إشعار
يتطلب الوصول إلى هذه الصفحة تخويلاً. يمكنك محاولة تسجيل الدخول أو تغيير الدلائل.
يتطلب الوصول إلى هذه الصفحة تخويلاً. يمكنك محاولة تغيير الدلائل.
Microsoft Fabric allows users to operationalize machine learning models with the scalable PREDICT function. This function supports batch scoring in any compute engine. Users can generate batch predictions directly from a Microsoft Fabric notebook or from the item page of a given ML model.
In this article, you learn how to apply PREDICT by writing code yourself or through use of a guided UI experience that handles batch scoring for you.
Prerequisites
Get a Microsoft Fabric subscription. Or, sign up for a free Microsoft Fabric trial.
Sign in to Microsoft Fabric.
Switch to Fabric by using the experience switcher on the lower-left side of your home page.
Limitations
- The PREDICT function is currently supported for this limited set of ML model flavors:
- CatBoost
- Keras
- LightGBM
- ONNX
- Prophet
- PyTorch
- Sklearn
- Spark
- Statsmodels
- TensorFlow
- XGBoost
- PREDICT requires that you save ML models in the MLflow format, with their signatures populated
- PREDICT does not support ML models with multi-tensor inputs or outputs
Call PREDICT from a notebook
PREDICT supports MLflow-packaged models in the Microsoft Fabric registry. If an already trained and registered ML model exists in your workspace, you can skip to step 2. If not, step 1 provides sample code to guide you through training a sample logistic regression model. You can use this model to generate batch predictions at the end of the procedure.
Train an ML model and register it with MLflow. The next code sample uses the MLflow API to create a machine learning experiment, and then start an MLflow run for a scikit-learn logistic regression model. The model version is then stored and registered in the Microsoft Fabric registry. Visit the how to train ML models with scikit-learn resource for more information about training models and tracking your own experiments.
import mlflow import numpy as np from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes from mlflow.models.signature import infer_signature mlflow.set_experiment("diabetes-demo") with mlflow.start_run() as run: lr = LogisticRegression() data = load_diabetes(as_frame=True) lr.fit(data.data, data.target) signature = infer_signature(data.data, data.target) mlflow.sklearn.log_model( lr, "diabetes-model", signature=signature, registered_model_name="diabetes-model" )Load in test data as a Spark DataFrame. To generate batch predictions with the ML model trained in the previous step, you need test data in the form of a Spark DataFrame. In the following code, substitute the
testvariable value with your own data.# You can substitute "test" below with your own data test = spark.createDataFrame(data.frame.drop(['target'], axis=1))Create an
MLFlowTransformerobject to load the ML model for inferencing. To create anMLFlowTransformerobject to generate batch predictions, you must perform these actions:- specify the
testDataFrame columns you need as model inputs (in this case, all of them) - choose a name for the new output column (in this case,
predictions) - provide the correct model name and model version for generation of those predictions.
If you use your own ML model, substitute the values for the input columns, output column name, model name, and model version.
from synapse.ml.predict import MLFlowTransformer # You can substitute values below for your own input columns, # output column name, model name, and model version model = MLFlowTransformer( inputCols=test.columns, outputCol='predictions', modelName='diabetes-model', modelVersion=1 )- specify the
Generate predictions using the PREDICT function. To invoke the PREDICT function, use the Transformer API, the Spark SQL API, or a PySpark user-defined function (UDF). The following sections show how to generate batch predictions with the test data and ML model defined in the previous steps, using the different methods to invoke the PREDICT function.
PREDICT with the Transformer API
This code invokes the PREDICT function with the Transformer API. If you use your own ML model, substitute the values for the model and test data.
# You can substitute "model" and "test" below with values
# for your own model and test data
model.transform(test).show()
PREDICT with the Spark SQL API
This code invokes the PREDICT function with the Spark SQL API. If you use your own ML model, substitute the values for model_name, model_version, and features with your model name, model version, and feature columns.
Note
Use of the Spark SQL API for prediction generation still requires creation of an MLFlowTransformer object (as shown in step 3).
from pyspark.ml.feature import SQLTransformer
# You can substitute "model_name," "model_version," and "features"
# with values for your own model name, model version, and feature columns
model_name = 'diabetes-model'
model_version = 1
features = test.columns
sqlt = SQLTransformer().setStatement(
f"SELECT PREDICT('{model_name}/{model_version}', {','.join(features)}) as predictions FROM __THIS__")
# You can substitute "test" below with your own test data
sqlt.transform(test).show()
PREDICT with a user-defined function
This code invokes the PREDICT function with a PySpark UDF. If you use your own ML model, substitute the values for the model and features.
