Manage your dependencies on GitHub
It's common for software projects to depend on external packages or dependencies. Managing these external dependencies can consume resources and affect productivity. These dependencies can also include vulnerabilities that introduce security threats. A vulnerability is a flaw in a project's code that can be exploited to damage the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the project or other projects that use its code. You might not even notice vulnerabilities right away, because they exist outside of the code on which you work.
In this unit, you'll learn about the GitHub tools for managing your dependencies:
- The dependency graph
- The GitHub Advisory Database
- Dependabot
The dependency graph
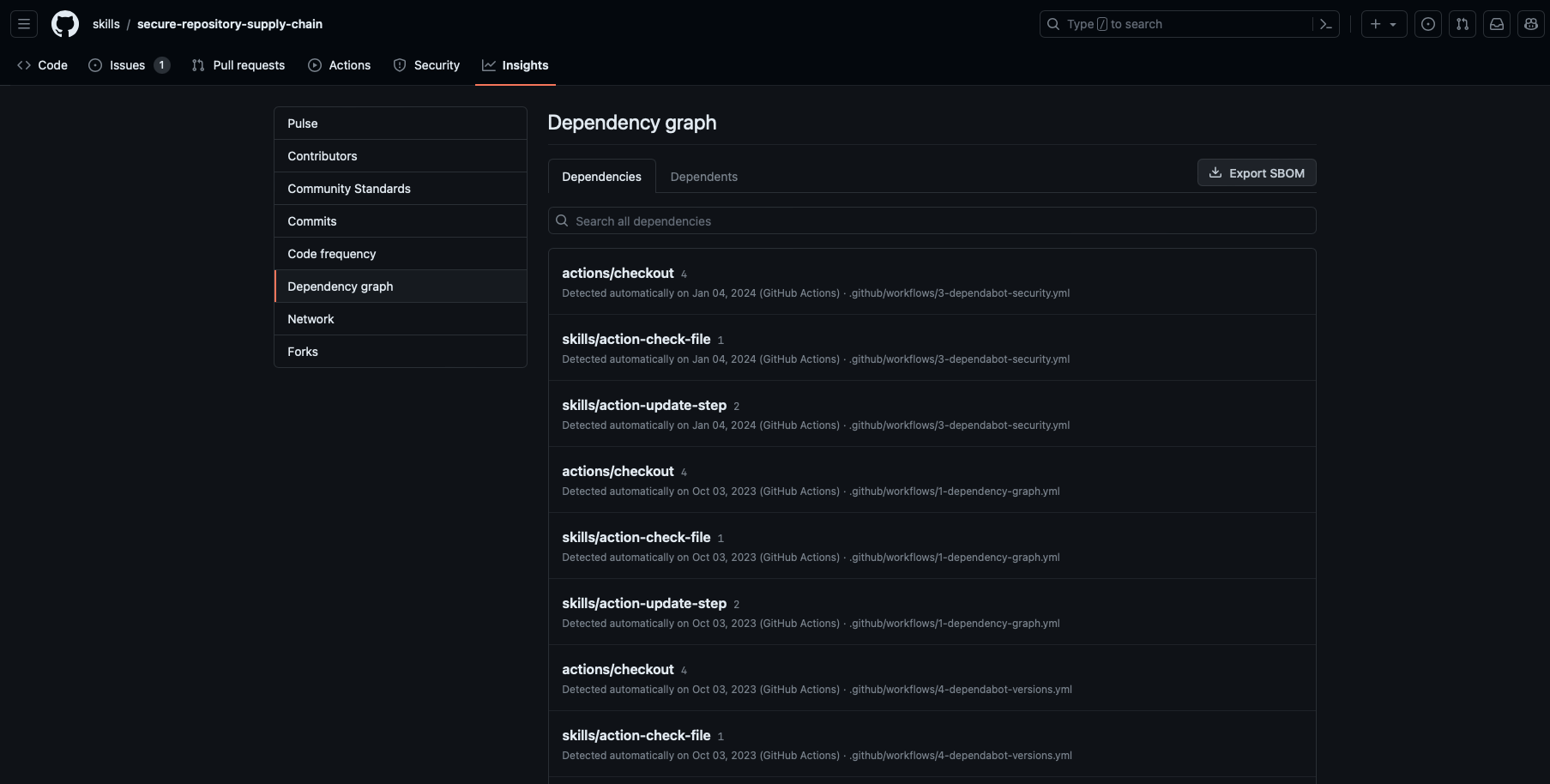
The dependency graph is a summary of a repository's manifest and lock files. These files contain metadata about your project. The dependency graph is automatically generated for public repositories and includes the following information:
- Dependencies, which are the ecosystem and packages on which the repository depends.
