Examine automatic device management in Azure IoT Hub
Automatic device management in Azure IoT Hub automates many of the repetitive and complex tasks of managing large device fleets. With automatic device management, you can target a set of devices based on their properties, define a desired configuration, and then let IoT Hub update the devices when they come into scope. This update is done using an automatic device configuration or automatic module configuration, which lets you summarize completion and compliance, handle merging and conflicts, and roll out configurations in a phased approach.
Note
Automatic device management requires the Standard tier of the IoT Hub service.
Automatic device management works by updating a set of device twins with desired properties and reporting a summary that's based on device twin reported properties. It introduces a new class and JSON document called a Configuration that has three parts:
- The target condition defines the scope of device twins to be updated. The target condition is specified as a query on device twin tags and/or reported properties.
- The target content defines the desired properties to be added or updated in the targeted device twins. The content includes a path to the section of desired properties to be changed.
- The metrics define the summary counts of various configuration states such as Success, In Progress, and Error. Custom metrics are specified as queries on device twin reported properties. System metrics are the default metrics that measure twin update status, such as the number of device twins that are targeted and the number of twins that have been successfully updated.
Automatic device configurations run for the first time shortly after the configuration is created and then at five-minute intervals. Metrics queries run each time the automatic device configuration runs. A maximum of 100 automatic configurations is supported on standard tier IoT hubs; ten on free tier IoT hubs. Throttling limits also apply.
Note
Automatic device management in Azure IoT Hub can be applied to module identities using module twins in a manner that is similar to the way this topic describes using device identities and device twins. For simplicity's sake, this topic focuses on the device and device twin implementation.
Implement twins
Automatic device configurations require the use of device twins to synchronize state between the cloud and devices.
Automatic module configurations require the use of module twins to synchronize state between the cloud and modules.
Use tags to target twins
Before you create a configuration, you must specify which devices or modules you want to affect. Azure IoT Hub identifies devices using tags in the device twin, and identifies modules using tags in the module twin. Each device or modules can have multiple tags, and you can define them any way that makes sense for your solution. For example, if you manage devices in different locations, add the following tags to a device twin:
"tags": {
"location": {
"state": "Washington",
"city": "Tacoma"
}
}
Create a configuration
You can use the Azure portal to begin the process of creating a configuration as follows:
- In the Azure portal, open your IoT hub.
- Select Configurations + Deployments in the left navigation pane.
- Select Add and then choose Device Twin Configuration or Module Twin Configuration from the drop-down list.
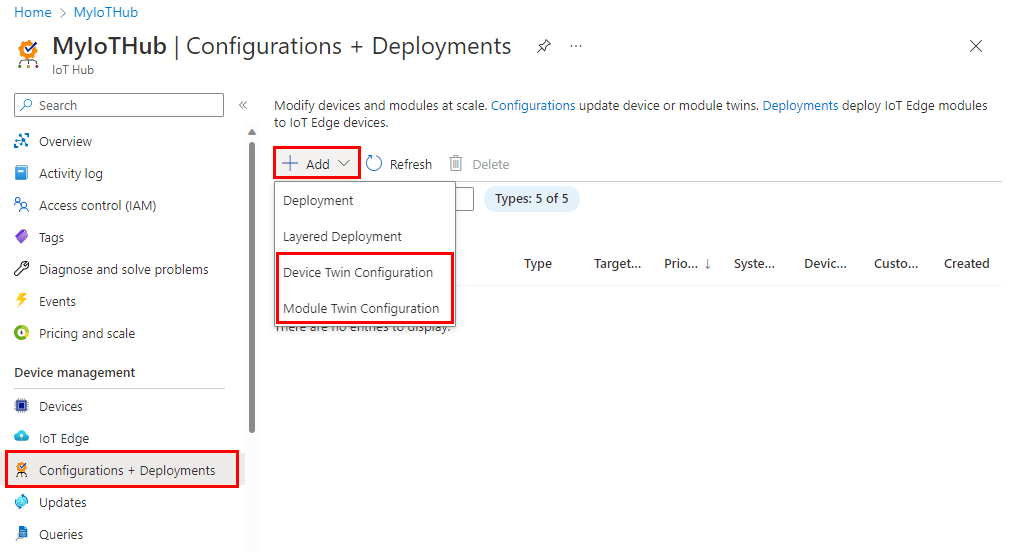
There are five steps to create a configuration.
