Define orchestration
To help you to determine Contoso's best options for running multiple container workloads on Windows Server, you need to understand Windows container orchestration and the types of container orchestration tools available.
What is Windows container orchestration?
Containers are perfectly suited to packaging and running applications in agile delivery environments and micro-service architectures. However, environments that use containers and micro-services can grow to span multiple containers and spread across many servers. Without automation, it can be challenging to manage and operate disparate, distributed container-based environments efficiently and at scale. Container-based environments can utilize an orchestrator to automate and manage large numbers of containers and control how the containers interact with one another.
A typical orchestrator performs the tasks in the following table.
| Task | Description |
|---|---|
| Scheduling | Determines each machine's suitability for running different container images and for managing resource requests. |
| Affinity/Anti-affinity | Allows sets of containers to run near each other for better performance or far apart for higher availability. |
| Health monitoring | Watches for container failures and automatically reschedules them. |
| Failover | Keeps track of what's running on each machine and reschedules containers from failed machines to healthy nodes. |
| Scaling | Adds or removes container instances manually or automatically according to demand. |
| Networking | Provides an overlay network that coordinates communication between containers and across multiple host machines. |
| Service discovery | Enables containers to locate each other automatically even as they move between host machines and change IP addresses. |
| Coordinated application upgrades | Manages container upgrades to reduce application downtime and facilitates rollback if something goes wrong. |
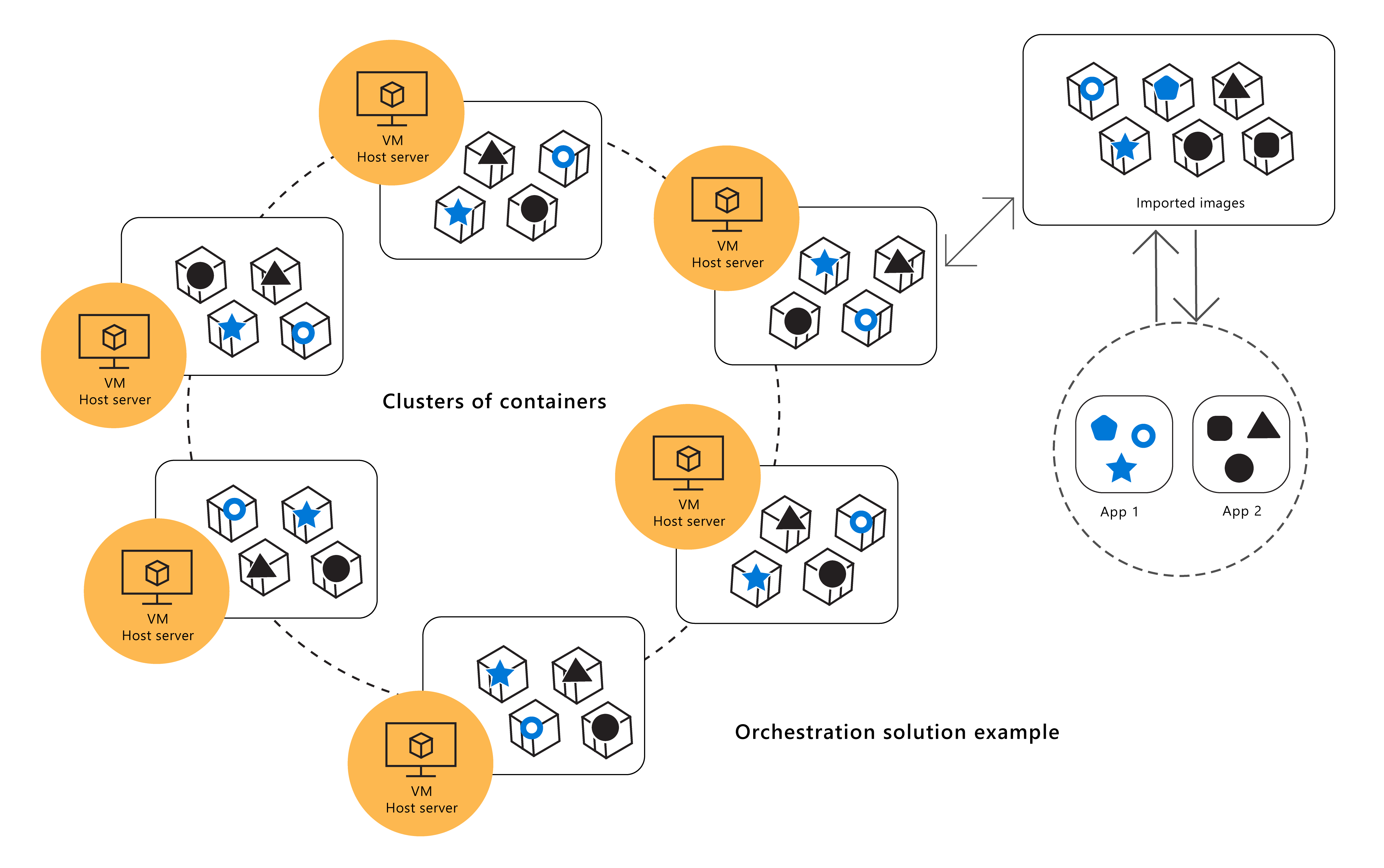
The following image is an example of some of the elements involved in orchestrating applications with containers and how they might interact. This image has various application types and container images. Applications are applied to container images and deployed to a cluster as a running container, with multiple containers running in each deployment instance. A separate host acts to coordinate some of these actions and tasks.
Types of container orchestration tools
There are several container orchestration tools available. Which orchestration tool you decide to use depends on the requirements of the specific architecture you want to manage. Common orchestration tools include those found in the following table.
| Orchestration tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes | The popular container orchestration tool Kubernetes is an open-source platform for deploying and managing containers at scale, in addition to their associated networking and storage components. Kubernetes' main focus is on managing application workloads, and not the underlying infrastructure components. Kubernetes is typically abbreviated as K8s, where the digit 8 represents the eight characters between the letters K and the s in the word Kubernetes. |
| Docker Swarm | Swarm mode is a Docker feature that provides built-in container orchestration capabilities. You can run a group of Docker hosts as a swarm cluster by setting their Docker engines to run together in swarm mode. Swarm is considered less extensible and complex than Kubernetes, but it's a good choice for Docker enthusiasts. Docker bundles both Swarm and Kubernetes with Docker Client for Windows. |
| Apache Mesos | The open-source distributed systems platform Mesos can abstract a datacenter's resources—including containers—into groups to provide a consolidated and powerful pool of compute resources. Mesos requires additional add-on frameworks to support full orchestration tasks. |
Note
Kubernetes is a widely adopted standard for container orchestration. Most cloud service providers offer Kubernetes-as-a-service to help their clients to deploy and manage containerized applications.
For example, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) integrates with Azure Container Registry (ACR) to provide a provisioning portal where you can secure your container clusters with Microsoft Entra ID and deploy your applications across Azure's datacenter offerings. By using AKS, you can take advantage of Azure's enterprise-grade features and, at the same time, continue to maintain your applications' portability with Kubernetes and the Docker image format.