- Dependents, which are the repositories and packages that depend on the repository.
The dependency graph uses the information from your lock and manifest files to provide a list of three kinds of dependencies:
- The direct dependencies explicitly defined in a manifest or lock file.
- The indirect dependencies, also known as transitive dependencies or subdependencies, which are dependencies used by packages that are dependencies of your project.
- The vendored dependencies that are checked into a specific directory in your repository but aren't referenced in your manifest file (only available for some package managers).
Enable the dependency graph for private repositories
As a repository administrator, you can also choose to enable the dependency graph for private repositories by completing these steps:
- Go to your GitHub repository.
- Select Settings.
- Select Code security and analysis.
- Select Enable in the dependency graph section.
Note
Dependent information is not included for private repositories.
View the dependency graph
You can view the dependency graph for your repository by following these steps:
- Go to your GitHub repository.
- Select your repository Insights.
- Select Dependency graph.
- You can select the Dependencies or Dependents tab from the Dependency graph view.
Supported package ecosystem for the dependency graph
This table lists the recommended and supported formats for files containing your dependencies. If you use these formats, your dependency graph is more accurate. Using the recommended file format means that your dependency graph reflects the current build setup and can report vulnerabilities for both direct and indirect dependencies.
We generally recommend lock files in your repository, because they define the exact versions of the direct and indirect dependencies that you're currently using. If you're using lock files, make sure the contributors to your repository are also using the same versions. If you use a manifest file (or equivalent), indirect dependencies aren't included in checks for vulnerable dependencies.
| Package manager | Languages | Recommended formats | All supported formats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composer | PHP | composer.lock |
composer.json, composer.lock |
dotnet CLI |
.NET languages (C#, C++, F#, VB) | .csproj, .vbproj, .nuspec, .vcxproj, .fsproj |
.csproj, .vbproj, .nuspec, .vcxproj, .fsproj, packages.config |
| Maven | Java, Scala | pom.xml |
pom.xml |
