How to ingest data into Fabric using the Azure Data Factory Copy activity
The Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse connector in Azure Data Factory (ADF) and Azure Synapse Analytics enables both read and write operations to Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse (both for tables and files). This connector gives you the ability to use your existing ADF and Synapse Pipelines and Mapping Data Flows to interact with Fabric Lakehouses. This article helps you configure Microsoft Fabric to allow service principal authentication and then demonstrates the Lakehouse Connector for both reading and writing to the Fabric Lakehouse.
For more information on Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse, see What is a lakehouse?
Azure Data Factory Lakehouse Connector
A new Lakehouse linked service connector and two new Datasets are now available for customers who want to start reading from and writing to the Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse. For a complete guide on the Lakehouse Connector, refer to Copy and transform data in Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse Files (Preview).
Authentication
Azure Data Factory linked service
The Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse connector requires a service principal (SPN)/app registration for authentication. To get started, you must create a new SPN or use an existing one. Microsoft Fabric allows for SPN access to either specific security groups or for the entire organization. If a specific security group is the option your organization uses, then the SPN used in the Lakehouse connector must belong to a security group that is added to the allowlist.
Note
Power BI API permissions (Delegated) are not needed
Access to Power BI APIs
From the Power BI admin portal, the Power BI tenant admin must enable Allow service principals to use Power BI APIs. The security group must be specified under the Allow service principals to use Power BI APIs setting or you can enable for the entire organization.
For a complete guide, refer to Embed Power BI content in an embedded analytics application with service principal and an application secret.
Note
When assigning the Security Group to the Workspace, there might be a delay for the service principal to be granted access to the Workspace due to permissions caching in Azure. If you require immediate access, you can use PowerShell to force a refresh of the user’s permissions. To do so, Open PowerShell as Administrator, then run the following commands:
Install-Module -Name MicrosoftPowerBIMgmt
Connect-PowerBIServiceAccount -Tenant '<TENANT ID>' -ServicePrincipal -Credential (Get-Credential)
Get-PowerBIWorkspace
Invoke-PowerBIRestMethod -URL 'https://api.powerbi.com/v1.0/myorg/RefreshUserPermissions' -Method Post -Body ''
Get-PowerBIWorkspace
Workspace access
Once the Security Group is added, the Security Group or the service principal must also be added to each Workspace as Member, Contributor, or Admin. Refer to Give users access to workspaces for more details.
Demo: Set up authentication
App registration service principal
Create or use an existing app registration service principal (SPN). Follow the steps in Register an application with Microsoft Entra ID and create a service principal.
Note
You do not need to assign a Redirect URI.

Security group
Create a new Microsoft Entra Security Group or use an existing one then add the SPN to it. Follow the steps in Create a basic group and add members to create a Microsoft Entra Security Group.

Power BI admin portal
From the Power BI admin portal, navigate to Developer settings and select Allow service principals to use Power BI APIs, then enable it. Then add the Security Group from the previous step. For more information on the Power BI admin portal tenant settings, see Tenant settings.

Note
Please ensure the setting Users can access data stored in OneLake with apps external to Fabric is enabled. Refer to Allow apps running outside of Fabric to access data via OneLake.
Workspace
Add the SPN or the service group to the workspace with Member, Contributor, or Admin access.
Azure Data Factory: Linked service
From Azure Data Factory, create a new Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse linked service.
Note
To find the workspace and Lakehouse IDs, navigate to your Fabric Lakehouse and identify it from the URL. For example: https://.../groups/<Workspace ID>>/lakehouses/<Lakehouse ID>
Azure Data Factory: Dataset
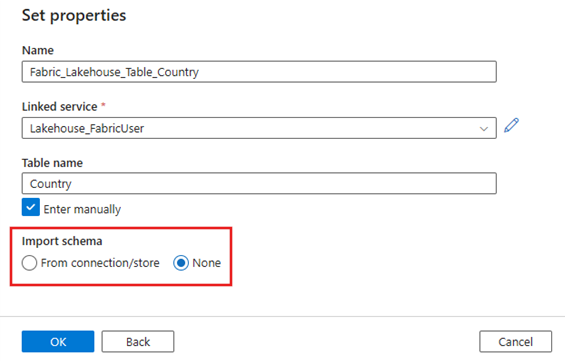
Create a Dataset that references the Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse linked service.
Note
Select None for the Import schema option if the table does not exist yet and you are manually specifying a new table name.

Demo: Write to a Fabric Lakehouse table with an ADF pipeline
Source
Create a new pipeline and add a Copy activity to the pipeline canvas. From the Source tab of the Copy activity, select a source dataset that you want to move into a Lakehouse table. In this example, we're referencing a .csv file from an Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2 account.
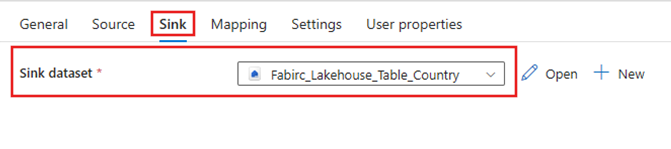
Sink
Navigate to the Copy activity's Sink tab and select the Fabric Lakehouse dataset that was created previously.
Run the pipeline
Run the pipeline to move the .csv data into the Fabric Lakehouse table.

Demo: Read from a Fabric Lakehouse table with an ADF pipeline
In the above section, we demonstrated how to use ADF to write to a Fabric Lakehouse Table. Now, let's read from a Fabric Lakehouse Table and write to a Parquet file in Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2 with a similar pipeline.
Source
Create a new pipeline and add a Copy activity to the pipeline canvas. From the Source tab of the Copy activity, select the Fabric Lakehouse dataset that was created previously.

Sink
Navigate to the Copy activity's Sink tab and select the destination dataset. In this example, the destination is Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen2), as a Parquet file.

Run the pipeline
Run the pipeline to move the data from the Fabric Lakehouse table into the Parquet file in ADLS Gen2.

Inspect the Parquet file in ADLS Gen2
The data from the Fabric Lakehouse table is now available in ADLS Gen2 as a Parquet file.

Summary
In this section, we explored the requirements for the Lakehouse Connector using service principal authentication to a Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse, then walked through an example for both reading and writing to the Lakehouse from an Azure Data Factory pipeline. This connector and capabilities are also available in Azure Data Factory Mapping Data Flows, Azure Synapse Analytics, and Azure Synapse Analytics Mapping Data Flows.
