Dynamic IP Security <dynamicIpSecurity>
Overview
The <dynamicIpSecurity> element provides a dynamic means of blocking malicious Web requests. Using dynamic IP restrictions means the administrator does not need to identify the IP addresses that need to be blocked. Instead, the administrator can configure the system so that it blocks any IP address that meets the set criteria. This can include blocking a remote client if the number of concurrent HTTP connection requests from that client exceeds a specific number, or blocking a client if the number of requests received over a period of time exceeds a specific number. The dynamic IP restrictions can be configured at either the server or site levels.
The administrator can specify which HTTP response status code will be returned if a client is blocked: Unauthorized (401); Forbidden (403); or Not Found (404). You can also set the Deny Action Type to Abort to drop the connection without returning any indication why.
If you enable the proxy mode, a request can be blocked by identifying the originating IP address of a client that connects to a web server through an HTTP proxy or load balancer. This is done by examining the x-forwarded-for-HTTP header.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <dynamicIpSecurity> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <dynamicIpSecurity> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <dynamicIpSecurity> element was introduced in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | N/A |
| IIS 7.0 | N/A |
| IIS 6.0 | N/A |
Setup
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
- In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features.
- In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
- On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Security, and then select IP and Domain Restrictions. Click Next.
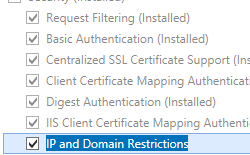 .
. - On the Select features page, click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Security, and then select IP Security.
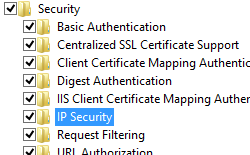
- Click OK.
- Click Close.
How To
How to add dynamic IP restrictions to deny access for a Web site
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or later:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or later:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, select the server name to add dynamic IP restrictions for the server, or expand Sites and then select a site to add dynamic IP restrictions for the site.
In the Home pane, double-click the IP Address and Domain Restrictions feature.
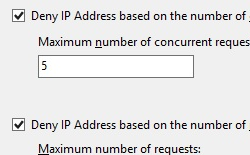
In the Actions pane, click Edit Dynamic Restriction Settings....
In the Dynamic IP Restriction Settings dialog box, specify whether to deny an IP address based on the number of concurrent samples and/or the request rate, specify whether to enable logging-only mode, and then click OK.
Configuration
The <dynamicIpSecurity> element is configured at the server or site level.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
denyAction |
Optional enum attribute. Specifies the default deny mode response that IIS should send back to clients. The default value is Forbidden.
|
||||||||||
enableLoggingOnlyMode |
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies that IIS will log requests from the client that would be rejected without actually rejecting them. The default value is false. |
||||||||||
enableProxyMode |
Optional Boolean attribute. Enables IIS not only to block requests from a client IP that is seen by IIS, but also to block requests from IP addresses that are received in the x-forwarded-for HTTP header. This header enables you to identify the originating IP address of a client that connects through an HTTP proxy or load balancer. This is referred to as proxy mode. The default value is false. |
Child Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
denyByConcurrentRequests |
Optional element. Specifies that certain remote clients will be blocked based on the number of requests received over time. |
denyByRequestRate |
Optional element. Specifies that certain remote clients will be blocked based on the number of concurrent HTTP connection requests from clients. |
Configuration Sample
The following configuration sample demonstrates how to set dynamic IP address restrictions.