from pyspark.sql.functions import col, pandas_udf, udf, lit
# You can substitute "model" and "features" below with your own values
my_udf = model.to_udf()
features = test.columns
test.withColumn("PREDICT", my_udf(*[col(f) for f in features])).show()
Generate PREDICT code from an ML model's item page
From the item page of any ML model, you can choose one of these options to start batch prediction generation for a specific model version, with the PREDICT function:
- Copy a code template into a notebook, and customize the parameters yourself
- Use a guided UI experience to generate PREDICT code
Use a guided UI experience
The guided UI experience walks you through these steps:
- Select the source data for scoring
- Map the data correctly to your ML model inputs
- Specify the destination for your model outputs
- Create a notebook that uses PREDICT to generate and store prediction results
To use the guided experience,
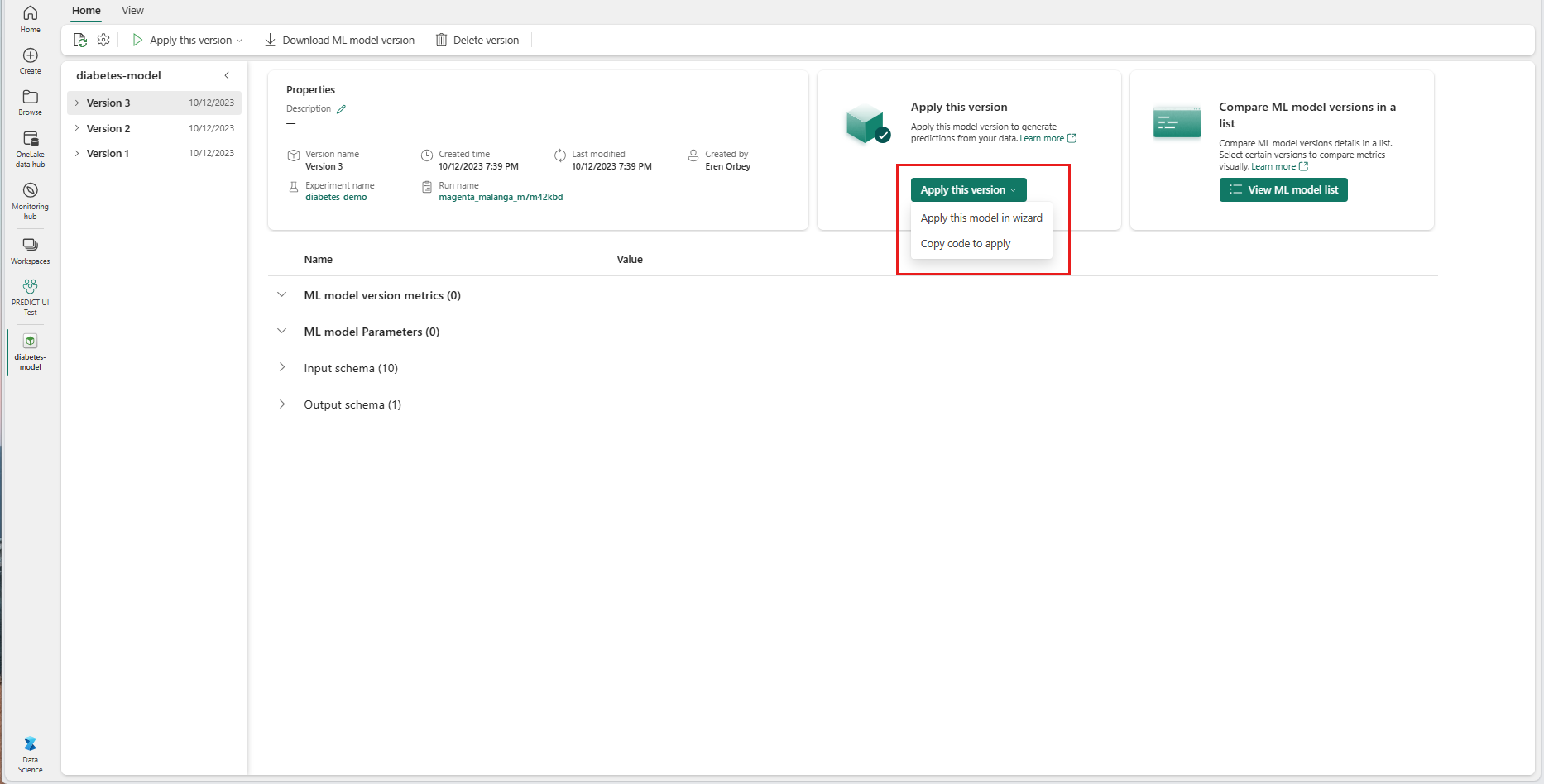
Navigate to the item page for a given ML model version.
From the Apply this version dropdown, select Apply this model in wizard.
At the "Select input table" step, the "Apply ML model predictions" window opens.
