Azure kaynağı için ölçümleri analiz etme
Ölçümler, düzenli aralıklarla otomatik olarak toplanan ve kaynağın bazı yönlerini açıklayan sayısal değerlerdir. Örneğin, bir ölçüm size bir sanal makinenin işlemci kullanımını, depolama hesabındaki boş alanı veya sanal ağ için gelen trafiği gösterebilir.
Ölçüm gezgini, Azure portal Azure İzleyici'nin bir özelliğidir. Bunu kullanarak ölçüm değerlerinden grafikler oluşturabilir, eğilimleri görsel olarak ilişkilendirebilir ve ölçüm değerlerindeki ani artışları ve düşüşleri araştırabilirsiniz. Azure kaynaklarınız tarafından oluşturulan ölçümlerden grafikler çizmek ve bunların sistem durumunu ve kullanımını araştırmak için ölçüm gezginini kullanın.
Bu öğreticide şunların nasıl yapıldığını öğreneceksiniz:
- Azure kaynağı için ölçüm gezginini açın.
- Grafiğe çizecek ölçümü seçin.
- Ölçüm değerlerinin farklı toplamalarını gerçekleştirin.
- Grafiğin zaman aralığını ve ayrıntı düzeyini değiştirin.
Aşağıdaki videoda, bu öğreticide açıklanan yordamdan daha kapsamlı bir senaryo gösterilmektedir. Ölçümler hakkında yeniyseniz, önce bu makaleyi okuyun ve daha fazla bilgi edinmek için videoyu görüntüleyin.
Önkoşullar
Bu öğreticideki adımları tamamlamak için izlenecek bir Azure kaynağı gerekir. Azure aboneliğinizde ölçümleri destekleyen herhangi bir kaynağı kullanabilirsiniz. Kaynağın ölçümleri destekleyip desteklemediğini belirlemek için Azure portal menüsündeki menüsüne gidin. Ardından menünün İzleme bölümünde Ölçümler seçeneğinin bulunduğunu doğrulayın.
Ölçüm gezginini açma
Kaynağınızın menüsünün İzleme bölümünde Ölçümler'i seçin. Kapsam zaten kaynağınızla doldurulmuş. Aşağıdaki örnek bir depolama hesabı içindir, ancak diğer Azure hizmetleri benzer görünür.
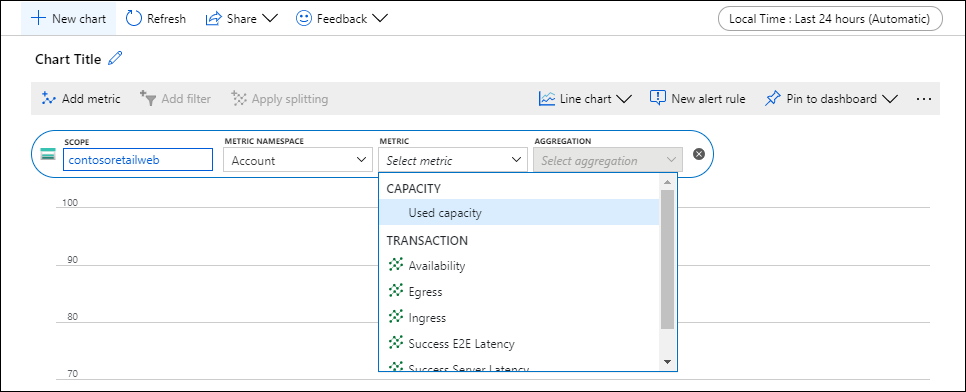
Kapsamda birden fazla ad alanı varsa bir Ad Alanı seçin. Ad alanı, ölçümleri kolayca bulabilmeniz için düzenlemenin bir yoludur. Örneğin, depolama hesaplarının Dosya, Tablo, Blob ve Kuyruk ölçümlerini depolamak için ayrı ad alanları vardır. Birçok kaynak türünün yalnızca bir ad alanı vardır.
Seçili kapsam ve ad alanı için kullanılabilir ölçümler listesinden bir ölçüm seçin.
Alternatif olarak ölçüm Toplama'yı da değiştirebilirsiniz. Bu seçenek, ölçüm değerlerinin grafın zaman ayrıntı düzeyi boyunca nasıl toplanacaklarını tanımlar. Örneğin, zaman tanecikliği 15 dakika olarak ayarlanırsa ve toplama Toplam olarak ayarlanırsa, grafikteki her nokta her 15 dakikalık segment üzerinde toplanan tüm değerlerin toplamı olur.
Aynı grafikte birden çok ölçümün çizildiğini görmek istiyorsanız Ölçüm ekle'yi seçin ve bu adımları yineleyin. Tek bir görünümde birden çok grafik için Yeni grafik'i seçin.
