Manage admin roles with Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management (preview)
[This article is prerelease documentation and is subject to change.]
Use Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management (PIM) to manage high-privileged admin roles in the Power Platform admin center.
Important
- This is a preview feature.
- Preview features aren't meant for production use and may have restricted functionality. These features are available before an official release so that customers can get early access and provide feedback.
- To sign up for this preview, fill out the preview sign-up form.
Prerequisites
- Remove old system administrator role assignments in your environments. You can use PowerShell scripts to inventory and remove unwanted users from the System Administrator role in one or more Power Platform environments.
- You must sign up for the preview by filling out the preview sign-up form.
Changes to feature support
Microsoft doesn't automatically assign the System Administrator role for users with these Microsoft Entra ID roles (also called tenant admins):
- Global administrator
- Power Platform administrator
- Dynamics 365 administrator
Tenant admins can continue to sign in, to the Power Platform admin center, with these privileges:
- Enable or disable tenant level settings
- View analytics information for environments
- View capacity consumption
Tenant admins can't perform activities that require direct access to Dataverse data. Examples of these activities include:
- Updating the security role for a user in an environment
- Installing apps for an environment
Important
Tenant admins must do another step before they can perform activities requiring access to Dataverse. They must elevate themselves to the System Administrator role in the environment where they need access. All elevation actions are logged to Microsoft Purview.
Self-elevate to the system administrator role
Currently, we only support elevation using PowerShell. Future updates will include more enhancements in the Power Platform admin center.
Set up PowerShell
Install the MSAL PowerShell module. You only need to install the module once.
Install-Module -Name MSAL.PS
For more information about setting up PowerShell, see Quick Start Web API with PowerShell and Visual Studio Code.
Note
Users who call the self-elevation API must be a global admin, Power Platform admin, or Dynamic 365 admin. Otherwise, you get an access denied message.
Step 1: Run the script to elevate
In this PowerShell script, you:
- Authenticate, using the Power Platform API.
- Build an
httpquery with your environment ID. - Call the API endpoint to request elevation.
Add your environment ID
Get your Environment ID from the Environments tab of the Power Platform Admin Center.
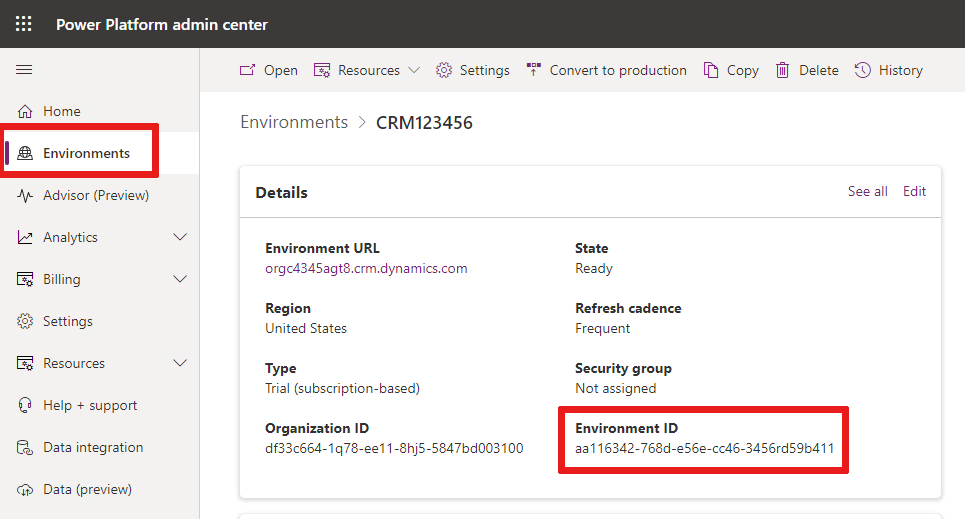
Add your unique
<environment id>to the script.
Run the script
Copy and paste the script into a PowerShell console.
