decision process. |
| Oracle inventory script artifacts | Includes a PL/SQL query that hits Oracle system tables and provides a count of objects by schema type, object type, and status. It also provides a rough estimate of 'Raw Data' in each schema and the sizing of tables in each schema, with results stored in a CSV format. |
| Automate SSMA Oracle assessment collection & consolidation | A set of resources that uses a .csv file as entry (sources.csv in the project folders) to produce the xml files that are needed to run SSMA assessment in console mode. The source.csv file is provided by the customer based on an inventory of existing Oracle instances. The output files are AssessmentReportGeneration_source_1.xml, ServersConnectionFile.xml, and VariableValueFile.xml. |
| SSMA issues and possible remedies when migrating Oracle databases | Discusses how Oracle enables you to assign a non-scalar condition in the WHERE clause. However, SQL Server doesn't support this type of condition. As a result, SSMA for Oracle doesn't convert queries with a non-scalar condition in the WHERE clause, instead generating an error O2SS0001. This white paper provides more details on the issue and ways to resolve it. |
| Oracle to SQL Server migration handbook | Focuses on the tasks associated with migrating an Oracle schema to the latest version of SQL Server base. If the migration requires changes to features and functionality, the possible effect of each change on the applications that use the database must be considered carefully. |
| Oracle to SQL Server - Database Compare utility | SSMA for Oracle Tester is the recommended tool to automatically validate the database object conversion and data migration, and it's a superset of Database Compare functionality. If you're looking for an alternative data validation option, you can use the Database Compare utility to compare data, down to the row or column level in all or selected tables, rows, and columns. |
The Data SQL Engineering team developed these resources. This team's core charter is to unblock and accelerate complex modernization for data platform migration projects to Microsoft's Azure data platform.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for