Running containers with Kubernetes
Containers are a virtualization technology. In many ways, they’re similar to virtual machines (VMs), but containers don't have their own internal operating system (OS). Containers share part of the OS with their hosts. As such, a single VM can run many containers. However, each container is still self contained with its own code, data, and dependencies.
One of the main benefits of using containers for cloud native applications is reliability. This is because containers are immutable: a container image tested in a QA environment is the exact same container image that's deployed to production.
You can build and run containers in Docker. Docker is software for containers that provides a widely used standard for packaging and distributing containerized applications. With Docker, you can also store and share container images.
Using containers in the cloud
Azure Container Registry provides storage for Docker container images in the cloud, based on the open-source Docker Registry 2.0. Azure Container Registry provides many security benefits, such as:
- Authentication for who can see and use your images.
- You can sign images to increase trust and reduce the chances of an image becoming accidentally, or intentionally, corrupted.
- All images stored in a container registry are encrypted at rest.
Azure Container Registry also lets you automate tasks like container image builds and app redeployments when an image is rebuilt.
Using Azure Container Registry
In our example scenario, your team needs to host a Docker image in Kubernetes that connects messages from smart fridges to a management web app. We'll create a container registry to store the image, and later, ACR will connect to an AKS cluster for image deployment.
Manage containers in the cloud
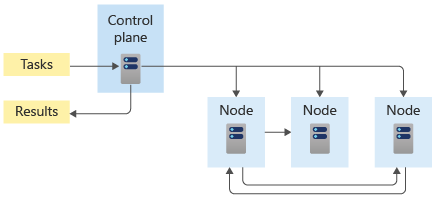
Kubernetes orchestrates containers by managing VMs for you and scheduling containers to run in those VMs based on your resource requirements. If the need arises, you can automatically scale to multiple identical containers.
AKS and Kubernetes
AKS handles Kubernetes for you by deploying, managing, and scaling Kubernetes clusters. If you have to replace or replicate a container, AKS automatically routes and balances traffic in the cluster. AKS makes it simple to deploy, manage, and connect containerized applications, providing massive savings in development time, application deployment, and security obligations.
Creating the smart fridge solution
In our scenario, we'll use AKS to host containers in the cloud. The smart fridges will send REST messages to the cloud, where AKS will receive them and route them to a container. The container will run a Node.js program that routes messages to a management web app.