# Set your environment ID
$environmentId = "<your environment id>"
Import-Module MSAL.PS
# Authenticate
$AuthResult = Get-MsalToken -ClientId '49676daf-ff23-4aac-adcc-55472d4e2ce0' -Scope 'https://api.powerplatform.com/.default'
$Headers = @{
Authorization = "Bearer $($AuthResult.AccessToken)"
'Content-Type' = "application/json"
}
$uri = "https://api.powerplatform.com/usermanagement/environments/$environmentId/user/applyAdminRole?api-version=2022-03-01-preview";
try {
$postRequestResponse = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Headers $Headers -Uri $uri
}
catch {
# Dig into the exception to get the Response details.
Write-Host "Response CorrelationId:" $_.Exception.Response.Headers["x-ms-correlation-id"]
Write-Host "StatusCode:" $_.Exception.Response.StatusCode.value__
Write-Host "StatusDescription:" $_.Exception.Response.StatusDescription
$result = $_.Exception.Response.GetResponseStream()
$reader = New-Object System.IO.StreamReader($result)
$reader.BaseStream.Position = 0
$reader.DiscardBufferedData()
$responseBody = $reader.ReadToEnd();
Write-Host $responseBody
}
$output = $postRequestResponse | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 2
Write-Host $output
Step 2: Confirm the result
Upon success, you see an output similar to the following output. Look for "Code": "UserExists" as evidence that you successfully elevated your role.
{
"errors": [],
"information": [
{
"Subject": "Result",
"Description": "[\"SyncMode: Default\",\"Instance df12c345-7b56-ee10-8bc5-6045bd005555 exists\",\"Instance df85c664-7b78-ee11-8bc5-6045bd005555 in enabled state\",\"Instance Url found https://orgc1234567.crm.dynamics.com\",\"User found in AD tenant\",\"User in enabled state in AD tenant\",\"SystemUser with Id:11fa11ab-4f75-ee11-9999-6045bd12345a, objectId:d111c55c-aab2-8888-86d4-ece1234f11e6 exists in instance\"]",
"Code": "UserExists"
},
{ ... }
}
Errors
You might see an error message if you don't have the right permissions.
"Unable to assign System Administrator security role as the user is not either a Global admin, Power Platform admin, or Dynamics 365 admin. Please review your role assignments in Entra ID and try again later. For help, please reach out to your administrator."
Step 3: Clean up activity
Run Remove-RoleAssignmentFromUsers to remove users from the System Administrator security role after the assignment expires in PIM.
-roleName: "System Administrator" or another role-usersFilePath: Path to CSV file with list of user principal names (one per line)-environmentUrl: Found at admin.powerplatform.microsoft.com-processAllEnvironments: (Optional) Process all your environments-geo: A valid GEO-outputLogsDirectory: Path where log files are written
Example script
Remove-RoleAssignmentFromUsers
-roleName "System Administrator"
-usersFilePath "C:\Users\<My-Name>\Desktop\<names.csv>"
-environmentUrl "<my-name>-environment.crm.dynamics.com"
# Or, include all your environments
-processAllEnvironments $true
-geo "NA"
-outputLogsDirectory "C:\Users\<My-Name>\Desktop\<log-files>"
Known limitations
When the caller is a system administrator, the self-elevate call returns a success rather than notifying the caller that the system administrator already exists.
The user making the call must have tenant admin. For a full list of users who meet the tenant admin criteria, see Changes to feature support
The elevation API can only be invoked by the user who needs to elevate their status. It doesn't support making API calls on behalf of another user for elevation purposes.
The Microsoft Power Platform CoE Starter Kit no longer works and we're working on updating the kit.
Once you elevate a user through Entra Privileged Identity Management, wait for two hours for the changes to sync from Entra to Power Platform before you sign in to Power Platform admin center.
Role assignments through groups aren't supported. Make sure that you assign roles directly to the user.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for