- Name and label
- Twin settings
- Target devices or modules
- Specify metrics
- Review configuration
The following sections walk through each step.
Name and label
- Give your configuration a unique name that is up to 128 lowercase letters. Lowercase letters and the following special characters are allowed:
-+%_*!'Spaces are not allowed. - Add labels to help track your configurations. Labels are Name, Value pairs that describe your configuration. For example,
HostPlatform,LinuxorVersion,3.0.1. - Select Next to move to the next step.
Twin settings
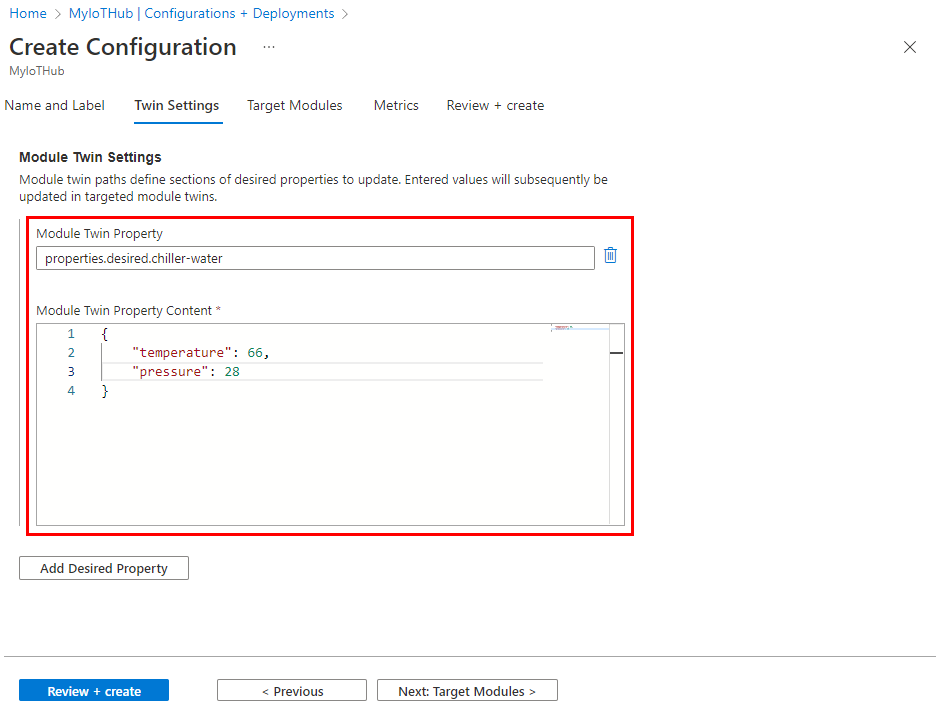
This section defines the content to be set in targeted device twin or module twin desired properties. There are two inputs for each set of settings. The first is the Module Twin Property, which is the path to the JSON section within the twin desired properties that are set. The second is the JSON content to be inserted in that section.
For example, you could set the Module Twin Property to properties.desired.chiller-water and then provide the following JSON content:
{
"temperature": 66,
"pressure": 28
}
You can also set individual settings by specifying the entire path in the Module Twin Property and the value in the Module Twin Property Content with no brackets. For example, set the Module Twin Property to properties.desired.chiller-water.temperature and set the Module Twin Property Content to 66. Then create a new twin setting for the pressure property.
If two or more configurations target the same Module Twin Property, the Content from the highest priority configuration will apply (priority is defined in section Target devices or modules as follows).
If you wish to remove a property, set the property value to null.
You can add more settings by selecting Add Desired Property.
Target devices or modules
Use the tags property from your device twins to target the specific devices that should receive this configuration. You can also target devices by device twin reported properties.
Since multiple configurations may target the same device or module, you should give each configuration a priority number. If there's ever a conflict, the configuration with the highest priority wins:
Enter a positive integer for the configuration Priority. The highest numerical value is considered the highest priority. If two configurations have the same priority number, the one that was created most recently wins.
