Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft Graph is a protected API gateway for accessing data in Microsoft cloud services like Microsoft Entra ID and Microsoft 365. It's protected by the Microsoft identity platform, which authorizes and verifies that an app is authorized to call Microsoft Graph.
This article provides an overview of the requirements for an app to be authorized to access data via any Microsoft Graph API. If you're already familiar with how authentication and authorization works, explore Microsoft identity platform code samples or Microsoft Graph tutorials for apps that are built using different Microsoft Graph SDKs and that call Microsoft Graph APIs.
Register the application
Before your app can be authorized to call any Microsoft Graph API, the Microsoft identity platform must first be aware of it. This process doesn't involve uploading your application code to the platform. Rather, it involves registering the app in the Microsoft Entra admin center to establish its configuration information including the following core parameters:
- Application ID: A unique identifier assigned by the Microsoft identity platform.
- Redirect URI/URL: One or more endpoints at which your app receives responses from the Microsoft identity platform. The Microsoft identity platform assigns the URI to native and mobile apps.
- Credential: Can be a client secret (a string or password), a certificate, or a federated identity credential. Your app uses the credential to authenticate with the Microsoft identity platform. This property is only required for confidential client applications; It isn't required for public clients like native, mobile, and single page applications. For more information, see Public client and confidential client applications.
You then add this information back to your code once, and the app uses the information every time it needs to prove its identity during an authentication process, before it can be authorized to access your data.
For more information, see Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform.
Access scenarios
An app can access data in one of two ways as illustrated in the following image.
- Delegated access, an app acting on behalf of a signed-in user.
- App-only access, an app acting with its own identity.
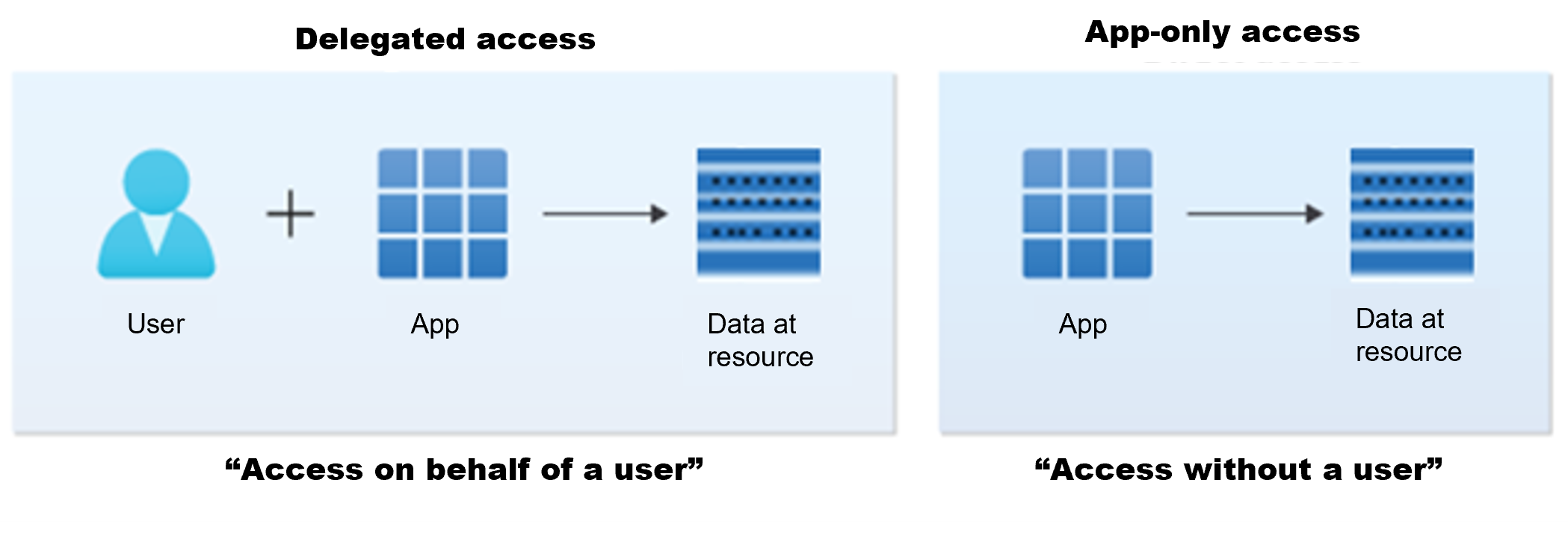
Delegated access (access on behalf of a user)
In this access scenario, a user signs into a client application which calls Microsoft Graph on their behalf. Both the client app and the user must be authorized to make the request.
For the client app to be authorized to access the data on behalf of the signed-in user, it must have the required permissions, which it receives through a combination of two factors:
- Delegated permissions, also referred to as scopes: The permissions exposed by Microsoft Graph and that represent the operations that the app can perform on behalf of the signed-in user. The app might be allowed to perform an operation on behalf of one user but not another.
- User permissions: The permissions that the signed-in user has to the resource. The user might be the owner of the resource, the resource might be shared with them, or they might be assigned permissions through a role-based access control system (RBAC) such as Microsoft Entra RBAC.
