Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
This isn't the latest version of this article. For the current release, see the .NET 9 version of this article.
Warning
This version of ASP.NET Core is no longer supported. For more information, see the .NET and .NET Core Support Policy. For the current release, see the .NET 9 version of this article.
Important
This information relates to a pre-release product that may be substantially modified before it's commercially released. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
For the current release, see the .NET 9 version of this article.
This tutorial shows you how to build and run a Windows Forms Blazor app. You learn how to:
- Create a Windows Forms Blazor app project
- Run the app on Windows
Prerequisites
- Supported platforms (Windows Forms documentation)
- Visual Studio 2022 with the .NET desktop development workload
Visual Studio workload
If the .NET desktop development workload isn't installed, use the Visual Studio installer to install the workload. For more information, see Modify Visual Studio workloads, components, and language packs.
Create a Windows Forms Blazor project
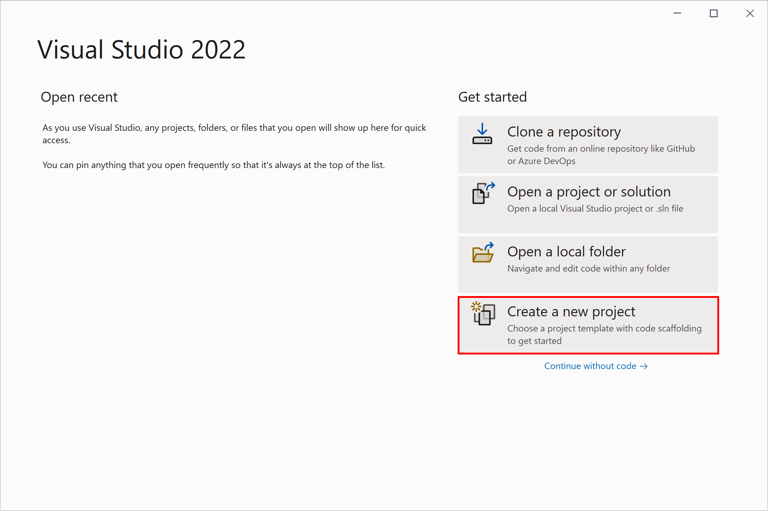
Launch Visual Studio. In the Start Window, select Create a new project:
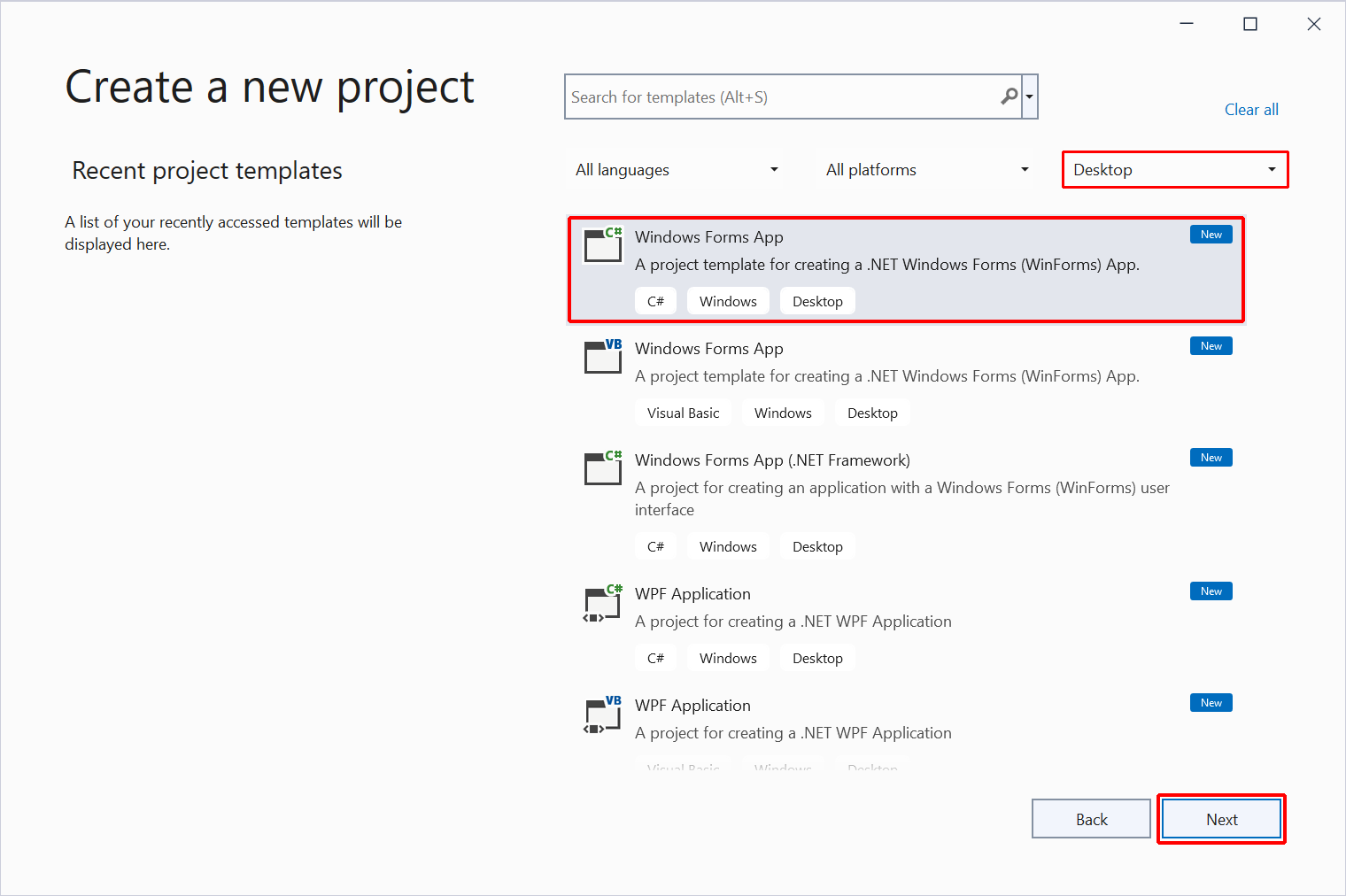
In the Create a new project dialog, filter the Project type dropdown to Desktop. Select the C# project template for Windows Forms App and select the Next button:
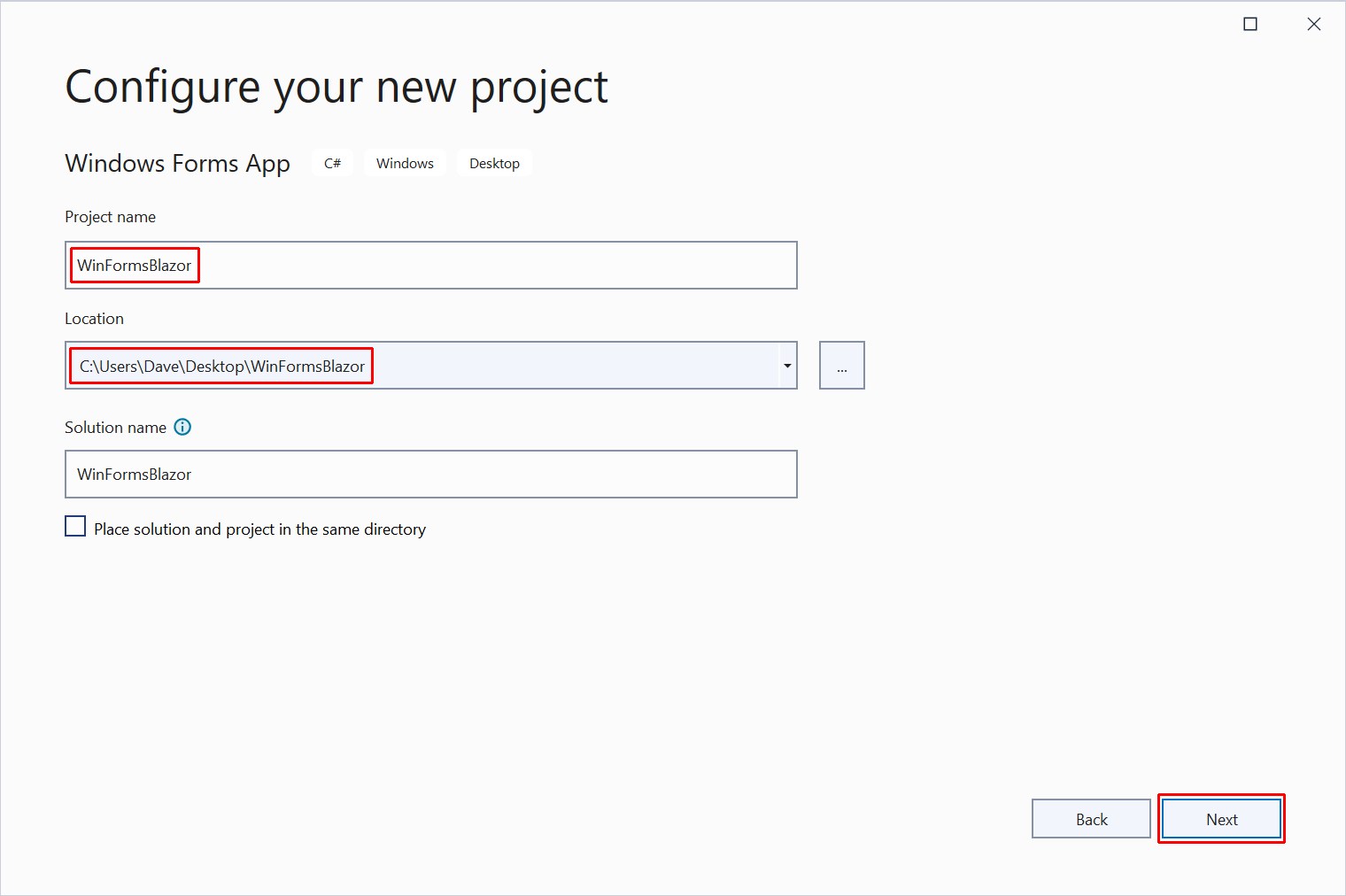