Zaman aralığı ve ayrıntı düzeyi seçme
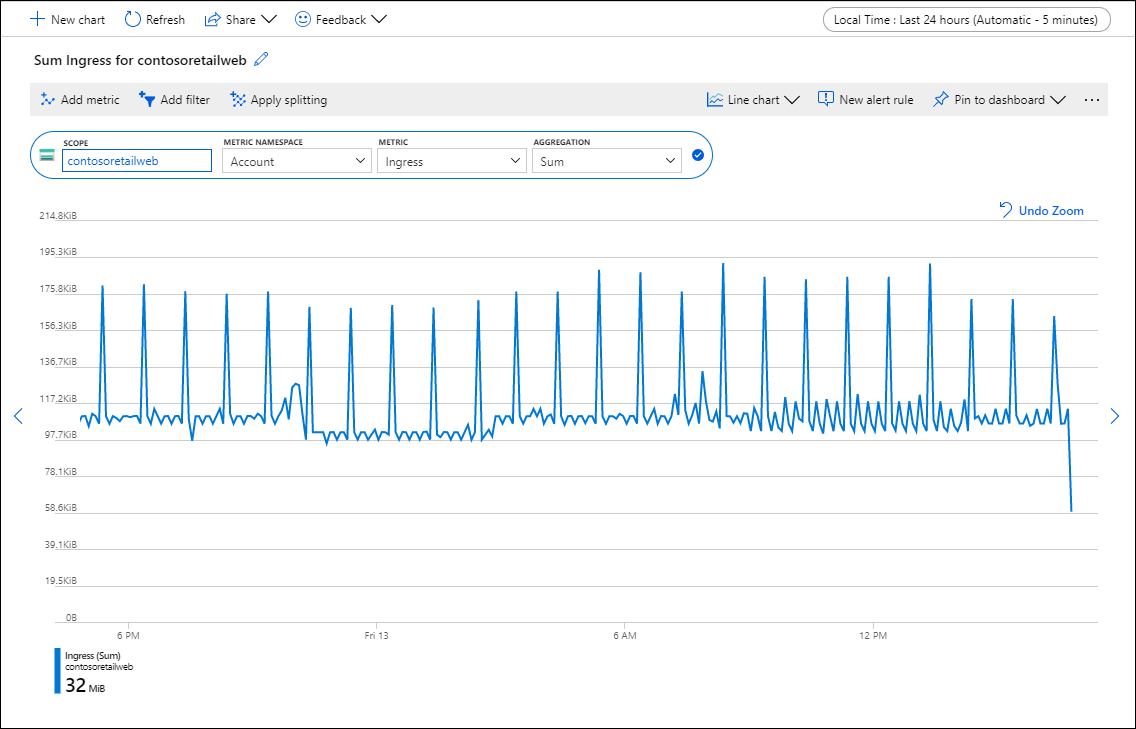
Grafik varsayılan olarak en son 24 saatlik ölçüm verilerini gösterir.
Grafiğin Zaman aralığını veya her veri noktasının zaman aralığını tanımlayan Zaman ayrıntı düzeyini değiştirmek için zaman seçiciyi kullanın. Grafik, belirtilen zaman ayrıntı düzeyine göre örneklenen tüm değerleri hesaplamak için belirtilen toplamayı kullanır.
Grafiğin ani artış veya düşüş gibi ilginç bir alanını araştırmak için zaman fırçasını kullanın. Fare işaretçisini alanın başına getirin, sol fare düğmesini tıklatıp basılı tutun, alanın diğer tarafına sürükleyin ve düğmeyi bırakın. Grafik bu zaman aralığını yakınlaştıracaktır.
Boyut filtreleri ve bölme uygulama
Ölçümleriniz üzerinde daha fazla analiz yapmak ve verilerinizdeki olası aykırı değerleri belirlemek için kullanabileceğiniz gelişmiş özellikler için aşağıdaki başvurulara bakın:
- Filtreleme, grafiğe hangi boyut değerlerinin dahil olduğunu seçmenizi sağlar. Örneğin, yalnızca bir sunucu yanıt süresi ölçümü grafiği oluştururken başarılı istekleri göstermek isteyebilirsiniz.
- Bölme, grafiğin bir boyutun her değeri için ayrı çizgiler görüntüleyip görüntülemediğini veya değerleri tek bir satırda toplayıp toplamadığını denetler. Örneğin, tüm sunucu örneklerinde ortalama yanıt süresi için bir satır görmek isteyebilirsiniz. Ya da her sunucu için ayrı satırlar isteyebilirsiniz.
Filtreleme ve bölme uygulanmış grafik örneklerine bakın.
Gelişmiş grafik ayarları
Grafik stilini ve başlığını özelleştirebilir ve gelişmiş grafik ayarlarını değiştirebilirsiniz. Özelleştirmeyi bitirdiğinizde, çalışmanızı kaydetmek için grafiği bir panoya sabitleyin. Ölçüm uyarılarını da yapılandırabilirsiniz. Bu seçenekler ve Azure İzleyici ölçüm gezgininin diğer gelişmiş özellikleri hakkında bilgi edinmek için bkz. Azure ölçüm gezgininin gelişmiş özellikleri.
Sonraki adımlar
Azure İzleyici'de ölçümlerle çalışmayı öğrendiğinize göre, bir ölçüm değeri olası bir sorunu gösterdiğinde bildirim almak üzere bir ölçüm uyarısı kuralı oluşturmayı öğrenin.