Sample scenario: Delegated access in Microsoft Graph
The https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/me endpoint is the access point to the signed-in user's information, which represents a resource that's protected by the Microsoft identity platform. For delegated access, the two factors are fulfilled as follows:
- The app must be granted a supported Microsoft Graph delegated permission, for example, the User.Read delegated permission, on behalf of the signed-in user.
- The signed-in user in this scenario is the owner of the data.
Note
Endpoints and APIs with the /me alias operate on the signed-in user only and are therefore called in delegated access scenarios.
As an alternative to Microsoft Graph delegated permissions, an app can also be assigned permissions through a role-based access control system such as Microsoft Entra RBAC.
App-only access (access without a user)
In this access scenario, the application can interact with data on its own, without a signed in user. App-only access is used in scenarios such as automation and backup, and is mostly used by apps that run as background services or daemons. It's suitable when it's undesirable to have a user signed in, or when the data required can't be scoped to a single user.
For a client app to be authorized to access the data with their own identity, it must have the required permissions, which it receives through one of the following ways:
- The app is assigned supported Microsoft Graph application permissions, also called app roles
- The app is assigned ownership of the resource that it intends to manage
Note
As an alternative to Microsoft Graph application permissions, an app can also be assigned permissions through a role-based access control system such as Microsoft Entra RBAC.
Sample scenario: App-only access in Microsoft Graph
The https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/users/delta endpoint allows you to poll changes to user data. In app-only access, the app must be granted a supported permission, for example, the User.Read.All Microsoft Graph application permission to be allowed to successfully query and receive changes in user data.
Microsoft Graph permissions
As mentioned earlier, an app must have permissions to access the data that it wants to access, regardless of the access scenario.
Microsoft Graph exposes granular permissions that control access to Microsoft Graph resources, like users, groups, and mail. Two types of permissions are available for the supported access scenarios:
- Delegated permissions: Also called scopes, allow the application to act on behalf of the signed-in user.
- Application permissions: Also called app roles, allow the app to access data on its own, without a signed-in user.
As a developer, you decide which Microsoft Graph permissions to request for your app based on the access scenario and the operations you want to perform. When a user signs in to an app, the app must specify the permissions that it needs to be included in the access token. These permissions:
- May be preauthorized for the application by an administrator.
- May be consented by the user directly.
- If not preauthorized, may require administrator privileges to grant consent. For example, for permissions with a greater potential security impact.
For more information about permissions and consent, see Introduction to permissions and consent.
For more information about Microsoft Graph permissions and how to use them, see the Overview of Microsoft Graph permissions.
Note
As a best practice, request the least privileged permissions that your app needs in order to access data and function correctly. Requesting permissions with more than the necessary privileges is poor security practice, which may cause users to refrain from consenting and affect your app's usage.
Access tokens
To access a protected resource, an application must prove that it's authorized to do so by submitting a valid access token. The application gets this access token when it makes an authentication request to the Microsoft identity platform which in turn uses the access token to verify that the app is authorized to call Microsoft Graph.
Access tokens that the Microsoft identity platform issues contain claims which are details about the application and in delegated access scenarios, the signed-in user. Web APIs such as Microsoft Graph that are secured by the Microsoft identity platform use the claims to validate the caller and to ensure that the caller is authorized to perform the operation they're requesting. For delegated access scenarios, the permissions of both the calling user and the app are part of the claims. For application scenarios the permissions of the app are part of the claims. For more information about the pieces that constitute access tokens, see Access token claims reference.
To call Microsoft Graph, the app makes an authorization request by attaching the access token as a Bearer token to the Authorization header in an HTTP request. For example, the following call that returns the profile information of the signed-in user (the access token has been shortened for readability):
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/me/ HTTP/1.1
Host: graph.microsoft.com
Authorization: Bearer EwAoA8l6BAAU ... 7PqHGsykYj7A0XqHCjbKKgWSkcAg==
To learn more about Microsoft identity platform access tokens, see ID tokens in the Microsoft identity platform.
Get an access token
We recommend that you use authentication libraries to manage your token interactions with the Microsoft identity platform. Authentication libraries abstract many protocol details like validation, cookie handling, token caching, and maintaining secure connections, that lets you focus your development on your app's functionality. Microsoft publishes open-source client libraries and server middleware.
For the Microsoft identity platform endpoint:
- Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) client libraries are available for various frameworks including for .NET, JavaScript, Android, and iOS. All platforms are in production-supported preview, and, in the event breaking changes are introduced, Microsoft guarantees a path to upgrade.
- Server middleware from Microsoft is available for .NET core and ASP.NET (OWIN OpenID Connect and OAuth) and for Node.js (Microsoft identity platform Passport.js).
- The Microsoft identity platform is also compatible with many third-party authentication libraries.
For a complete list of Microsoft client libraries, Microsoft server middleware, and compatible third-party libraries, see Microsoft identity platform documentation.
You can alternatively use the Microsoft identity platform endpoints directly without the help of an authentication library. For more information, see the following articles: