Configure failover group - CLI
This article explains how to configure disaster recovery for SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc with the CLI. Before you proceed, review the information and prerequisites in SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc - disaster recovery.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites must be met before setting up failover groups between two instances of SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc:
- An Azure Arc data controller and an Arc enabled SQL managed instance provisioned at the primary site with
--license-typeas one ofBasePriceorLicenseIncluded. - An Azure Arc data controller and an Arc enabled SQL managed instance provisioned at the secondary site with identical configuration as the primary in terms of:
- CPU
- Memory
- Storage
- Service tier
- Collation
- Other instance settings
- The instance at the secondary site requires
--license-typeasDisasterRecovery. This instance needs to be new, without any user objects.
Note
- It is important to specify the
--license-typeduring the managed instance creation. This will allow the DR instance to be seeded from the primary instance in the primary data center. Updating this property post deployment will not have the same effect.
Deployment process
To set up an Azure failover group between two instances, complete the following steps:
- Create custom resource for distributed availability group at the primary site
- Create custom resource for distributed availability group at the secondary site
- Copy the binary data from the mirroring certificates
- Set up the distributed availability group between the primary and secondary sites
either in
syncmode orasyncmode
The following image shows a properly configured distributed availability group:
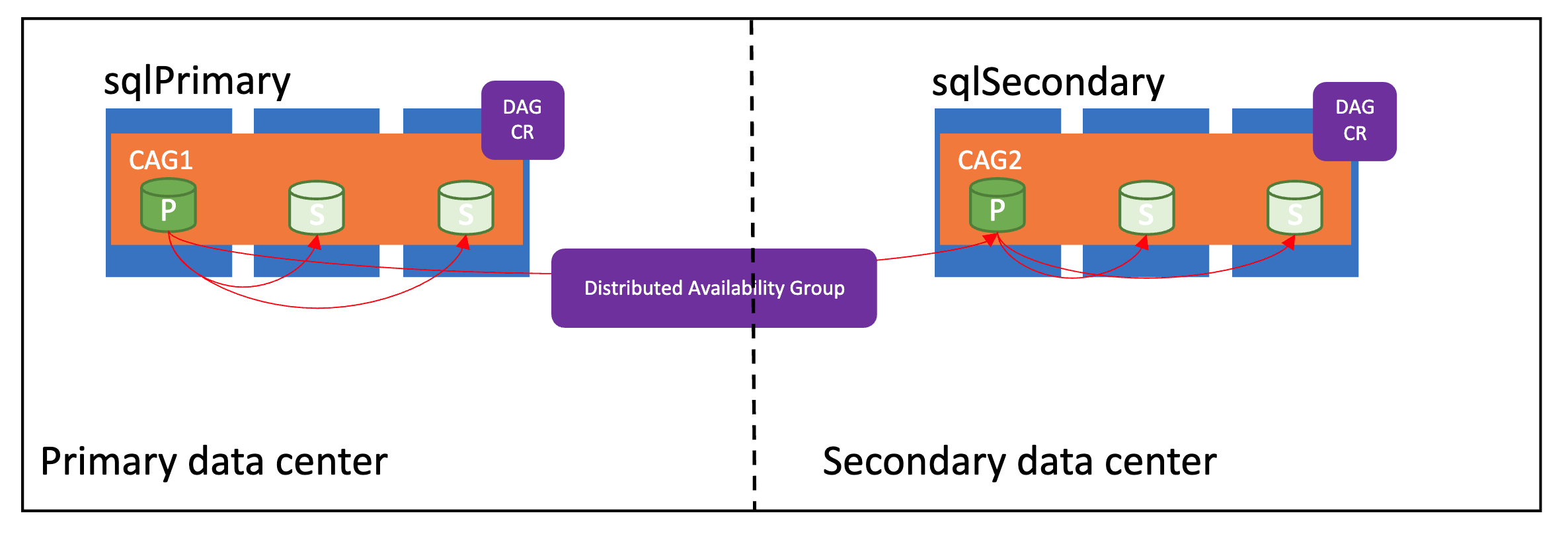
Synchronization modes
Failover groups in Azure Arc data services support two synchronization modes - sync and async. The synchronization mode directly impacts how the data is synchronized between the instances, and potentially the performance on the primary managed instance.
