إشعار
يتطلب الوصول إلى هذه الصفحة تخويلاً. يمكنك محاولة تسجيل الدخول أو تغيير الدلائل.
يتطلب الوصول إلى هذه الصفحة تخويلاً. يمكنك محاولة تغيير الدلائل.
The Visual Filters API allows you to filter data in Power BI visuals. The main difference between the filter API and other ways of selecting data is how it affects other visuals in the report. When a filter is applied to a visual, only the filtered data will be visible in all visuals, despite highlight support by other visuals.
To enable filtering for the visual, the capabilities.json file should contain a filter object in the general section.
"objects": {
"general": {
"displayName": "General",
"displayNameKey": "formattingGeneral",
"properties": {
"filter": {
"type": {
"filter": true
}
}
}
}
}
Note
Visual filters API interfaces are available in the powerbi-models package. This package also contains classes to create filter instances.
npm install powerbi-models --saveIf you're using an older (earlier than 3.x.x) version of the tools, include
powerbi-modelsin the visuals package. For more information, see the short guide, Add the Advanced Filter API to the custom visual. To find out which version you’re using, check theapiVersionin the pbiviz.json file.
All filters use the IFilter interface, as shown in the following code:
export interface IFilter {
$schema: string;
target: IFilterTarget;
}
Where target is a table column in the data source.
There are three filter APIs:
The Basic Filter API
Basic filter interface is shown in the following code:
export interface IBasicFilter extends IFilter {
operator: BasicFilterOperators;
values: (string | number | boolean)[];
}
Where:
operatoris an enumeration with the values In, NotIn, and All.valuesare values for the condition.
Example of a basic filter
The following example returns all rows where col1 equals the value 1, 2, or 3.
let basicFilter = {
target: {
column: "Col1"
},
operator: "In",
values: [1,2,3]
}
The SQL equivalent of the above example is:
SELECT * FROM table WHERE col1 IN ( 1 , 2 , 3 )
To create a filter, you can use the BasicFilter class in powerbi-models.
If you are using an older version of the tool, you should get an instance of models in the window object by using window['powerbi-models'], as shown in the following code:
let categories: DataViewCategoricalColumn = this.dataView.categorical.categories[0];
let target: IFilterColumnTarget = {
table: categories.source.queryName.substr(0, categories.source.queryName.indexOf('.')),
column: categories.source.displayName
};
let values = [ 1, 2, 3 ];
let filter: IBasicFilter = new window['powerbi-models'].BasicFilter(target, "In", values);
The visual invokes the filter by calling the applyJsonFilter() method on the host interface, IVisualHost, which is provided to the visual in the constructor method.
IVisualHost.applyJsonFilter(filter, "general", "filter", FilterAction.merge);
The Advanced Filter API
The Advanced Filter API enables complex cross-visual data-point selection and filtering queries that are based on multiple criteria, such as LessThan, Contains, Is, IsBlank, and so on).
This filter was introduced in the Visuals API version 1.7.0.
As opposed to the Basic API, in the Advanced Filter API:
- The
targetrequires both atableandcolumnname (the Basic API just hadcolumn). - Operators are And and Or (as opposed to In).
- The filter uses conditions (less than, greater than etc.) instead of values with the interface:
interface IAdvancedFilterCondition {
value: (string | number | boolean);
operator: AdvancedFilterConditionOperators;
}
Condition operators for the operator parameter are:
None, LessThan, LessThanOrEqual, GreaterThan, GreaterThanOrEqual, Contains, DoesNotContain, StartsWith, DoesNotStartWith, Is, IsNot, IsBlank, and "IsNotBlank"`
let categories: DataViewCategoricalColumn = this.dataView.categorical.categories[0];
let target: IFilterColumnTarget = {
table: categories.source.queryName.substr(0, categories.source.queryName.indexOf('.')), // table
column: categories.source.displayName // col1
};
let conditions: IAdvancedFilterCondition[] = [];
conditions.push({
operator: "LessThan",
value: 0
});
let filter: IAdvancedFilter = new window['powerbi-models'].AdvancedFilter(target, "And", conditions);
// invoke the filter
visualHost.applyJsonFilter(filter, "general", "filter", FilterAction.merge);
The SQL equivalent is:
SELECT * FROM table WHERE col1 < 0;
For the complete sample code for using the Advanced Filter API, go to the Sampleslicer visual repository.
