Solution ideas
This article describes a solution idea. Your cloud architect can use this guidance to help visualize the major components for a typical implementation of this architecture. Use this article as a starting point to design a well-architected solution that aligns with your workload's specific requirements.
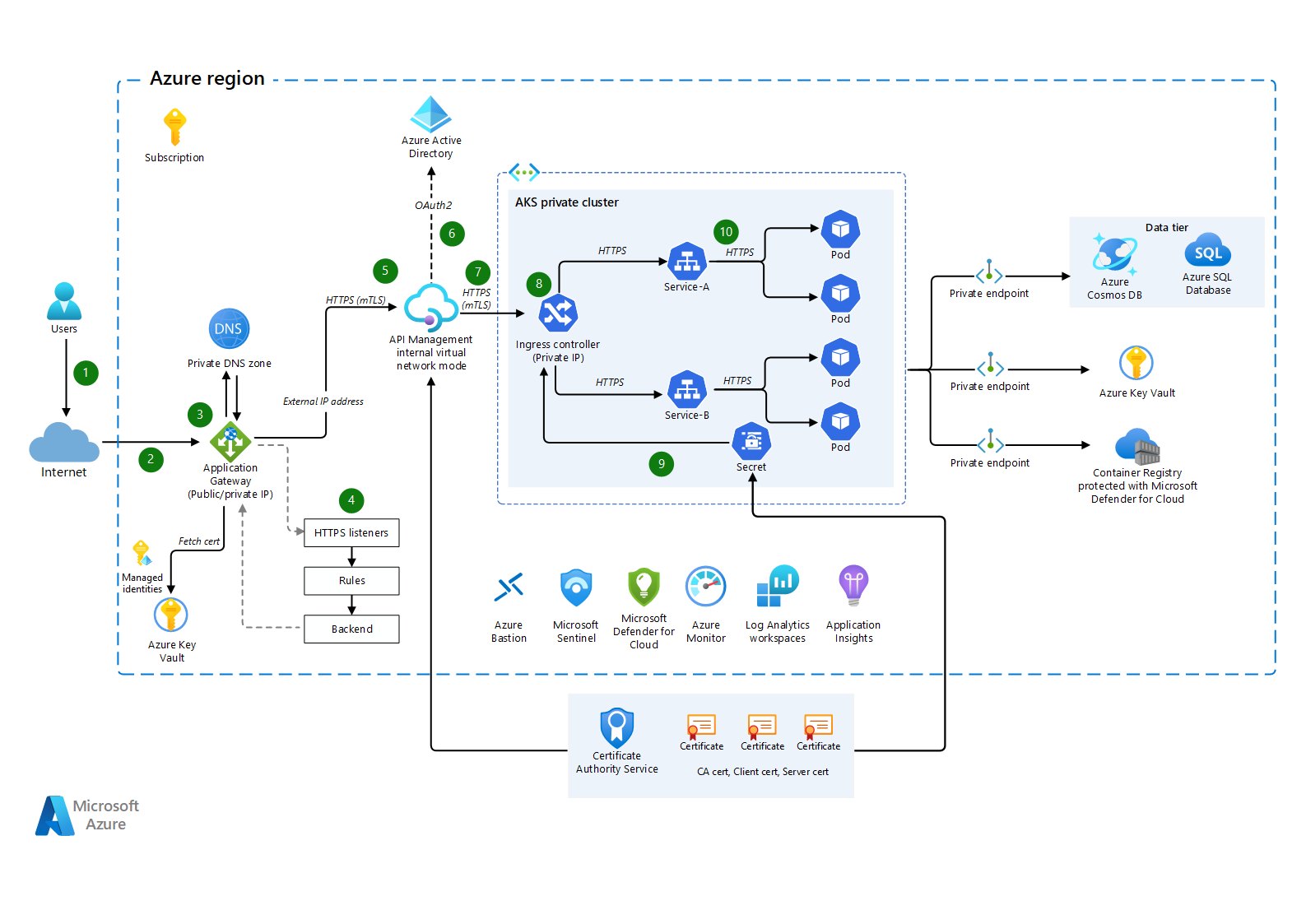
This solution demonstrates how to integrate Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and Azure API Management via mutual TLS (mTLS) in an architecture that provides end-to-end encryption.