In the Configure your new project dialog:
- Set the Project name to WinFormsBlazor.
- Choose a suitable location for the project.
- Select the Next button.
In the Additional information dialog, select the framework version with the Framework dropdown list. Select the Create button:
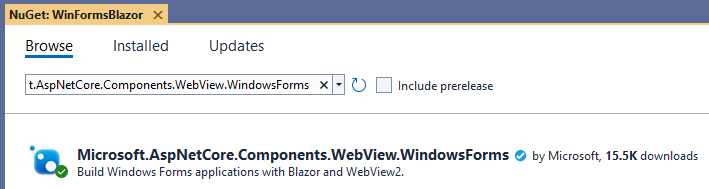
Use NuGet Package Manager to install the Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms NuGet package:
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project's name, WinFormsBlazor, and select Edit Project File to open the project file (WinFormsBlazor.csproj).
At the top of the project file, change the SDK to Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Razor:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk.Razor">
Save the changes to the project file (WinFormsBlazor.csproj).
Add an _Imports.razor file to the root of the project with an @using directive for Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web.
_Imports.razor:
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web
Save the _Imports.razor file.
Add a wwwroot folder to the project.
Add an index.html file to the wwwroot folder with the following markup.
wwwroot/index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>WinFormsBlazor</title>
<base href="/" />
<link href="css/bootstrap/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="css/app.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="WinFormsBlazor.styles.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">Loading...</div>
