Create a Litigation hold
You can place a mailbox on Litigation hold to retain all mailbox content, including deleted items and the original versions of modified items. When you place a user mailbox on Litigation hold, content in the user's archive mailbox (if it's enabled) is also retained. When you create a hold, you can specify a hold duration (also called a time-based hold) so that deleted and modified items are retained for a specified period and then permanently deleted from the mailbox. Or you can just retain content indefinitely (called an infinite hold) or until the Litigation hold is removed. If you do specify a hold duration period, it's calculated from the date a message is received or a mailbox item is created.
Here's what happens when you create a Litigation hold.
- Items that are permanently deleted by the user are retained in the Recoverable Items folder in the user's mailbox for the duration of the hold.
- Items that are purged from the Recoverable Items folder by the user are retained for the duration of the hold.
- The storage quota for the Recoverable Items folder is increased from 30 GB to 110 GB.
- Items in the user's primary and the archive mailboxes are retained
Tip
If you're not an E5 customer, use the 90-day Microsoft Purview solutions trial to explore how additional Purview capabilities can help your organization manage data security and compliance needs. Start now at the Microsoft Purview compliance portal trials hub. Learn details about signing up and trial terms.
Assign an Exchange Online Plan 2 license
To place an Exchange Online mailbox on Litigation hold, it must be assigned an Exchange Online Plan 2 license. If a mailbox is assigned an Exchange Online Plan 1 license, you would have to assign it a separate Exchange Online Archiving license to place it on hold.
Place a mailbox on Litigation hold
Here are the steps to place a mailbox on Litigation hold using the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Go to the Microsoft 365 admin center and then select Users > Active users.
Select the user that you want to place on Litigation hold.
On the properties flyout page, select the Mail tab, and then under More actions, select Manage litigation hold.

On the Manage litigation hold flyout page, select the Turn on litigation hold checkbox and then enter the following optional information:
Hold duration (days): Use this box to create a time-based hold and specify how long mailbox items are held when the mailbox is placed on Litigation hold. The duration is calculated from the date a mailbox item is received or created. When the hold duration expires for a specific item, that item will no longer be preserved. If you leave this box blank, items are preserved indefinitely or until the hold is removed. Use days to specify the duration.
Note visible to the user: Use this box to inform the user their mailbox is on Litigation hold. The note will appear on the Account Information page in the user's mailbox if they're using Outlook 2010 or later. To access this page, users can select File in Outlook.
Web page with more information for the user: Use this box to direct the user to a website for more information about Litigation hold. This URL appears on the Account Information page in the user's mailbox if they're using Outlook 2010 or later. To access this page, users can select File in Outlook.
. Select Save changes on the Litigation hold flyout page to create the hold.
The system displays a banner saying it might take up to 240 minutes for the change to take effect.
Create a Litigation hold using PowerShell
You can also create a Litigation hold by running the following command in Exchange Online PowerShell:
Set-Mailbox <username> -LitigationHoldEnabled $true
The previous command preserves items indefinitely because the hold duration isn't specified. To create a time-based hold, using the following command:
Set-Mailbox <username> -LitigationHoldEnabled $true -LitigationHoldDuration <number of days>
You can also run the following command to verify if the mailbox is placed on Litigation hold:
Get-Mailbox <username> | FL LitigationHoldEnabled
A value of True indicates that the mailbox is on litigation hold/
For more information, see Set-Mailbox.
How does Litigation hold work?
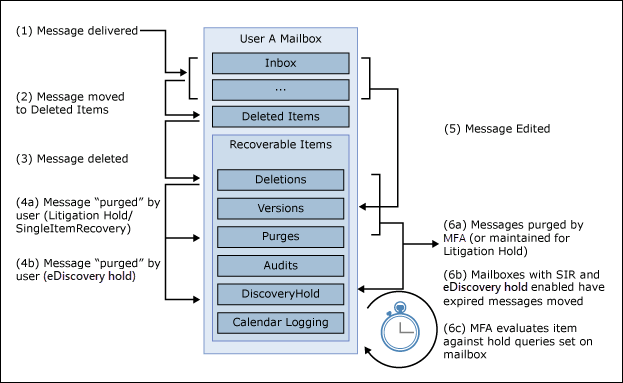
In the normal deleted item workflow, a mailbox item is moved to the Deletions subfolder in the Recoverable Items folder when a user permanently deletes it (Shift + Delete) or deletes it from the Deleted Items folder. A deletion policy (which is a retention tag configured with a Delete retention action) also moves items to the Deletions subfolder when the retention period expires. When a user purges an item in the Recoverable Items folder or when the deleted item retention period expires for an item, it's moved to the Purges subfolder in the Recoverable Items folder and marked for permanent deletion. It will be purged from Exchange the next time the mailbox is processed by the Managed Folder Assistant (MFA).
When a mailbox is placed on Litigation hold, items in the Purges subfolder are preserved for the hold duration specified by the Litigation hold. The hold duration is calculated from the original date an item was received or created, and defines how long items in the Purges subfolder are held. When the hold duration expires for an item in the Purges subfolder, the item is marked for permanent deletion and will be purged from Exchange the next time the mailbox is processed by the MFA. If an indefinite hold is placed on a mailbox, items will never be purged from the Purges subfolder.
The following illustration shows the subfolders in the Recoverable Items folders and the hold workflow process.
Note
If a hold associated with an eDiscovery case is placed on a mailbox, purged items are moved from the Deletions subfolder to the DiscoveryHolds subfolder and are preserved until the mailbox is released from the eDiscovery hold.
Feedback
Binnenkort beschikbaar: In de loop van 2024 zullen we GitHub Issues geleidelijk uitfaseren als het feedbackmechanisme voor inhoud. Het wordt vervangen door een nieuw feedbacksysteem. Zie voor meer informatie: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Feedback verzenden en weergeven voor