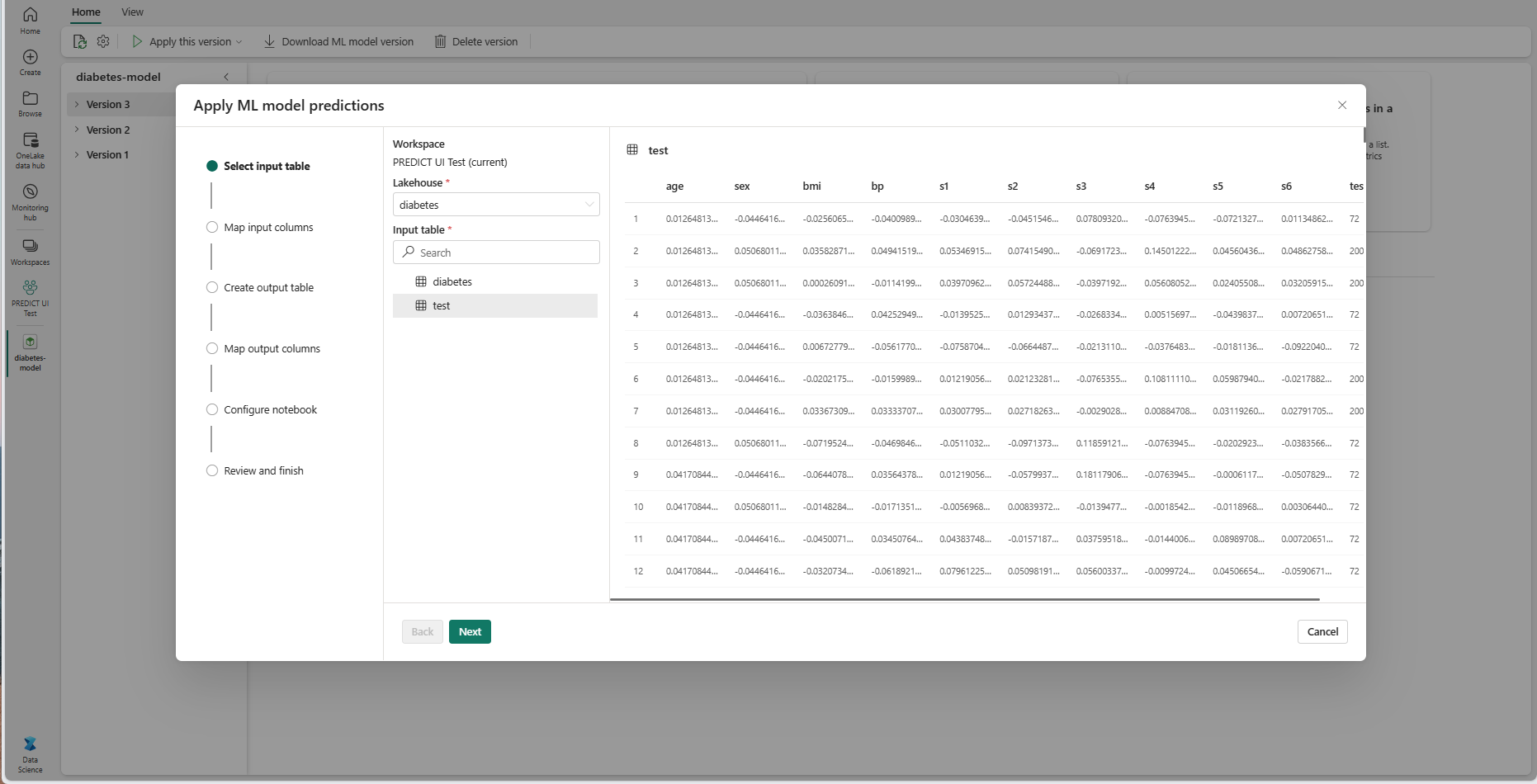
Select an input table from a lakehouse in your current workspace.
Select Next to go to the "Map input columns" step.