If primary and secondary sites are within a few miles of each other, use sync mode. Otherwise use async mode to avoid any performance impact on the primary site.
Configure Azure failover group - direct mode
Follow the steps below if the Azure Arc data services are deployed in directly connected mode.
Once the prerequisites are met, run the below command to set up Azure failover group between the two instances:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc create --name <name of failover group> --mi <primary SQL MI> --partner-mi <Partner MI> --resource-group <name of RG> --partner-resource-group <name of partner MI RG>
Example:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc create --name sql-fog --mi sql1 --partner-mi sql2 --resource-group rg-name --partner-resource-group rg-name
The above command:
- Creates the required custom resources on both primary and secondary sites
- Copies the mirroring certificates and configures the failover group between the instances
Configure Azure failover group - indirect mode
Follow the steps below if Azure Arc data services are deployed in indirectly connected mode.
Provision the managed instance in the primary site.
az sql mi-arc create --name <primaryinstance> --tier bc --replicas 3 --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8sSwitch context to the secondary cluster by running
kubectl config use-context <secondarycluster>and provision the managed instance in the secondary site that will be the disaster recovery instance. At this point, the system databases are not part of the contained availability group.Note
It is important to specify
--license-type DisasterRecoveryduring the managed instance. This will allow the DR instance to be seeded from the primary instance in the primary data center. Updating this property post deployment will not have the same effect.az sql mi-arc create --name <secondaryinstance> --tier bc --replicas 3 --license-type DisasterRecovery --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8sMirroring certificates - The binary data inside the Mirroring Certificate property of the managed instance is needed for the Instance Failover Group CR (Custom Resource) creation.
This can be achieved in a few ways:
(a) If using
azCLI, generate the mirroring certificate file first, and then point to that file while configuring the Instance Failover Group so the binary data is read from the file and copied over into the CR. The cert files are not needed after failover group creation.(b) If using
kubectl, directly copy and paste the binary data from the managed instance CR into the yaml file that will be used to create the Instance Failover Group.Using (a) above:
Create the mirroring certificate file for primary instance:
az sql mi-arc get-mirroring-cert --name <primaryinstance> --cert-file </path/name>.pem --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8sExample:
az sql mi-arc get-mirroring-cert --name sqlprimary --cert-file $HOME/sqlcerts/sqlprimary.pem --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8sConnect to the secondary cluster and create the mirroring certificate file for secondary instance:
az sql mi-arc get-mirroring-cert --name <secondaryinstance> --cert-file </path/name>.pem --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8sExample:
az sql mi-arc get-mirroring-cert --name sqlsecondary --cert-file $HOME/sqlcerts/sqlsecondary.pem --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8sOnce the mirroring certificate files are created, copy the certificate from the secondary instance to a shared/local path on the primary instance cluster and vice-versa.
Create the failover group resource on both sites.
Note
Ensure the SQL instances have different names for both primary and secondary sites, and the
shared-namevalue should be identical on both sites.az sql instance-failover-group-arc create --shared-name <name of failover group> --name <name for primary failover group resource> --mi <local SQL managed instance name> --role primary --partner-mi <partner SQL managed instance name> --partner-mirroring-url tcp://<secondary IP> --partner-mirroring-cert-file <secondary.pem> --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8sExample:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc create --shared-name myfog --name primarycr --mi sqlinstance1 --role primary --partner-mi sqlinstance2 --partner-mirroring-url tcp://10.20.5.20:970 --partner-mirroring-cert-file $HOME/sqlcerts/sqlinstance2.pem --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8sOn the secondary instance, run the following command to set up the failover group custom resource. The
--partner-mirroring-cert-filein this case should point to a path that has the mirroring certificate file generated from the primary instance as described in 3(a) above.az sql instance-failover-group-arc create --shared-name <name of failover group> --name <name for secondary failover group resource> --mi <local SQL managed instance name> --role secondary --partner-mi <partner SQL managed instance name> --partner-mirroring-url tcp://<primary IP> --partner-mirroring-cert-file <primary.pem> --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8sExample:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc create --shared-name myfog --name secondarycr --mi sqlinstance2 --role secondary --partner-mi sqlinstance1 --partner-mirroring-url tcp://10.10.5.20:970 --partner-mirroring-cert-file $HOME/sqlcerts/sqlinstance1.pem --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8s
Retrieve Azure failover group health state
Information about the failover group such as primary role, secondary role, and the current health status can be viewed on the custom resource on either primary or secondary site.
