Security in hybrid cloud environments
Tailwind Traders plans to adopt a hybrid cloud posture. This move will make its environment more complicated than it was when workloads were deployed only on-premises. Also, the security configuration and telemetry of these workloads will be increasingly complex.
In this unit, you'll learn how Tailwind Traders can monitor the configuration of its on-premises and cloud workloads and be alerted to any suspicious activity. You'll also learn how Tailwind Traders can streamline updates to its on-premises and cloud server operating systems.
What is Microsoft Defender for Cloud?
Microsoft Defender for Cloud allows you to assess the security configuration of various workloads. You can use Microsoft Defender for Cloud to:
- Implement security best practices across infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), data, and on-premises resources.
- Track security configuration compliance against regulatory standards.
- Protect data by identifying suspicious activity, such as patterns associated with the exfiltration of data.
- Classify data hosted in SQL databases.
In hybrid environments, Defender for Cloud can be integrated with the Log Analytics agent to collect event-log events, event-tracing telemetry, and crash dump files. Defender for Cloud can then perform an analysis of that data to make recommendations or generate alerts that can be forwarded to an organization's Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM) system.
Tailwind Traders currently uses a variety of tools to assess whether the security configuration of its Windows Server and Linux workloads complies with published third-party standards. By adopting Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Tailwind Traders will be able to monitor and remediate the security configuration of its server operating systems on-premises and its growing deployment of workloads in the cloud as it adopts more hybrid technologies.
What is Microsoft Sentinel?
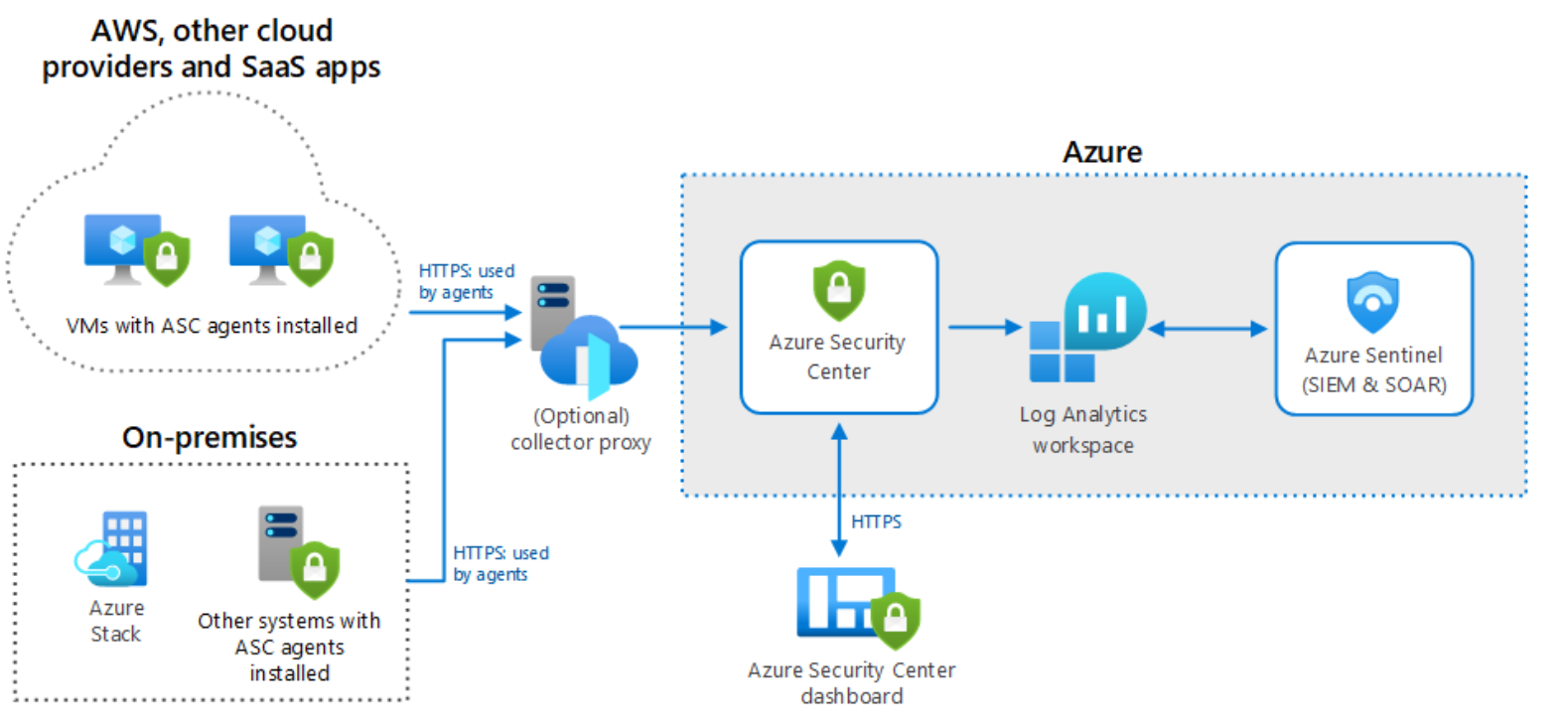