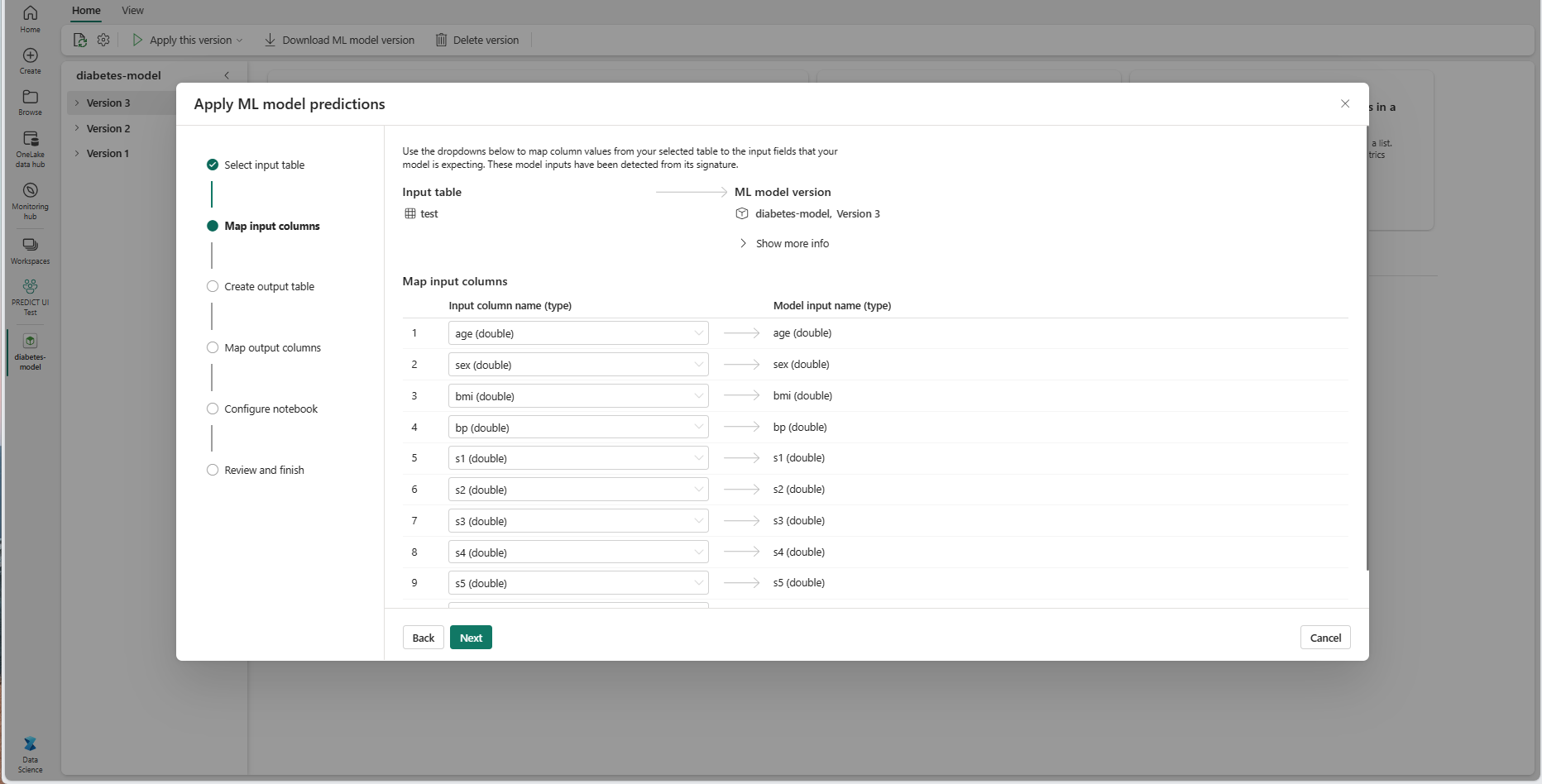
Map column names from the source table to the ML model's input fields, which are pulled from the signature of the model. You must provide an input column for all of the required fields of the model. Additionally, the source column data types must match the expected data types of the model.
Tip
The wizard prepopulates this mapping if the names of the input table columns match the column names logged in the ML model signature.
