Dynamics 365 opportunity overview
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Sales lets organizations manage their whole sales lifecycle process, from start to finish. Although every organization is different, a typical sales lifecycle resembles the following image.
When prospects or customers express qualified interest in buying your products or services, they're considered opportunities.
An opportunity is a potential sale. Leads become opportunities after they're determined to be viable customers. Unlike lead records, which typically include only basic information, opportunity records provide more specific details, like potential revenue, timelines, and information about products or services.
Organizations use opportunities to forecast revenue. As opportunities are entered, the future value of their potential sales is estimated to provide a sales pipeline forecast. As opportunities are closed, the actual revenue that's generated is compared with the forecasted revenue. Working on an opportunity might involve several customer interactions, like meetings, phone calls, or tasks. Often, the sales team's effectiveness at managing this phase can make the difference between a win and a loss.
Effective opportunity management can involve several tasks. Here are some examples:
Assigning and sharing opportunities with the most appropriates individuals or teams
Tracking product and service details for items that the customer is interested in
Providing the most appropriate literature to the customer
Managing and tracking sales activities that are related to the opportunity
Tracking stakeholders and competitors
Moving opportunities through a sales process workflow
Opportunities are an important part of the sales process since a sales team typically spends most of its time and effort on them. In addition to opportunities, Dynamics 365 Sales includes several components that are used not only to sell to customers but to help maintain a healthy long-term relationship with customers. Here are some of the most commonly used sales components.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Customer | A customer can be either an account or a contact. In business-to-business (B2B) scenarios, a customer is typically an account. In business-to-consumer (B2C) scenarios, a customer is typically a contact. For opportunities, a customer represents the potential customer that an opportunity applies to. |
| Account | An account represents a business or organization. An account can be set as the potential customer for an opportunity. |
| Contact | A contact represents a single individual. A contact can be set as the potential customer for an opportunity. |
| Activities | An activity is a type of table that offers tracking and scheduling options. Opportunities often have multiple activities for things like tasks, appointments, and phone calls. |
| Business process flow | A business process flow (BPF) is a type of automation in Microsoft Power Platform. A BPF appears on a table page and gives users guidance and a predictable action plan for gathering data. For opportunities, Business Process Flows guide users through the steps and phases that are necessary to convert an opportunity to a sale. |
| Lead | Leads are used to determine someone's viability as a potential customer. Qualified leads are converted to opportunities. |
| Product catalog | A product catalog is a collection of records that facilitate management of products, price lists, discounts, and product families for sales transactions. Products from a product catalog can be added to opportunities as line items. |
| Quote | A quote is a formal offer for products or services that are proposed to a customer at specific prices and related payment terms. Quotes can be created from opportunity records. |
| Order | An order is a confirmed request for the delivery of goods and services at specified terms. Alternatively, it's a quotation that has been accepted by a customer. |
| Invoice | An invoice is an order or a record of a sale that has been billed to the customer. It includes details about the products or services that were bought. |
The following image shows an example of a sales process from beginning to end.
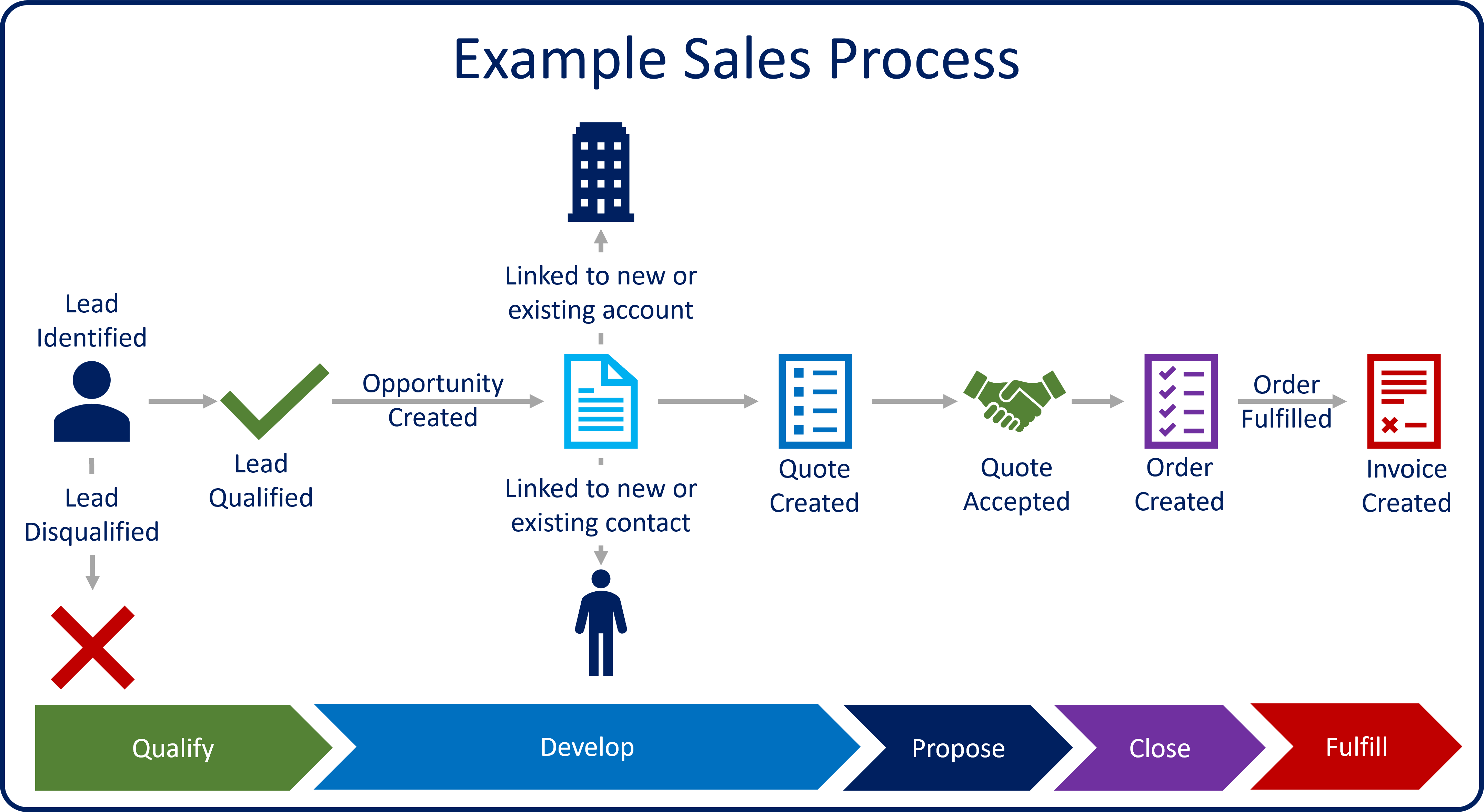
In the preceding image, a lead has contacted your organization about products and services. An account executive has reached out to the lead to gather more information and to determine whether the lead and your organization will be a good fit for each other.
If the account executive determines that there's a good fit, the lead is qualified as an opportunity.
If the lead is an existing customer, a new opportunity is created and associated with an existing account and/or contact record.
If the lead is a new customer, new account, contact, and opportunity records are created.
Alternatively, if the account executive determines that there isn't a good fit, the lead is disqualified, and the sales process ends.
Details are added to the opportunity. These details include the products and services that the lead is interested in, the estimated revenue, and timelines.
A quote is added to the opportunity. The quote represents the formal proposal to the customer.
When the customer agrees to the quote, an order is generated. The quote and opportunity that are associated with the order are closed.
After the order is fulfilled, an invoice is generated to bill the customer.