Exercise - Detect the user's location using Xamarin.Essentials
The app has a UI and a viewmodel. In this unit, you'll add location lookup to the viewmodel using Xamarin.Essentials.
Enable location permissions
All mobile platforms have security around user information and certain hardware, such as camera, photo library, and the user's location. Before an app can access the user's location, the user has to grant permission - either by implicitly granting these permissions at install time or by choosing to grant a permission at runtime. When you view a UWP app in the store, the listing will show the permissions that the app needs. By installing the app, you implicitly grant permission. These permissions are configured in an app manifest file.
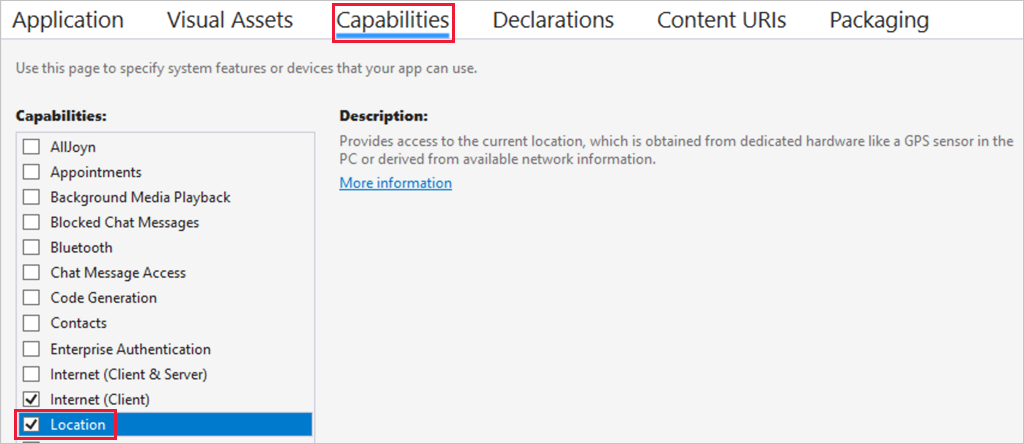
In the
ImHere.UWPapp project, open thePackage.appxmanifestfile.Head to the Capabilities tab and check the Location capability.
Query for the user's location
There are two ways to get the user's location - the last known or the current. The current location can take some time to get because the device may need to establish a GPS link and wait for the accurate location to be retrieved. The fastest way is to get the last known location detected by the device. The last known location is potentially less accurate but is a much faster call. Locations come as the latitude and longitude in decimal degrees and the altitude of the device in meters above sea level.
Open the
MainViewModelclass in theImHere.NET Standard project.Add a using directive for the
Xamarin.Essentialsnamespace.using Xamarin.Essentials;In the
SendLocationmethod, make a call to theGetLastKnownLocationAsyncstatic method on theGeolocationclass in theXamarin.Essentialsnamespace.Location location = await Geolocation.GetLastKnownLocationAsync();Update the
Messageproperty with the user's location if one is found.if (location != null) { Message = $"Location found: {location.Latitude}, {location.Longitude}."; }The full code for this method is below.
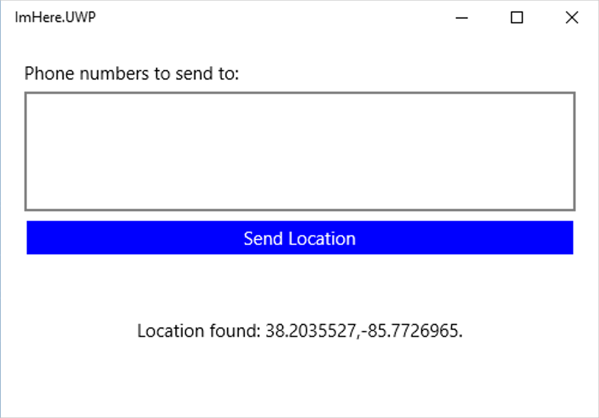
async Task SendLocation() { Location location = await Geolocation.GetLastKnownLocationAsync(); if (location != null) { Message = $"Location found: {location.Latitude}, {location.Longitude}."; } }Run the app and select the Send Location button to see the location on the UI. Location for your device must be turned on in Location privacy settings.
Note
This app uses the last known location. In a production-quality app, you would want to get the current accurate location with a time-out, and if one is not found in time, fall back to the last known. You can read more on how to do this in the Xamarin.Essentials Geolocation docs.
This app does not have error handling. In a production-quality app, you should handle any exceptions that occur, such as if the location was not available.
Summary
In this unit, you learned how to use Xamarin.Essentials to get the user's location. In the next unit, you'll create the Azure Functions to act as a back end for the mobile app.