Select Next to go to the "Create output table" step.
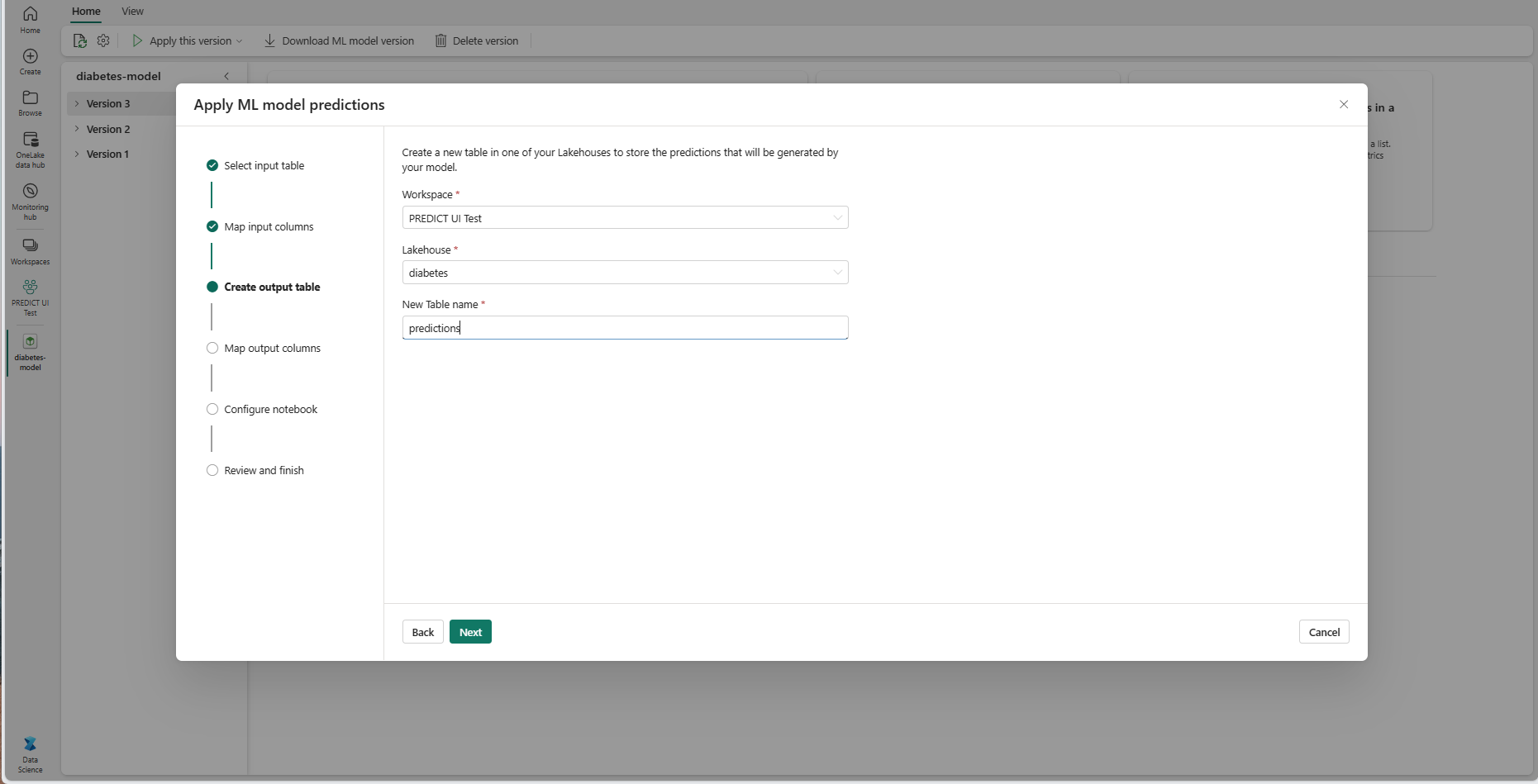
Provide a name for a new table within the selected lakehouse of your current workspace. This output table stores your ML model's input values, and it appends the prediction values to that table. By default, the output table is created in the same lakehouse as the input table. You can change the destination lakehouse.
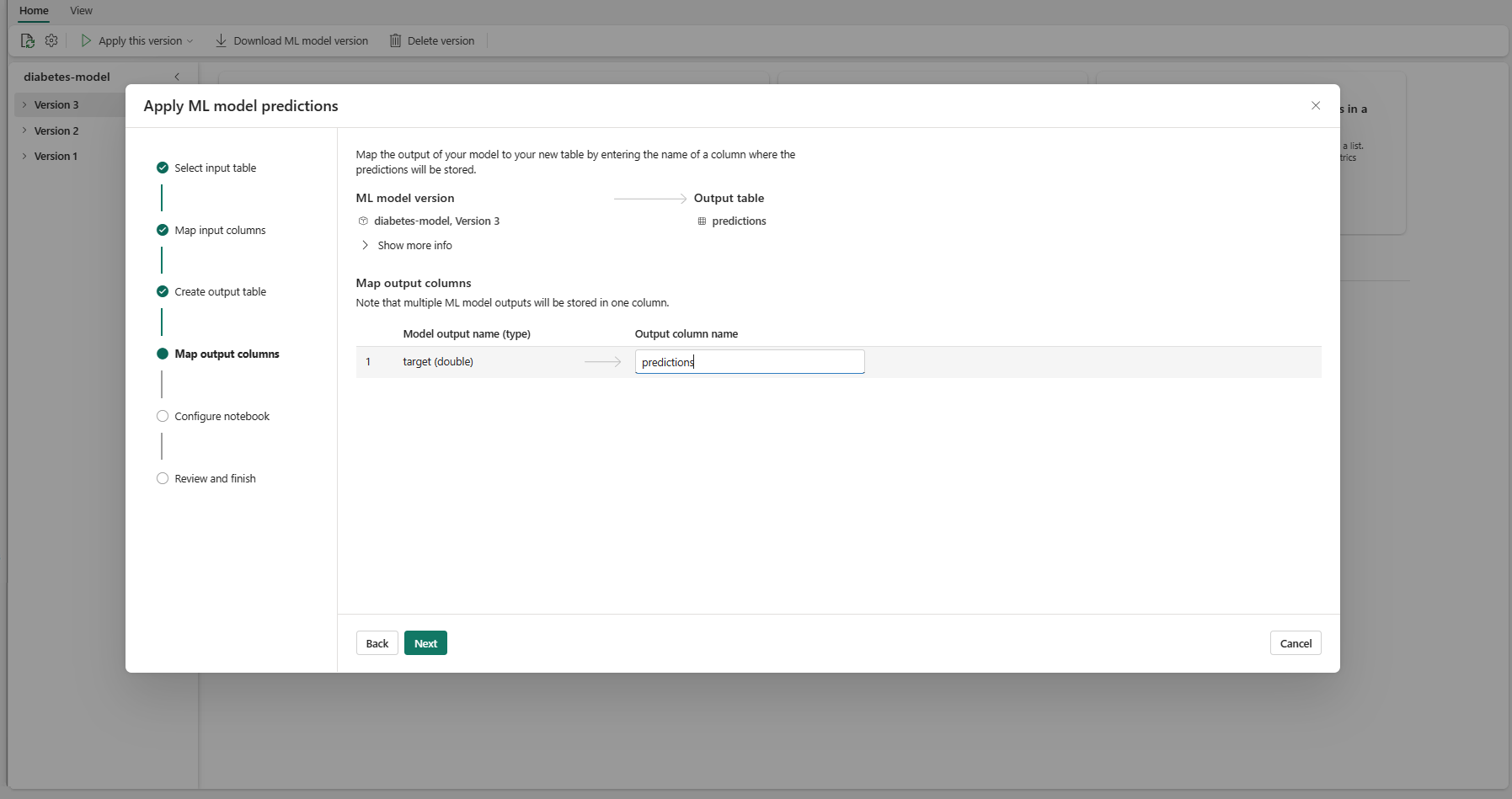
Select Next to go to the "Map output columns" step.