Microsoft Sentinel allows organizations with hybrid cloud solutions to ingest telemetry from security event logs for both on-premises and the cloud. Microsoft Sentinel is both a SIEM and a Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) solution.
SIEM solutions store and analyze log data and event telemetry that they ingest from external sources. Microsoft Sentinel supports the ingestion of data from on-premises, Azure, and third-party cloud locations, including from other SIEM systems. SOAR solutions allow you to orchestrate analysis of data. They assist you in creating an automated response to known threats.
The following image shows a Sentinel hybrid architecture.
Microsoft Sentinel can perform the following tasks when it's supporting hybrid environments:
- Collect data across cloud-based and on-premises users, devices, applications, and infrastructure.
- Use AI and deep learning to identify potentially malicious activity in event data.
- Detect threats through analysis of event data based on attack signatures generated by Microsoft's security research.
- Automate the response to incidents with known characteristics by using security playbooks.
Sentinel includes built-in workbooks that assist in the analysis of data and can provide recommendations for you. You can then quickly comprehend suspicious security telemetry instead of sorting through it to try to understand its meaning. You can also import or use custom workbooks based on the experiences of other security researchers who have found effective methods of security telemetry analysis that differ from those included in Sentinel.
Tailwind Traders currently has an on-premises SIEM system that collects and analyzes event-log data from a variety of computers and devices. Although this SIEM system was adequate when Tailwind Traders had only an on-premises deployment, adopting Microsoft Sentinel will allow Tailwind Traders to extend this capacity into its hybrid cloud.
It's also likely that Tailwind Traders will connect its existing SIEM solution to Sentinel. This connection will give the company the benefits of Sentinel's AI and deep learning without having to substantially modify the existing on-premises configuration.
What is Azure Automation Update Management?