Concepts
Azure API management allows secure access to back-end services through multiple mechanisms. At the transport (network) layer, Azure API management can present client certificates to the backend and can additionally verify the certificate presented by the back-end server. In this mutual TLS authentication scenario, the following steps occur:
- Azure API management connects to the backend server (in this scenario, to the ingress controller running in AKS).
- The back-end server (the ingress controller in AKS) presents the server certificate.
- Azure API management validates the server certificate.
- Azure API management presents the client certificate to the server (the ingress controller in AKS).
- The server (the ingress controller in AKS) validates the certificate presented by Azure API Management.
- The server (the ingress controller in AKS) grants access to the request being proxied through Azure API management.
Architecture
Download a Visio file of this architecture.
Dataflow
- A user makes a request to the application endpoint from the internet.
- Azure Application Gateway receives traffic as HTTPS and presents a public certificate previously loaded from Azure Key Vault to the user.
- Application Gateway uses private keys to decrypt traffic (SSL offload), performs web application firewall inspections, and re-encrypts traffic by using public keys (end-to-end encryption).
- Application Gateway applies rules and backend settings based on the backend pool and sends traffic to the API Management backend pool over HTTPS.
- API Management is deployed in internal virtual network mode (Developer or Premium tier only) with a private IP address. It receives traffic as HTTPS with custom domain PFX certificates.
- Microsoft Entra ID provides authentication and applies API Management policies via OAuth and optionally client certificate validation. Please see the steps to receive and verify client certificates in Azure API Management.
- API Management sends traffic via HTTPS to an ingress controller for an AKS private cluster, using the client certificate trusted by the AKS ingress controller.
- The AKS ingress controller receives the HTTPS traffic and verifies the client certificate presented by Azure API management. Most enterprise-level ingress controllers support mTLS. The AKS ingress controller responds to Azure API management with SSL server certificate, which is validated by API management.
- The ingress controller processes TLS secrets (Kubernetes Secrets) by using cert.pem and key.pem. The ingress controller decrypts traffic by using a private key (offloaded). For enhanced-security secret management that's based on requirements, CSI driver integration with AKS is available.
- The ingress controller re-encrypts traffic by using private keys and sends traffic over HTTPS to AKS pods. Depending on your requirements, you can configure AKS ingress as HTTPS backend or passthrough.
Components
- Application Gateway. Application Gateway is a web traffic load balancer that you can use to manage traffic to web applications. In this scenario, Azure Application Gateway is the Layer 7 WAF that performs SSL termination and content inspection.
- AKS. AKS provides fully managed Kubernetes clusters for deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. In this scenario, the backend logic / microservices are deployed in AKS.
- Azure Container Registry. Container Registry is a managed, private Docker registry service on Azure. You can use Container Registry to store private container images, which are deployed to the cluster.
- Microsoft Entra ID. In this scenario, the client requests can contain an OAuth 2.0 token, which will be authorized by Azure API management against Microsoft Entra ID using the validate Microsoft Entra token policy.
- Managed identities. Managed identities provide an automatically managed identity in Microsoft Entra ID for applications to use when connecting to resources that support Microsoft Entra authentication. In this scenario, AKS managed identity can be used to authenticate against backend systems such as Azure SQL database and Azure Cosmos DB.
- Azure SQL Database. SQL Database is a fully managed and intelligent relational database service that's built for the cloud. You can use SQL Database to create a high-availability, high-performance data storage layer for your modern cloud applications. In this scenario, Azure SQL database is used as the data persistence layer for structured data.
- Azure Cosmos DB. Azure Cosmos DB is a fully managed NoSQL database service for building and modernizing scalable, high-performance applications. In this scenario, Azure Cosmos DB is used as the data persistence layer for semi-structured data.
- API Management. You can use Azure API Management to publish APIs to your developers, partners, and employees. In this scenario, Azure API management is used to provide secure and managed access to microservices and business logic hosted in AKS.