Use the provided text fields to name the columns of the output table that stores the ML model predictions.
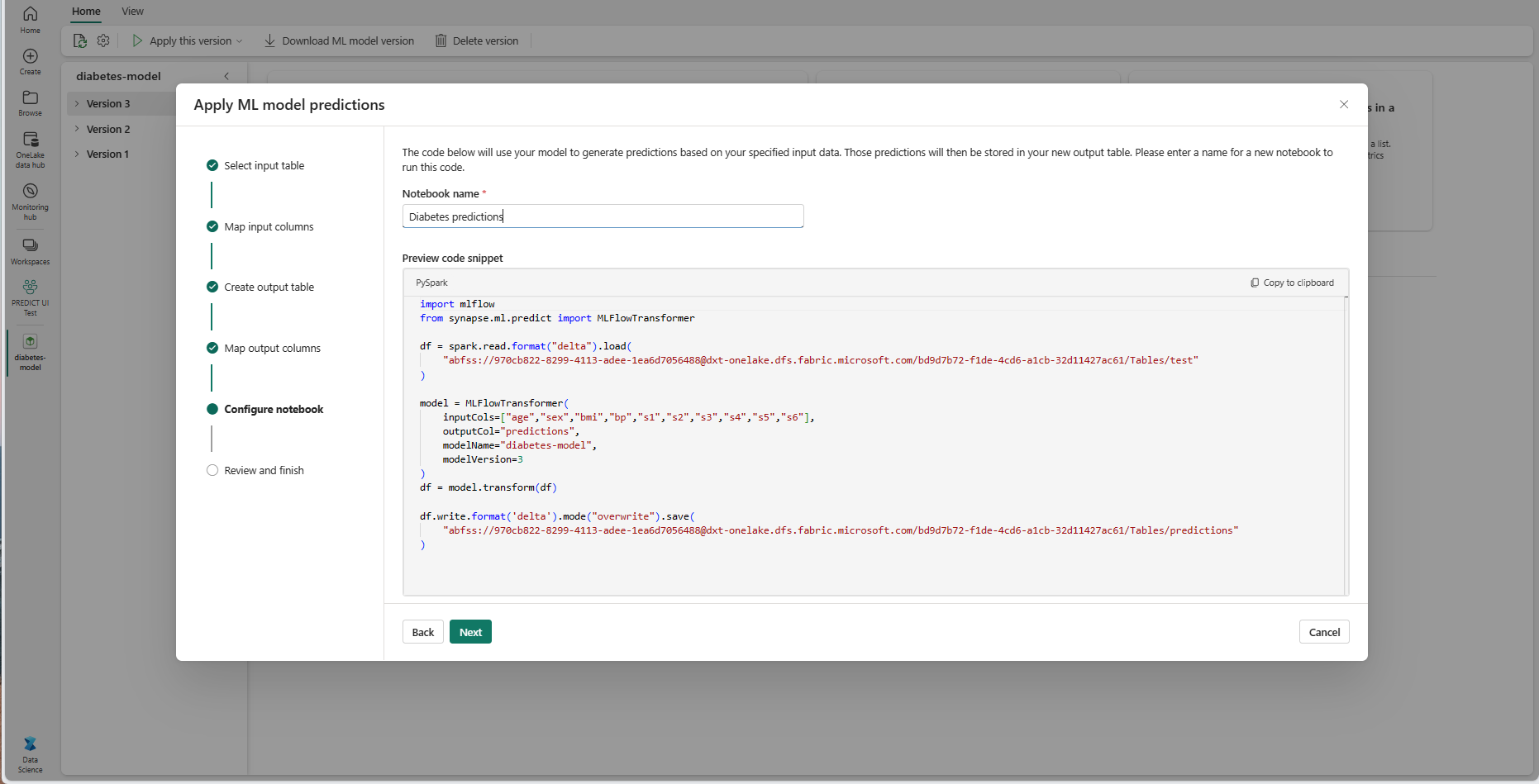
Select Next to go to the "Configure notebook" step.