Enter a Target condition to determine which devices are targeted with this configuration. The condition is based on device twin tags or device twin reported properties and should match the expression format. For example,
tags.environment='test'orproperties.reported.chillerProperties.model='4000x'. You can specify*to target all devices.
For automatic module configuration, use a query to specify tags or reported properties from the modules registered to the IoT hub. For example, from devices.modules where tags.environment='test' or from devices.modules where properties.reported.chillerProperties.model='4000x'. The wildcard cannot be used to target all modules.
Specify metrics
Metrics provide summary counts of the various states that a device may report back after applying configuration content. For example, you may create a metric for pending settings changes, a metric for errors, and a metric for successful settings changes.
Each configuration can have up to five custom metrics.
- Enter a name for Metric Name.
- Enter a query for Metric Criteria. The query is based on device twin reported properties. The metric represents the number of rows returned by the query.
For example:
SELECT deviceId FROM devices
WHERE properties.reported.chillerWaterSettings.status='pending'
You can include a clause that the configuration was applied, for example:
/* Include the double brackets. */
SELECT deviceId FROM devices
WHERE configurations.[[yourconfigname]].status='Applied'
If you're building a metric to report on configured modules, select moduleId from devices.modules. For example:
SELECT deviceId, moduleId FROM devices.modules
WHERE properties.reported.lastDesiredStatus.code = 200
Review configuration
Review your configuration information, then select Submit.
Monitor a configuration
To view the details of a configuration and monitor the devices running it, use the following steps:
- In the Azure portal, go to your IoT hub.
- Select Configurations + Deployments in Device management.
- Inspect the configuration list. For each configuration, you can view the following details:
- ID - the name of the configuration.
- Target condition - the query used to define targeted devices or modules.
- Priority - the priority number assigned to the configuration.
- Creation time - the timestamp from when the configuration was created. This timestamp is used to break ties when two configurations have the same priority.
- System metrics - metrics that are calculated by IoT Hub and cannot be customized by developers. The Targeted metric specifies the number of device twins that match the target condition. The Applied metric specifies the number of device twins that have been modified by the configuration, which can include partial modifications when a separate, higher priority configuration also made changes.
- Custom metrics - metrics that have been specified by the developer as queries against device twin reported properties. Up to five custom metrics can be defined per configuration.
- Select the configuration that you want to monitor.
- Inspect the configuration details. You can use tabs to view specific details about the devices that received the configuration.
- Target Devices or Target Modules - the devices or modules that match the target condition.
- Metrics - a list of system metrics and custom metrics. You can view a list of devices that are counted for each metric by selecting the metric in the drop-down and then selecting View Devices or View Modules.
- Labels - key-value pairs used to describe a configuration. Labels have no impact on functionality.
- Device Twin Settings or Module Twin Settings - the twin settings that are set by the configuration, if any.
Modify a configuration
When you modify a configuration, the changes immediately replicate to all targeted devices or modules.
If you update the target condition, the following updates occur:
- If a device twin didn't meet the old target condition, but meets the new target condition and this configuration is the highest priority for that device twin, then this configuration is applied to the device twin.
- If a device twin no longer meets the target condition, the settings from the configuration are removed and the device twin are modified by the next highest priority configuration.
- If a device twin currently running this configuration no longer meets the target condition and doesn't meet the target condition of any other configurations, then the settings from the configuration are removed and no other changes are made on the twin.
To modify a configuration, use the following steps:
- In the Azure portal, go to your IoT hub.
- Select Configurations + Deployments in Device management.
- Select the configuration that you want to modify.
- You can make updates to the following fields:
- Priority
- Metrics
- Target condition
- Labels
- Select Save.
- Follow the steps in Monitor a configuration to watch the changes roll out.
Delete a configuration
When you delete a configuration, any device twins take on their next highest priority configuration. If device twins don't meet the target condition of any other configuration, then no other settings are applied.
- In the Azure portal, go to your IoT hub.
- Select Configurations + Deployments in Device management.
- Use the checkbox to select the configuration that you want to delete.
- Select Delete.
- A prompt will ask you to confirm.