Run the below command on primary and/or the secondary site to list the failover groups custom resource:
kubectl get fog -n <namespace>
Describe the custom resource to retrieve the failover group status, as follows:
kubectl describe fog <failover group cr name> -n <namespace>
Failover group operations
Once the failover group is set up between the managed instances, different failover operations can be performed depending on the circumstances.
Possible failover scenarios are:
The instances at both sites are in healthy state and a failover needs to be performed:
- perform a manual failover from primary to secondary without data loss by setting
role=secondaryon the primary SQL MI.
- perform a manual failover from primary to secondary without data loss by setting
Primary site is unhealthy/unreachable and a failover needs to be performed:
- the primary SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc is down/unhealthy/unreachable
- the secondary SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc needs to be force-promoted to primary with potential data loss
- when the original primary SQL Managed Instance enabled by Azure Arc comes back online, it will report as
Primaryrole and unhealthy state and needs to be forced into asecondaryrole so it can join the failover group and data can be synchronized.
Manual failover (without data loss)
Use az sql instance-failover-group-arc update ... command group to initiate a failover from primary to secondary. Any pending transactions on the geo-primary instance are replicated over to the geo-secondary instance before the failover.
Directly connected mode
Run the following command to initiate a manual failover, in direct connected mode using ARM APIs:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --name <shared name of failover group> --mi <primary instance> --role secondary --resource-group <resource group>
Example:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --name myfog --mi sqlmi1 --role secondary --resource-group myresourcegroup
Indirectly connected mode
Run the following command to initiate a manual failover, in indirect connected mode using kubernetes APIs:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --name <name of failover group resource> --role secondary --k8s-namespace <namespace> --use-k8s
Example:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --name myfog --role secondary --k8s-namespace my-namespace --use-k8s
Forced failover with data loss
In the circumstance when the geo-primary instance becomes unavailable, the following commands can be run on the geo-secondary DR instance to promote to primary with a forced failover incurring potential data loss.
On the geo-secondary DR instance, run the following command to promote it to primary role, with data loss.
Note
If the --partner-sync-mode was configured as sync, it needs to be reset to async when the secondary is promoted to primary.
Directly connected mode
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --name <shared name of failover group> --mi <instance> --role force-primary-allow-data-loss --resource-group <resource group> --partner-sync-mode async
Example:
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --name myfog --mi sqlmi2 --role force-primary-allow-data-loss --resource-group myresourcegroup --partner-sync-mode async
Indirectly connected mode
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --k8s-namespace my-namespace --name secondarycr --use-k8s --role force-primary-allow-data-loss --partner-sync-mode async
When the geo-primary instance becomes available, run the below command to bring it into the failover group and synchronize the data:
Directly connected mode
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --name <shared name of failover group> --mi <old primary instance> --role force-secondary --resource-group <resource group>
Indirectly connected mode
az sql instance-failover-group-arc update --k8s-namespace my-namespace --name secondarycr --use-k8s --role force-secondary
Optionally, the --partner-sync-mode can be configured back to sync mode if desired.
Post failover operations
Once you perform a failover from primary site to secondary site, either with or without data loss, you may need to do the following:
- Update the connection string for your applications to connect to the newly promoted primary Arc SQL managed instance
- If you plan to continue running the production workload off of the secondary site, update the
--license-typeto eitherBasePriceorLicenseIncludedto initiate billing for the vCores consumed.
Related content
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for