Provide a name for a new notebook that runs the generated PREDICT code. The wizard displays a preview of the generated code at this step. If you want, you can copy the code to your clipboard and paste it into an existing notebook.
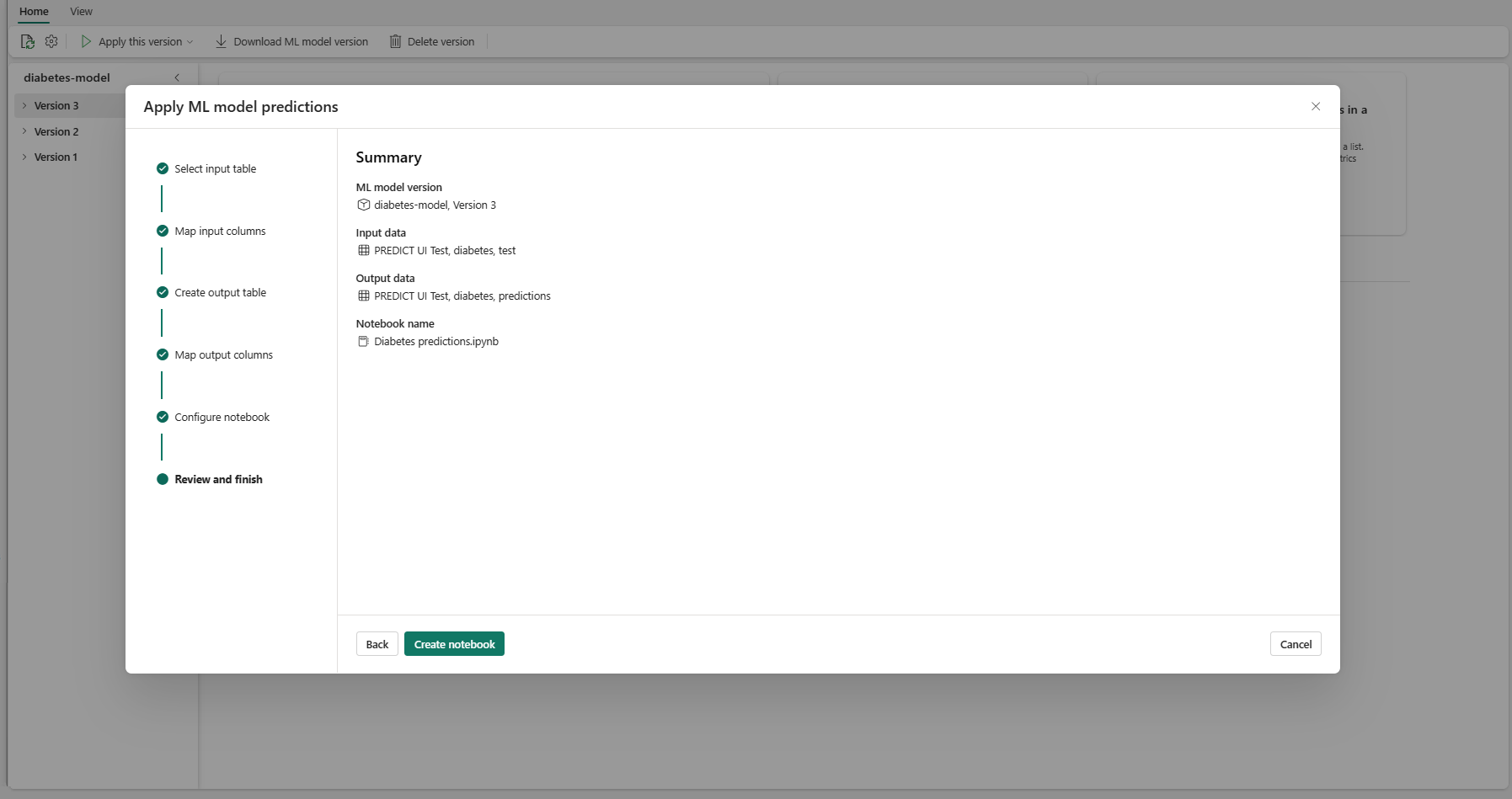
Select Next to go to the "Review and finish" step.
Review the details on the summary page, and select Create notebook to add the new notebook with its generated code to your workspace. You're taken directly to that notebook, where you can run the code to generate and store predictions.
Use a customizable code template
To use a code template for generating batch predictions:
- Go to the item page for a given ML model version.
