Describe how security policies and initiatives improve cloud security posture
Microsoft Defender for Cloud enables organizations to manage the security of their resources and workloads in the cloud and on-premises and improve their overall security posture. It does this by using policy definitions and security initiatives, so it's important to understand these terms.
An Azure Policy definition, created in Azure policy, is a rule about specific security conditions that you want controlled. Azure policy supports built-in definitions but you can also create your own custom policy definitions.
A security initiative is a collection of Azure Policy definitions, or rules, grouped together towards a specific goal or purpose. Security initiatives simplify management of your policies by grouping a set of policies together, logically, as a single item.
To implement policy definitions or initiatives, you assign them to any scope of resources that are supported, such as management groups, subscriptions, resource groups, or individual resources.
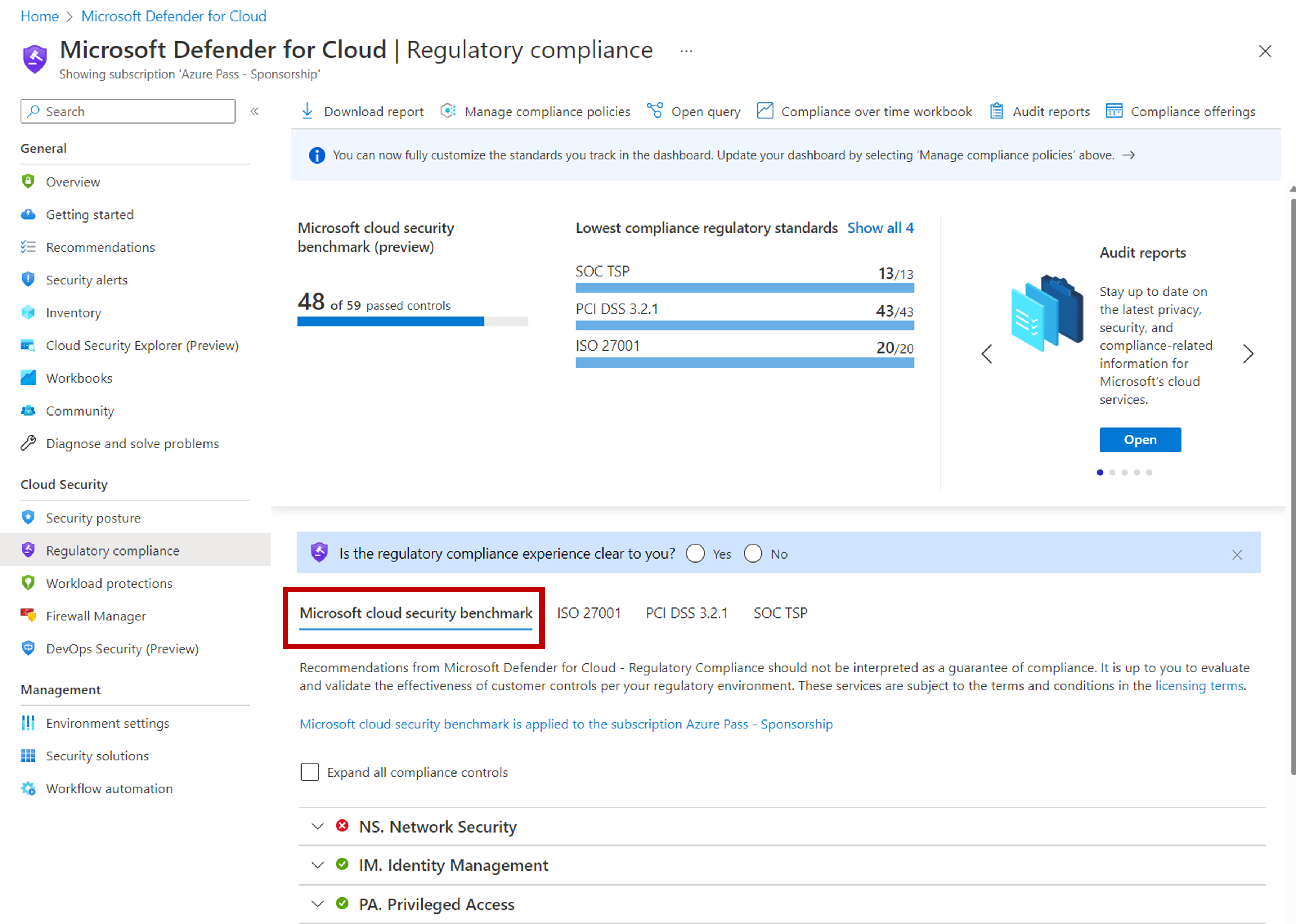
Microsoft Defender for Cloud applies security initiatives to your subscriptions. These initiatives contain one or more security policies. Each of those policies results in a security recommendation for improving your security posture.