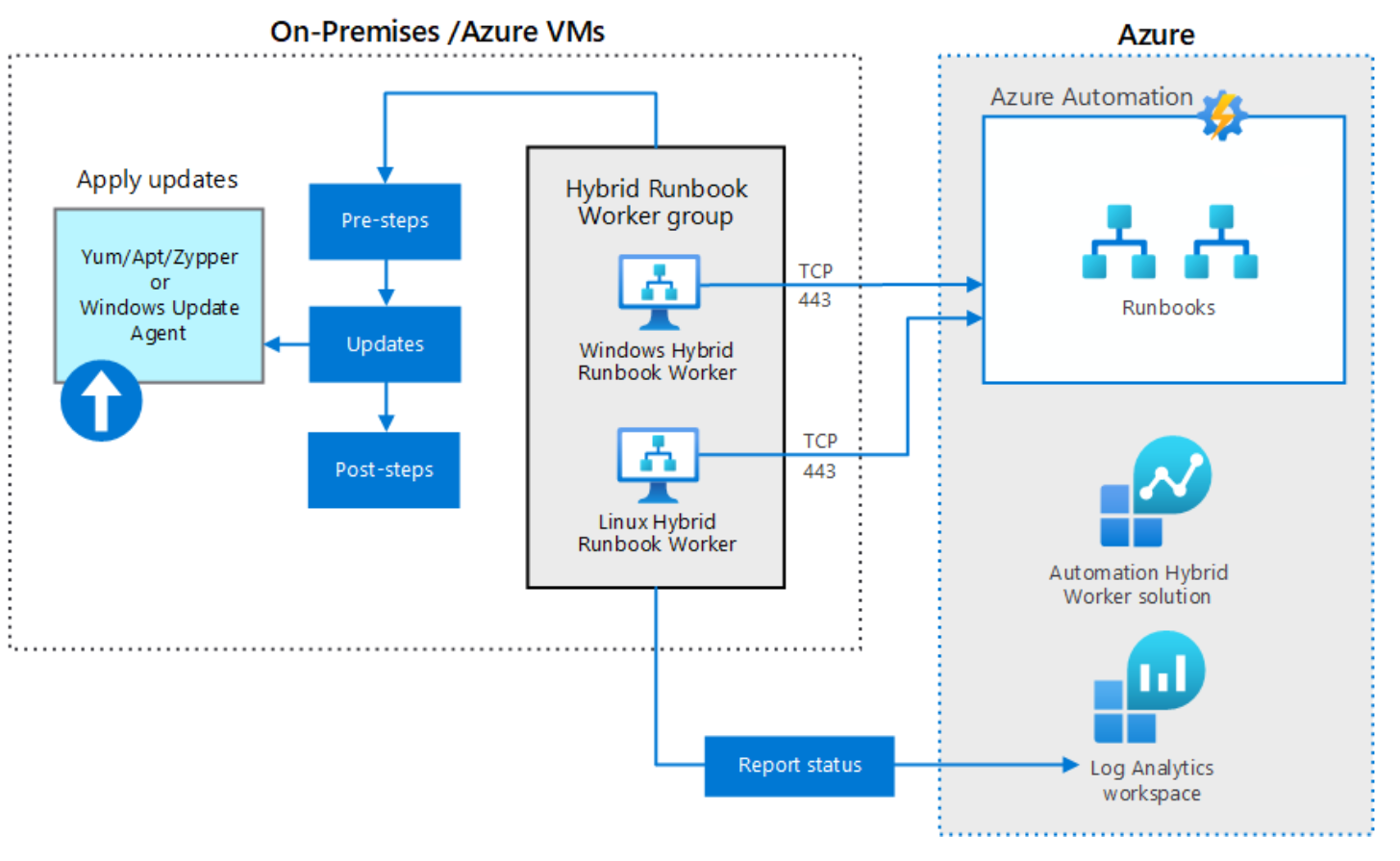
Azure Automation Update Management allows you to manage the updates to your on-premises and cloud server operating systems by using a single console in the cloud. Update Management works with Microsoft Windows Server workloads and with supported Linux operating system workloads running physically and virtually.
Update Management can use Microsoft Update or Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) as a source of updates for Windows Server operating systems. Update Management can also use a public or custom Linux package repository for updates to Linux operating systems. Update Management allows you to determine which updates are currently missing from enrolled operating systems.
The following diagram shows how Update Management integrates with Azure Automation and Log Analytics workspaces.
When you configure an update deployment, you specify:
- Whether the update deployment targets Windows or Linux computers. You can't target both types at the same time.
- The specific enrolled servers that you want to target with the deployment.
- The update classifications that should be installed.
- Whether specific updates should be included or excluded.
- The schedule for the deployment, including whether the deployment should occur periodically.
- Any pre-update and post-update scripts that should be run.
- The maximum length of the maintenance window, with the last 20 minutes of the window devoted to system restart.
- Restart options that determine whether the system should restart if required for updates to complete installation.
Tailwind Traders currently uses WSUS and other tools to manage the updates to its on-premises Windows and Linux operating systems. By configuring its operating system workloads for IaaS virtual machines (both on-premises and in the cloud) to connect to Azure Software Update, Tailwind Traders can ensure that all operating systems that host critical workloads stay up to date.