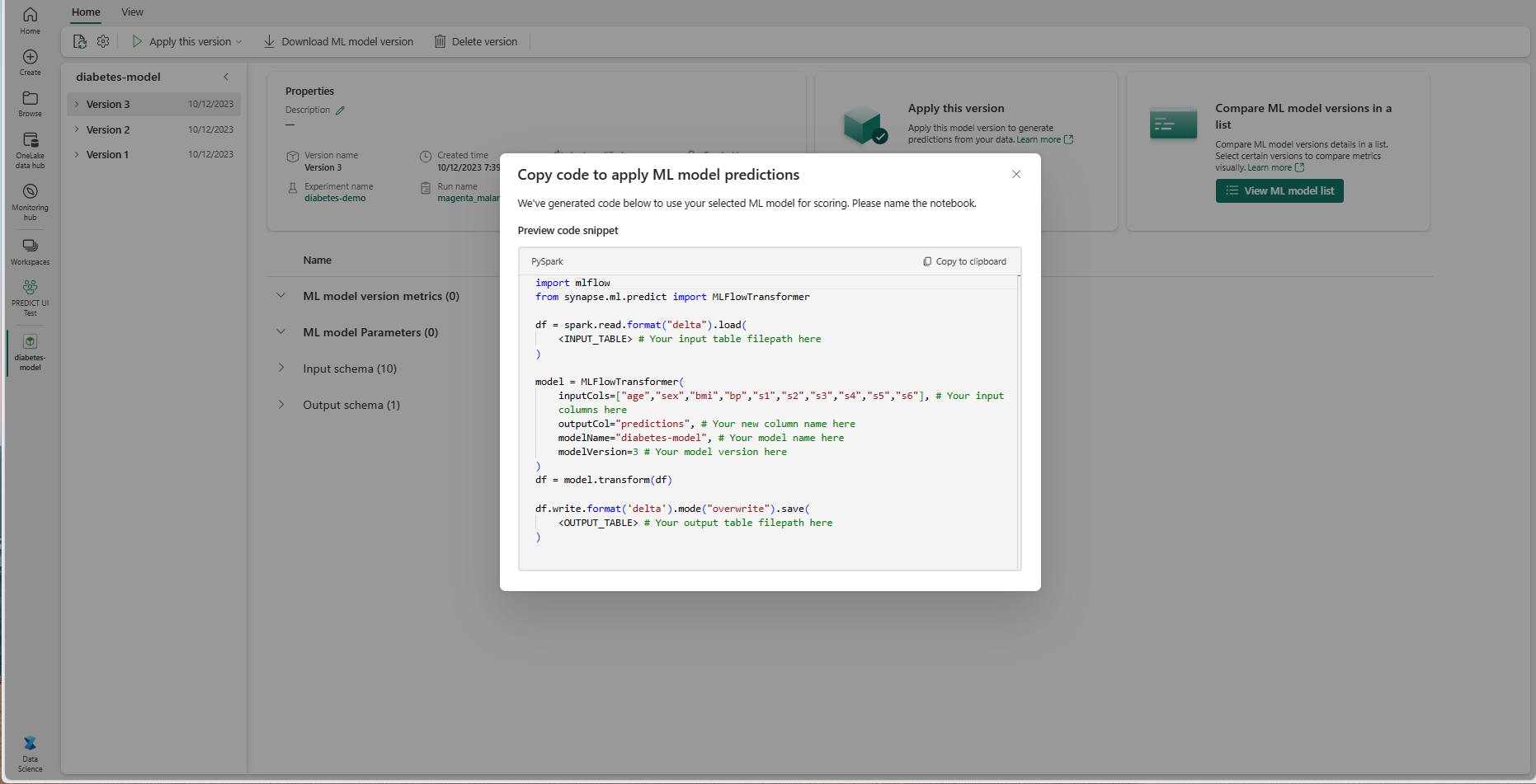
- Select Copy code to apply from the Apply this version dropdown. The selection allows you to copy a customizable code template.
You can paste this code template into a notebook to generate batch predictions with your ML model. To successfully run the code template, you must manually replace the following values:
<INPUT_TABLE>: The file path for the table that provides inputs to the ML model<INPUT_COLS>: An array of column names from the input table to feed to the ML model<OUTPUT_COLS>: A name for a new column in the output table that stores predictions<MODEL_NAME>: The name of the ML model to use for generating predictions<MODEL_VERSION>: The version of the ML model to use for generating predictions<OUTPUT_TABLE>: The file path for the table that stores the predictions
import mlflow
from synapse.ml.predict import MLFlowTransformer
df = spark.read.format("delta").load(
<INPUT_TABLE> # Your input table filepath here
)
model = MLFlowTransformer(
inputCols=<INPUT_COLS>, # Your input columns here
outputCol=<OUTPUT_COLS>, # Your new column name here
modelName=<MODEL_NAME>, # Your ML model name here
modelVersion=<MODEL_VERSION> # Your ML model version here
)
df = model.transform(df)
df.write.format('delta').mode("overwrite").save(
<OUTPUT_TABLE> # Your output table filepath here
)