<div id="blazor-error-ui" data-nosnippet>
An unhandled error has occurred.
<a href="" class="reload">Reload</a>
<a class="dismiss">🗙</a>
</div>
<script src="_framework/blazor.webview.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Inside the wwwroot folder, create a css folder to hold stylesheets.
Add an app.css stylesheet to the wwwroot/css folder with the following content.
wwwroot/css/app.css:
html, body {
font-family: 'Helvetica Neue', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
}
h1:focus {
outline: none;
}
a, .btn-link {
color: #0071c1;
}
.btn-primary {
color: #fff;
background-color: #1b6ec2;
border-color: #1861ac;
}
.valid.modified:not([type=checkbox]) {
outline: 1px solid #26b050;
}
.invalid {
outline: 1px solid red;
}
.validation-message {
color: red;
}
#blazor-error-ui {
background: lightyellow;
bottom: 0;
box-shadow: 0 -1px 2px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
display: none;
left: 0;
padding: 0.6rem 1.25rem 0.7rem 1.25rem;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
z-index: 1000;
}
#blazor-error-ui .dismiss {
cursor: pointer;
position: absolute;
right: 0.75rem;
top: 0.5rem;
}
Inside the wwwroot/css folder, create a bootstrap folder. Inside the bootstrap folder, place a copy of bootstrap.min.css. You can obtain the latest version of bootstrap.min.css from the Bootstrap website. Because all of the content at the site is versioned in the URL, a direct link can't be provided here. Therefore, follow navigation bar links to Docs > Download to obtain bootstrap.min.css.