The Tuple Filter API (multi-column filter)
The Tuple Filter API was introduced in Visuals API 2.3.0. It is similar to the Basic Filter API, but it allows you to define conditions for several columns and tables.
The filter interface is shown in the following code:
interface ITupleFilter extends IFilter {
$schema: string;
filterType: FilterType;
operator: TupleFilterOperators;
target: ITupleFilterTarget;
values: TupleValueType[];
}
Where
targetis an array of columns with table names:declare type ITupleFilterTarget = IFilterTarget[];The filter can address columns from various tables.
$schemais https://powerbi.com/product/schema#tuple.filterTypeis FilterType.Tuple.operatorallows use only in the In operator.valuesis an array of value tuples. Each tuple represents one permitted combination of the target column values.
declare type TupleValueType = ITupleElementValue[];
interface ITupleElementValue {
value: PrimitiveValueType
}
Complete example:
let target: ITupleFilterTarget = [
{
table: "DataTable",
column: "Team"
},
{
table: "DataTable",
column: "Value"
}
];
let values = [
[
// the first column combination value (or the column tuple/vector value) that the filter will pass through
{
value: "Team1" // the value for the `Team` column of the `DataTable` table
},
{
value: 5 // the value for the `Value` column of the `DataTable` table
}
],
[
// the second column combination value (or the column tuple/vector value) that the filter will pass through
{
value: "Team2" // the value for `Team` column of `DataTable` table
},
{
value: 6 // the value for `Value` column of `DataTable` table
}
]
];
let filter: ITupleFilter = {
$schema: "https://powerbi.com/product/schema#tuple",
filterType: FilterType.Tuple,
operator: "In",
target: target,
values: values
}
// invoke the filter
visualHost.applyJsonFilter(filter, "general", "filter", FilterAction.merge);
Important
The order of the column names and condition values is important.
The SQL equivalent of the above code is:
SELECT * FROM DataTable WHERE ( Team = "Team1" AND Value = 5 ) OR ( Team = "Team2" AND Value = 6 );
Restore the JSON filter from the data view
Starting with API version 2.2.0, you can restore the JSON filter from VisualUpdateOptions, as shown in the following code:
export interface VisualUpdateOptions extends extensibility.VisualUpdateOptions {
viewport: IViewport;
dataViews: DataView[];
type: VisualUpdateType;
viewMode?: ViewMode;
editMode?: EditMode;
operationKind?: VisualDataChangeOperationKind;
jsonFilters?: IFilter[];
}
When you switch bookmarks, Power BI calls the update method of the visual, and the visual gets a corresponding filter object. For more information, see Add bookmark support for Power BI visuals.
Sample JSON filter
Some sample JSON filter code is shown in the following image:
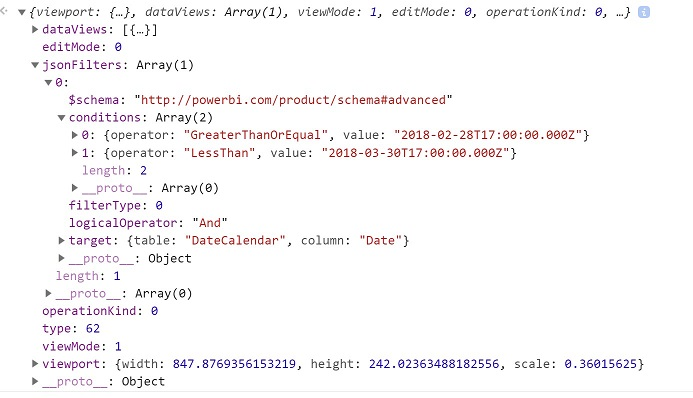
Clear the JSON filter
To reset or clear the filter, pass a null value to the filter API.
// invoke the filter
visualHost.applyJsonFilter(null, "general", "filter", FilterAction.merge);
Related content
Use Power BI visuals selections to add interactivity to a visual