<system.webServer>
<security>
<dynamicIpSecurity enableLoggingOnlyMode="true">
<denyByConcurrentRequests enabled="true" maxConcurrentRequests="10" />
<denyByRequestRate enabled="true" maxRequests="30"
requestIntervalInMilliseconds="300" />
</dynamicIpSecurity>
</security>
</system.webServer>
Sample Code
The following examples configure <dynamicIpSecurity> for a site.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity /denyAction:"Unauthorized" /enableProxyMode:"True" /enableLoggingOnlyMode:"True" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity /denyByConcurrentRequests.enabled:"True" /denyByConcurrentRequests.maxConcurrentRequests:"10" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity /denyByRequestRate.enabled:"True" /denyByRequestRate.maxRequests:"25" /denyByRequestRate.requestIntervalInMilliseconds:"210" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when using AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample {
private static void Main() {
using(ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager()) {
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection dynamicIpSecuritySection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity", "Default Web Site");
dynamicIpSecuritySection["denyAction"] = @"Forbidden";
dynamicIpSecuritySection["enableProxyMode"] = true;
dynamicIpSecuritySection["enableLoggingOnlyMode"] = true;
ConfigurationElement denyByConcurrentRequestsElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.GetChildElement("denyByConcurrentRequests");
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement["enabled"] = true;
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement["maxConcurrentRequests"] = 10;
ConfigurationElement denyByRequestRateElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.GetChildElement("denyByRequestRate");
denyByRequestRateElement["enabled"] = true;
denyByRequestRateElement["maxRequests"] = 10;
denyByRequestRateElement["requestIntervalInMilliseconds"] = 10;
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim dynamicIpSecuritySection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity", "Default Web Site")
dynamicIpSecuritySection("denyAction") = "Forbidden"
dynamicIpSecuritySection("enableProxyMode") = true
dynamicIpSecuritySection("enableLoggingOnlyMode") = true
Dim denyByConcurrentRequestsElement As ConfigurationElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.GetChildElement("denyByConcurrentRequests")
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement("enabled") = true
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement("maxConcurrentRequests") = 10
Dim denyByRequestRateElement As ConfigurationElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.GetChildElement("denyByRequestRate")
denyByRequestRateElement("enabled") = true
denyByRequestRateElement("maxRequests") = 10
denyByRequestRateElement("requestIntervalInMilliseconds") = 10
serverManager.CommitChanges
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var dynamicIpSecuritySection = adminManager.GetAdminSection ("system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site");
dynamicIpSecuritySection.Properties.Item("denyAction").Value = "Unauthorized";
dynamicIpSecuritySection.Properties.Item("enableProxyMode").Value = true;
dynamicIpSecuritySection.Properties.Item("enableLoggingOnlyMode").Value = true;
var denyByConcurrentRequestsElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.ChildElements.Item("denyByConcurrentRequests");
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement.Properties.Item("enabled").Value = true;
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement.Properties.Item("maxConcurrentRequests").Value = 10;
var denyByRequestRateElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.ChildElements.Item("denyByRequestRate");
denyByRequestRateElement.Properties.Item("enabled").Value = true;
denyByRequestRateElement.Properties.Item("maxRequests").Value = 25;
denyByRequestRateElement.Properties.Item("requestIntervalInMilliseconds").Value = 210;
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = CreateObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set dynamicIpSecuritySection = adminManager.GetAdminSection ("system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site")
dynamicIpSecuritySection.Properties.Item("denyAction").Value = "Unauthorized"
dynamicIpSecuritySection.Properties.Item("enableProxyMode").Value = true
dynamicIpSecuritySection.Properties.Item("enableLoggingOnlyMode").Value = true
Set denyByConcurrentRequestsElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.ChildElements.Item ("denyByConcurrentRequests")
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement.Properties.Item("enabled").Value = true
denyByConcurrentRequestsElement.Properties.Item("maxConcurrentRequests").Value = 10
Set denyByRequestRateElement = dynamicIpSecuritySection.ChildElements.Item("denyByRequestRate")
denyByRequestRateElement.Properties.Item("enabled").Value = true
denyByRequestRateElement.Properties.Item("maxRequests").Value = 25
denyByRequestRateElement.Properties.Item("requestIntervalInMilliseconds").Value = 210
adminManager.CommitChanges()
PowerShell
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity" -name "denyAction" -value "Unauthorized"
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity" -name "enableProxyMode" -value "True"
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity" -name "enableLoggingOnlyMode" -value "True"
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity/denyByConcurrentRequests" -name "enabled" -value "True"
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity/denyByConcurrentRequests" -name "maxConcurrentRequests" -value 20
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity/denyByRequestRate" -name "enabled" -value "True"
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity/denyByRequestRate" -name "maxRequests" -value 20
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -location 'Default Web Site' -filter "system.webServer/security/dynamicIpSecurity/denyByRequestRate" -name "requestIntervalInMilliseconds" -value 20
Feedback
Kommer snart: Under hela 2024 kommer vi att fasa ut GitHub-problem som feedbackmekanism för innehåll och ersätta det med ett nytt feedbacksystem. Mer information finns i: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Skicka och visa feedback för