- Azure Private Link. Private Link provides access to PaaS services that are hosted on Azure, so you can keep your data on the Microsoft network. In this scenario, the network connectivity from AKS to Azure SQL database, Azure Cosmos DB, and to Azure Container Registry is through private links.
- Key Vault. Key Vault can provide enhanced security for keys and other secrets. In this scenario, TLS certificates are stored in Azure Key Vault.
- Defender for Cloud. Defender for Cloud is a solution for cloud security posture management and cloud workload protection. It finds weak spots across your cloud configuration, helps strengthen the security of your environment, and can protect workloads across multicloud and hybrid environments from evolving threats. In this scenario, container images deployed in Azure Container Registry and Azure Kubernetes Service are scanned by Microsoft Defender for containers.
- Azure Monitor. You can use Monitor to collect, analyze, and act on telemetry data from your Azure and on-premises environments. Monitor helps you maximize the performance and availability of your applications and proactively identify problems.
- Log Analytics. You can use Log Analytics to edit and run log queries with data in Azure Monitor logs. In this scenario, diagnostic logs from Azure Application Gateway, AKS, API management, Azure SQL database, Azure Cosmos DB, etc. can be sent to log analytics workspace so that the logs can be analyzed based on requirements.
- Application Insights. Application Insights is an extension of Azure Monitor. It provides application performance monitoring. Azure API management and containers in Azure Kubernetes Service can be integrated to Application insights, so that application level traces can be obtained and analyzed.
- Microsoft Sentinel. Microsoft Sentinel is a cloud-native security information and event manager platform that uses built-in AI to help you analyze large volumes of data. In this scenario, Microsoft Sentinel is used as the SIEM solution to enhance the solution security.
- Azure Bastion. Azure Bastion is a fully managed service that provides RDP and SSH access to VMs without any exposure through public IP addresses. You can provision the service directly in your local or peered virtual network to get support for all VMs in that network. In this scenario, the private network resources are accessed through jump servers via Azure Bastion.
- Azure Private DNS. You can use Private DNS to manage and resolve domain names in a virtual network without adding a custom DNS solution. In this scenario, private DNS zones are used for name resolution for API management, Azure Cosmos DB, Azure SQL database, and Azure Container Registry.
Scenario details
You can use this solution to integrate AKS and API Management via mTLS in an architecture that provides end-to-end encryption.
Potential use cases
- AKS integration with API Management and Application Gateway, via mTLS.
- End-to-end mTLS between API Management and AKS.
- High security deployments for organizations that need end-to-end TLS. For example, organizations in the financial sector can benefit from this solution.
You can use this approach to manage the following scenarios:
- Deploy API Management in internal mode and expose APIs by using Application Gateway.
- Configure mTLS and end-to-end encryption for high security and traffic over HTTPS.
- Connect to Azure PaaS services by using an enhanced security private endpoint.
- Implement Defender for Containers security.
Mutual TLS configuration
Please see Secure backend services using client certificate authentication in Azure API Management for instructions on how to configure back-end certificates on Azure API management.
You will need to configure mTLS in the managed AKS ingress controller as well. The server certificate that AKS presents to APIM can either be imported directly as a Kubernetes secret or can be accessed via a Key Vault secret. See the article Set up a custom domain name and SSL certificate with the application routing add-on for details on configuring the server certificate in AKS managed ingress controller. You can perform client certificate authentication in the ingress controller to validate the certificate presented by API Management. You will need to provide the CA certificate to the AKS cluster to verify the client certificate presented by API Management. Annotations might need to be configured in the ingress controller to enforce client certificate validation using the CA certificate. For more details, please see the steps for client certificate authentication and a sample ingress YAML file with annotations.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributors.
Principal author:
- Saswat Mohanty | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
Other contributors:
- Mick Alberts | Technical Writer
- Arshad Azeem | Senior Cloud Solution Architect
- Raj Penchala | Principal Cloud Solution Architect
To see non-public LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
- Application Gateway
- AKS Roadmap
- AKS documentation
- AKS learning path
- API Management learning path
- API Management landing zone accelerator
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud Blog