Add the following Counter component to the root of the project, which is the default Counter component found in Blazor project templates.
Counter.razor:
<h1>Counter</h1>
<p>Current count: @currentCount</p>
<button class="btn btn-primary" @onclick="IncrementCount">Click me</button>
@code {
private int currentCount = 0;
private void IncrementCount()
{
currentCount++;
}
}
Save the Counter component (Counter.razor).
In Solution Explorer, double-click on the Form1.cs file to open the designer:
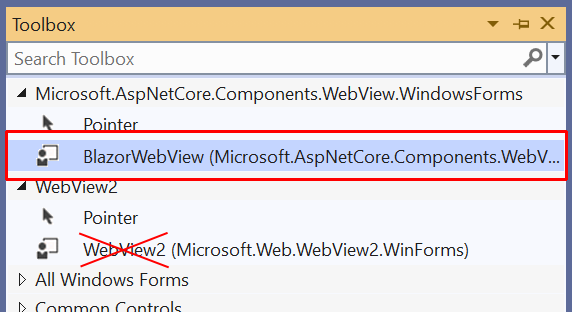
Open the Toolbox by either selecting the Toolbox button along the left edge of the Visual Studio window or selecting the View > Toolbox menu command.
Locate the BlazorWebView control under Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms. Drag the BlazorWebView from the Toolbox into the Form1 designer. Be careful not to accidentally drag a WebView2 control into the form.
Visual Studio shows the BlazorWebView control in the form designer as WebView2 and automatically names the control blazorWebView1:
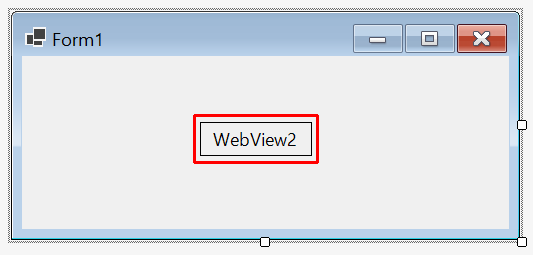
In Form1, select the BlazorWebView (WebView2) with a single click.
In the BlazorWebView's Properties, confirm that the control is named blazorWebView1. If the name isn't blazorWebView1, the wrong control was dragged from the Toolbox. Delete the WebView2 control in Form1 and drag the BlazorWebView control into the form.
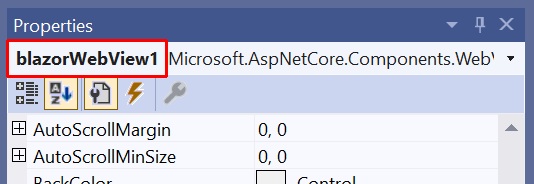
In the control's properties, change the BlazorWebView's Dock value to Fill:
In the Form1 designer, right-click Form1 and select View Code.
Add namespaces for Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms and Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection to the top of the Form1.cs file:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
Inside the Form1 constructor, after the InitializeComponent method call, add the following code:
var services = new ServiceCollection();
services.AddWindowsFormsBlazorWebView();
blazorWebView1.HostPage = "wwwroot\\index.html";
blazorWebView1.Services = services.BuildServiceProvider();
blazorWebView1.RootComponents.Add<Counter>("#app");
Note
The InitializeComponent method is automatically generated at app build time and added to the compilation object for the calling class.
The final, complete C# code of Form1.cs with a file-scoped namespace:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.WebView.WindowsForms;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace WinFormsBlazor;
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
var services = new ServiceCollection();
services.AddWindowsFormsBlazorWebView();
blazorWebView1.HostPage = "wwwroot\\index.html";
blazorWebView1.Services = services.BuildServiceProvider();
blazorWebView1.RootComponents.Add<Counter>("#app");
}
}
Run the app
Select the start button in the Visual Studio toolbar:

The app running on Windows:

Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Create a Windows Forms Blazor app project
- Run the app on Windows
Learn more about Blazor Hybrid apps:
ASP.NET Core