Security administrators can build their own custom security initiatives in Microsoft Defender for Cloud, but there's also a default, built-in security initiative named 'Microsoft cloud security benchmark' that is automatically assigned when you enable Microsoft Defender for Cloud on your subscription.
Microsoft cloud security benchmark
The Microsoft cloud security benchmark (MCSB) is a Microsoft-authored set of guidelines for security and compliance that provides best practices and recommendations to help improve the security of workloads, data, and services on Azure and your multicloud environment. The MCSB builds on the controls from the Center for Internet Security (CIS) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) with a focus on cloud-centric security.
The best way to understand the Microsoft cloud security benchmark is to view it on GitHub Microsoft_cloud_security_benchmark. Spoiler alert, it's an excel spreadsheet. The MCSB provides many columns of data. Some key pieces of information include:
- ID - Each line item in the MCSB has an identifier that maps to a specific recommendation.
- Control domain - A control is a high-level description of a feature or activity that needs to be addressed and isn't specific to a technology or implementation. MCSB control domains include network security, data protection, identity management, privileged access, incident response, endpoint security to name just a few.
- Mapping to industry frameworks - The recommendations included in the MCSB map to existing industry frameworks, such as the Center for Internet Security (CIS), the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) frameworks. This makes security and compliance easier for customer applications running on Azure services.
- Recommendation - For each control domain area there can be many distinct recommendations. For example, the "Network Security" control domain in MCSB v1 has 10 distinct recommendations identified as NS-1 through NS-10; in which the first recommendation identified as NS-1 is to establish network segmentation boundaries.
- Azure Guidance - Azure Guidance is focused on the "how" and it elaborates on the relevant technical features and ways to implement the controls in Azure. In the example of NS-1, the Azure guidance includes information regarding creating a virtual network, using network security groups (NSG), and using an application security group (ASG).
- AWS Guidance - The AWS guidance is focused on the "how" specific to AWS, explaining the AWS technical features and implementation basics.
The MCSB also includes links to information on implementation that relate to the Azure and AWS guidance, information about security functions at the customer organization who may be accountable, responsible, or consulted for the respective control, and more. An excerpt from the Microsoft cloud security benchmark version 1 (MCSB v1) and is shown as an example of the type of the content that is included in the MCSB. The image isn't intended to show the complete text for any of the line items.
Microsoft cloud security benchmark in Defender for Cloud
Microsoft Defender for Cloud continuously assesses an organization's hybrid cloud environment to analyze the risk factors according to the controls and best practices in the Microsoft cloud security benchmark. The regulatory compliance dashboard in Microsoft Defender for Cloud reflects the status of your compliance with the MCSB and any other standards that you've applied to your subscriptions.
Some of the controls used in the MCSB include network security, identity and access control, data protection, data recovery, incident response, and more.
What is a security recommendation?
Recommendations are the result of assessing your resources against the relevant policies and identifying resources that aren't meeting your defined requirements.
Defender for Cloud periodically analyzes the compliance status of your resources to identify potential security misconfigurations and weaknesses. It then provides you with recommendations on how to remediate those issues. Defender for Cloud makes its security recommendations based on your chosen initiatives and the MCSB default initiative. When a policy from an initiative is compared against your resources and finds one or more that aren't compliant, it's presented as a recommendation in Defender for Cloud.
Recommendations are actions for you to take to secure and harden your resources. Each recommendation provides you with the following information:
- A short description of the issue
- The remediation steps to carry out in order to implement the recommendation
- The affected resources
Security recommendations contain details that help you understand its significance and how to handle it.