| npm | JavaScript | package-lock.json |
package-lock.json, package.json |
| Python PIP | Python | requirements.txt, pipfile.lock |
requirements.txt, pipfile, pipfile.lock, setup.py* |
| RubyGems | Ruby | Gemfile.lock |
Gemfile.lock, Gemfile, *.gemspec |
| Yarn | JavaScript | yarn.lock |
package.json, yarn.lock |
For GitHub Enterprise Security versions 3.2:
| Package manager | Languages | Recommended formats | All supported formats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Go modules | Go | go.mod |
go.mod |
For GitHub Enterprise Security versions above 3.2 and GitHub AE:
| Package manager | Languages | Recommended formats | All supported formats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Go modules | Go | go.sum |
go.mod, go.sum |
For GitHub Enterprise Security versions above 3.3:
| Package manager | Languages | Recommended formats | All supported formats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python Poetry | Python | poetry.lock |
poetry.lock, pyproject.toml |
The GitHub Advisory Database
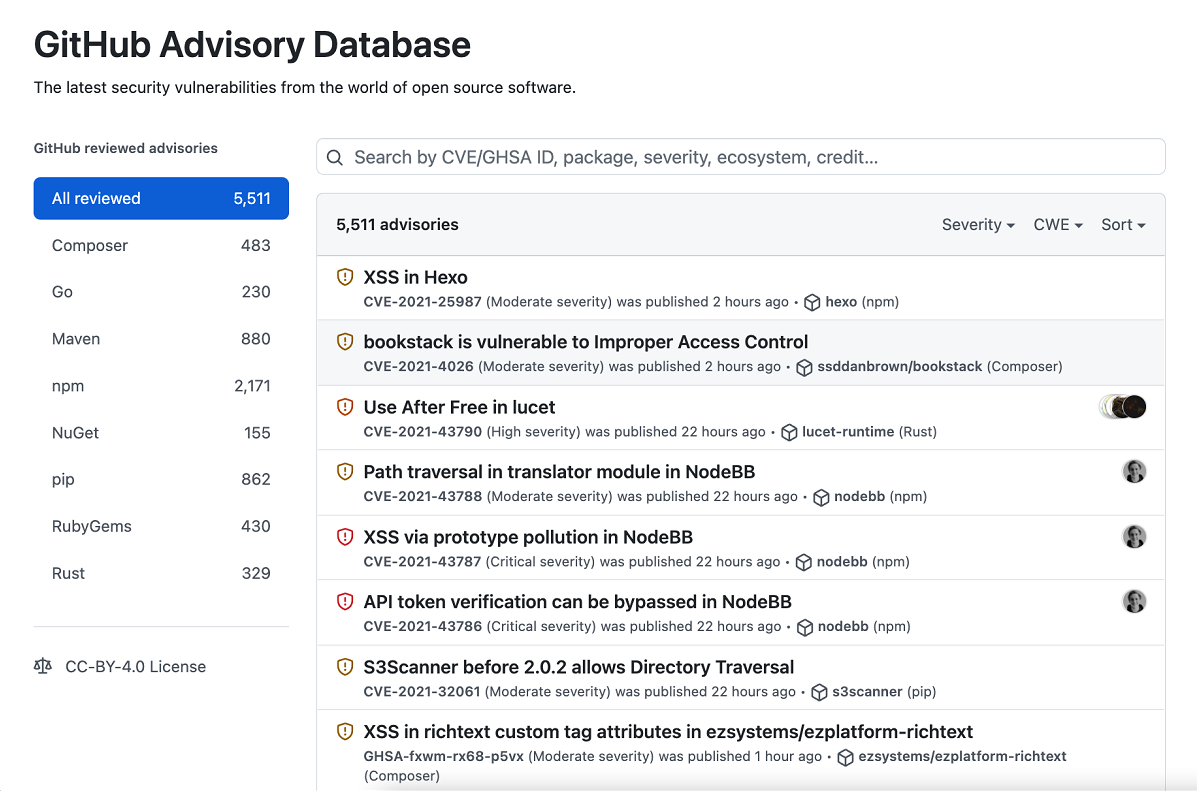
GitHub collects information on vulnerabilities and includes it in the GitHub Advisory Database. The GitHub Advisory Database is a curated list of security vulnerabilities related to packages tracked by the GitHub dependency graph. It contains detailed information about each dependency, including description, severity, and affected package. This database uses the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS), Section 5, to assign a severity level to each vulnerability: low, medium/moderate, high, and critical. The database is populated from the following four sources:
- The National Vulnerability Database
- A combination of machine learning and human reviews to detect vulnerabilities in public commits on GitHub
- Security advisories reported on GitHub
- The npm Security advisories database
Dependabot
Dependabot is a GitHub tool that automates managing your repository's dependencies. For Dependabot to work, the dependency graph must be enabled in a repository. Dependabot uses the dependency graph and the GitHub Advisory Database to provide three features:
- Dependabot alerts: Notify you about vulnerable dependencies in public repositories.
- Security updates: Automatically update or generate a pull request to update vulnerable dependencies.
- Version updates: Automatically update all the packages used by your repository.
In the remaining units, you'll learn more about using Dependabot in your repository.